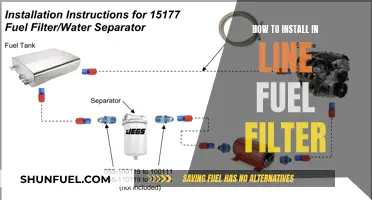
Connecting a 1/4-inch rubber fuel line is a crucial step in any vehicle's fuel system setup. This process involves ensuring a secure and leak-free connection between the fuel source and the engine. It's important to follow a step-by-step guide to achieve a proper installation, which includes preparing the necessary tools and materials, such as fuel line connectors, fuel line, and fuel-resistant tape. The process involves cleaning the fuel line and connectors, inserting the line into the connectors, and using the tape to secure the connection. This guide will provide a detailed explanation of each step to ensure a successful and safe fuel line installation.
What You'll Learn
- Preparation: Gather tools and materials, ensuring a clean and dry work area
- Line Inspection: Check for damage, kinks, or bends, replacing if necessary
- Fitting Selection: Choose appropriate fittings based on fuel type and pressure
- Assembly: Securely attach fittings to line, following manufacturer's instructions
- Testing: Run a test to ensure a tight seal and no leaks

Preparation: Gather tools and materials, ensuring a clean and dry work area
Before you begin the process of connecting a 1/4-inch rubber fuel line, it's crucial to prepare your workspace and gather the necessary tools and materials. Start by setting aside a dedicated area in your garage or workshop where you can work comfortably and without distractions. Ensure the area is well-lit and has ample space to move around. A clean and organized workspace is essential to avoid any potential hazards and to make the installation process smoother.
Gather all the required tools and materials beforehand to avoid any interruptions during the project. You will need the 1/4-inch rubber fuel line itself, preferably in the length you require, and ensure it is in good condition with no visible tears or damage. Additionally, you'll need fuel line connectors that match the size of your fuel line. These connectors should be made of compatible materials, such as rubber or vinyl, to ensure a secure and leak-free connection. It's a good idea to have a few extra connectors in case you need to make adjustments or have any mistakes.
In terms of tools, you'll require a pair of fuel line cutters or a sharp knife to cut the fuel line to the desired length. A fuel line crimping tool is essential for creating a secure connection between the line and the connector. It's also advisable to have a small brush or cloth to keep the work area clean and free of debris. Consider wearing gloves to protect your hands and ensure a neat finish.
Before you start the installation, double-check that all the components are in good shape and that you have everything you need. This simple preparation step can save you time and potential frustration later on. A well-prepared workspace and a comprehensive list of materials will make the entire process more efficient and less stressful. Remember, taking the time to prepare is an essential part of any successful DIY project.
EFI Fuel Line Options: Exploring the Best Choices for Performance
You may want to see also

Line Inspection: Check for damage, kinks, or bends, replacing if necessary
When inspecting a 1/4-inch rubber fuel line, it's crucial to ensure it is in optimal condition to prevent fuel leaks and maintain the integrity of your vehicle's fuel system. Here's a step-by-step guide to inspecting and maintaining the fuel line:
Visual Inspection: Begin by thoroughly examining the fuel line for any visible signs of damage. Look for cracks, tears, or any discolored areas on the rubber material. Check for any signs of deterioration, especially in areas where the line is exposed to the environment, such as under the vehicle or near the fuel tank. Inspect the entire length of the line, paying attention to bends and kinks, as these can be potential weak points.
Flexibility and Movement: Rubber fuel lines should be flexible and allow for movement without permanent deformation. Test the line by gently bending it at various angles and checking for any unusual stiffness or resistance. If you notice any rigid sections, it may indicate internal damage or a compromised structure.
Kinks and Bends: One of the most critical aspects of fuel line maintenance is ensuring it is free from kinks and sharp bends. These kinks can restrict fuel flow and potentially cause damage over time. Carefully examine the line for any sharp bends or kinks, especially where it connects to the fuel tank, pump, or other components. Smooth out any kinks you find, but be cautious not to over-bend the line, as this can also lead to issues.
Leakage and Connections: Inspect all connections and fittings for any signs of leakage. Check that the fuel line is securely attached to the fuel tank, pump, and other components. Over time, connections can loosen or corrode, leading to fuel leaks. If you notice any leaks, tighten the connections or replace the affected line segment.
Replacing Damaged Lines: If your inspection reveals any significant damage, kinks, or bends that cannot be resolved, it is essential to replace the fuel line promptly. Attempting to repair severely damaged lines may not be effective, and the risk of fuel leaks increases. Always use high-quality replacement lines that meet or exceed the original specifications to ensure compatibility and optimal performance.
Regular maintenance and inspections are vital to keeping your vehicle's fuel system reliable and efficient. By following these steps, you can identify and address potential issues with the 1/4-inch rubber fuel line, ensuring a safe and smooth driving experience.
Mastering the Art of Fuel Line Removal: A Step-by-Step Guide
You may want to see also

Fitting Selection: Choose appropriate fittings based on fuel type and pressure
When working with a 1/4-inch rubber fuel line, selecting the right fittings is crucial to ensure a safe and efficient fuel transfer system. The choice of fittings depends on several factors, primarily the type of fuel being used and the pressure it operates under. Different fuels, such as gasoline, diesel, or aviation fuel, have varying properties that require specific fitting materials and designs to prevent leaks and ensure compatibility.
For gasoline, which is typically less corrosive but can still cause degradation over time, fittings made from materials like brass or stainless steel are common. These metals offer good resistance to fuel degradation and corrosion, ensuring a long-lasting connection. For diesel fuel, which is more corrosive due to its sulfur content, fittings made from materials like aluminum or certain plastics may be preferred to avoid material degradation.
Pressure is another critical factor. High-pressure fuel systems, such as those found in racing cars or aircraft, require fittings that can withstand significant force without leaking. Fittings designed for high-pressure applications often feature robust construction and materials like hardened steel or specialized alloys. In contrast, low-pressure systems, such as those in small lawnmowers or garden equipment, may use simpler, less expensive fittings made from standard metals.
Additionally, consider the type of fitting needed. Common types include quick-connect fittings, which are easy to install and remove, and barbed fittings, which are more secure but require careful alignment. The choice depends on the specific application and the user's preference.
In summary, when selecting fittings for a 1/4-inch rubber fuel line, it's essential to consider the fuel type and pressure to ensure compatibility and safety. Proper fitting selection will help prevent leaks, maintain fuel quality, and ensure the overall reliability of the fuel system.
Audi 100 Fuel Line: Location and Access
You may want to see also

Assembly: Securely attach fittings to line, following manufacturer's instructions
When connecting a 1/4-inch rubber fuel line, it's crucial to follow the manufacturer's instructions for a secure and reliable attachment. This ensures the system's safety and efficiency. Here's a step-by-step guide to achieving this:
Prepare the Materials: Before beginning, ensure you have the necessary tools and materials. This includes the 1/4-inch rubber fuel line, appropriate fittings (such as quick-connect couplings or compression fittings), and any required sealing compounds or tape. Check the manufacturer's recommendations to ensure compatibility.
Clean and Prepare the Line: Start by cleaning the fuel line to remove any dirt, debris, or old fuel residue. Use a suitable cleaner and a soft brush to ensure a clean surface. This step is essential for a proper connection.
Attach the Fittings: Now, you can begin the assembly process. If using quick-connect couplings, simply slide the fitting onto the end of the fuel line, ensuring it is aligned correctly. Tighten the coupling securely, following the manufacturer's torque specifications to avoid over-tightening. For compression fittings, insert the fitting onto the line, ensuring the threads are aligned. Apply a bead of sealing compound or tape around the fitting's base, then screw it onto the line, tightening firmly.
Secure the Connection: After attaching the fittings, double-check the connections for tightness and security. Ensure there are no gaps or leaks around the fittings. You may need to use additional sealing materials or tape to reinforce the joints, especially if the line is exposed to vibrations or extreme conditions.
Test and Inspect: Once assembled, test the connection by applying slight pressure to the line and checking for any leaks. If everything is secure, the fuel line is now ready for use. Regularly inspect the connections for any signs of wear or damage, especially in high-pressure areas, to ensure the system's long-term reliability.
Quick Disconnect Fuel Line Connector: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Functionality
You may want to see also

Testing: Run a test to ensure a tight seal and no leaks
Before you begin the installation, it's crucial to test the connections to ensure a tight seal and prevent any potential leaks. This step is often overlooked, but it's an essential part of the process to guarantee the safety and efficiency of your fuel system. Here's a detailed guide on how to perform this test:
Preparation:
- Gather the necessary tools: You'll need a rubber fuel line, a fuel line connector, a wrench or pliers for tightening, and a container to catch any potential fuel leaks.
- Ensure you have a clean and dry work area to facilitate the testing process.
Testing Procedure:
- Connect the fuel line to the connector: Take the 1/4-inch rubber fuel line and carefully attach it to the connector. Ensure that the line is properly aligned with the connector's opening.
- Tighten the connection: Use your wrench or pliers to tighten the connector onto the fuel line. Apply firm pressure, but be careful not to overtighten, as this can damage the line. The goal is to achieve a secure, snug fit.
- Inspect for leaks: After tightening, inspect the connection for any signs of fuel leakage. Look for any visible drips or wet spots around the connector. If you notice any leaks, it indicates that the connection is not tight enough.
- Apply pressure: To further test the seal, gently squeeze the connected fuel line. Apply pressure at different points along the line to ensure there are no weak spots or potential leak points. If you feel any give or notice any leaks, you may need to re-tighten the connection.
- Use a fuel leak detector: For a more comprehensive test, you can use a fuel leak detector spray. Apply the spray around the connector and fuel line, then wait for a few minutes. If there are any leaks, the spray will create a visible mist, indicating the problem areas.
Troubleshooting:
If you encounter leaks during the testing phase, don't panic. It's a common issue and can be easily resolved. Start by re-tightening the connector and applying more pressure. If the leak persists, consider using a different connector or fuel line, as some materials may not be compatible. In rare cases, you might need to cut the affected line and re-install a new one.
Remember, taking the time to properly test and secure the fuel line connections is vital for the overall performance and safety of your vehicle's fuel system. It's a simple yet critical step that can prevent potential hazards and ensure a reliable fuel supply.
Locating the Fuel Filter: 2004 Pontiac Montana Guide
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
A 1/4 inch rubber fuel line is commonly used for fuel transfer applications, such as connecting a fuel pump to a fuel tank or transferring fuel between containers. It is flexible and durable, allowing for easy routing and installation.
To achieve a secure connection, you should use a fuel line clamp specifically designed for the 1/4 inch size. Tighten the clamp firmly but avoid over-tightening, as it can damage the fuel line. Ensure the clamp is made of a compatible material, often rubber or plastic, to prevent damage to the fuel line.
Yes, you can connect a 1/4 inch rubber fuel line to a metal fuel pump. However, it's important to use a fuel line adapter or a short piece of metal fuel line to bridge the connection. This helps prevent corrosion and ensures a reliable seal between the rubber and metal components.
The length of the 1/4 inch fuel line depends on your specific setup. As a general guideline, aim for a length that allows for easy routing and avoids excessive bends, which can restrict fuel flow. Typically, 3 to 6 feet of fuel line is sufficient for most fuel transfer applications.
To minimize the risk of fuel leaks, ensure that all connections are tight and secure. Check for any sharp bends or kinks in the fuel line, as these can cause leaks. Additionally, inspect the fuel line for any signs of damage, such as cracks or punctures, and replace it if necessary. Regularly maintaining and inspecting the fuel lines is essential for a safe and efficient fuel system.