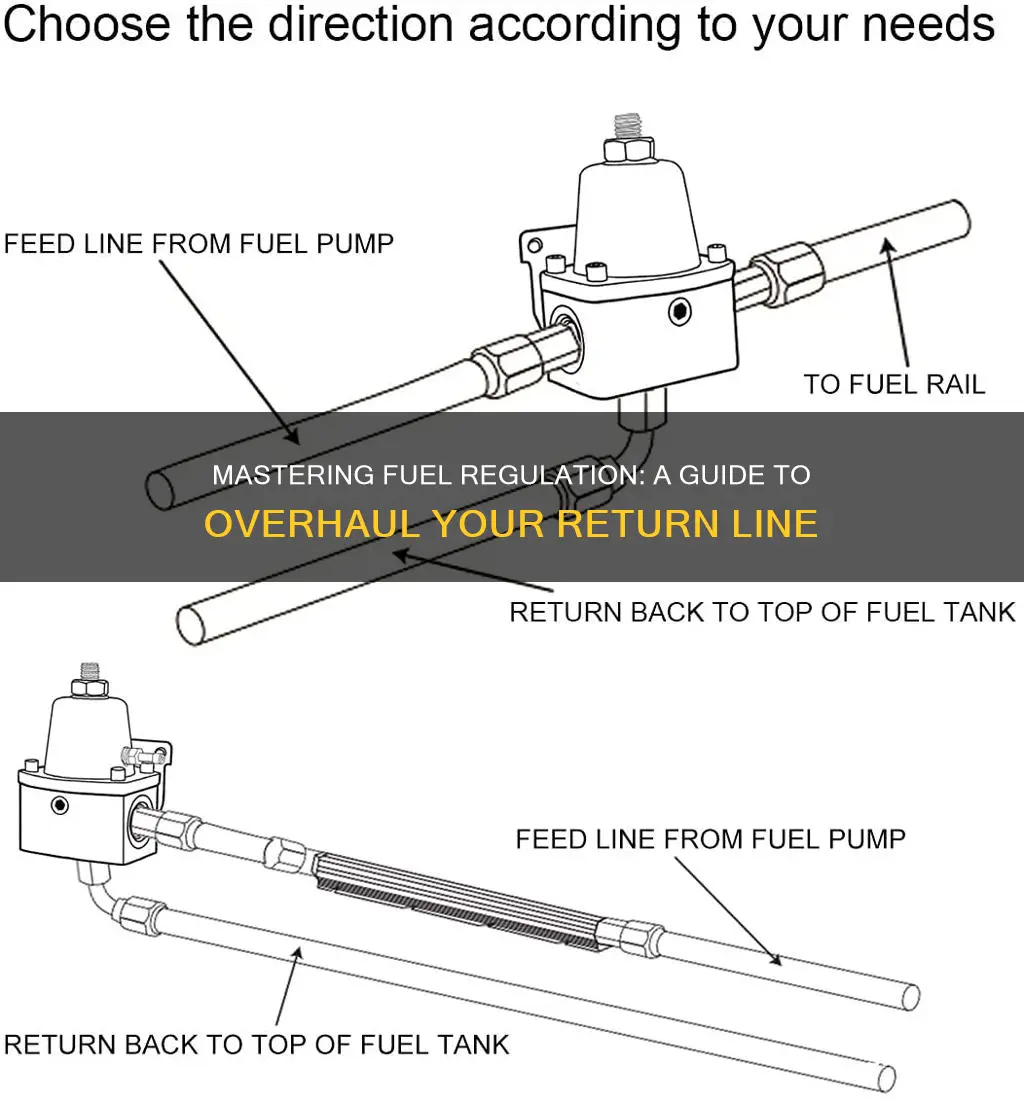
Understanding how to properly maintain and service the fuel regulator return line is crucial for ensuring optimal engine performance and longevity. This guide will provide a comprehensive overview of the process, covering everything from identifying common issues to implementing effective maintenance techniques. By following these steps, you can ensure that your fuel system operates efficiently, preventing potential problems and keeping your vehicle running smoothly.
What You'll Learn
- Fuel Pump and Filter Maintenance: Keep the fuel system clean to prevent blockages
- Return Line Material: Choose the right material for durability and compatibility
- Pressure Regulation: Ensure the return line maintains optimal fuel pressure
- Clamping and Routing: Secure and route the line to avoid damage
- Testing and Inspection: Regularly check for leaks and proper function

Fuel Pump and Filter Maintenance: Keep the fuel system clean to prevent blockages
Maintaining a clean fuel system is crucial for the optimal performance and longevity of your vehicle's engine. Over time, fuel pumps and filters can accumulate contaminants, leading to blockages and potential engine issues. Regular maintenance and cleaning of these components are essential to ensure a smooth and efficient fuel supply. Here's a comprehensive guide on how to keep your fuel pump and filter in top condition:
Fuel Filter Replacement: One of the most effective ways to maintain a clean fuel system is by regularly replacing the fuel filter. The fuel filter acts as a barrier, trapping contaminants such as dirt, rust, and debris that may be present in the fuel. Over time, these particles can accumulate and restrict fuel flow, leading to reduced engine performance. It is recommended to replace the fuel filter at regular intervals, typically every 30,000 to 50,000 miles, or as per your vehicle's manufacturer's guidelines. When replacing the filter, ensure you use the correct type and size to avoid any compatibility issues.
Fuel Pump Maintenance: The fuel pump is responsible for delivering fuel from the tank to the engine at the required pressure. Regular maintenance of the fuel pump is essential to prevent issues. Check for any signs of wear or damage, such as leaks or excessive noise. If you notice any problems, it's best to consult a professional mechanic. Keeping the fuel pump clean is also vital. Use a fuel system cleaner specifically designed for your vehicle to flush out any accumulated contaminants. This process helps remove varnish, deposits, and old fuel, ensuring the pump operates efficiently.
Fuel System Cleaning: To maintain a clean fuel system, consider using a fuel system cleaner during routine maintenance. These cleaners are designed to dissolve and remove deposits and varnish from the fuel lines, injectors, and other components. They can help improve fuel efficiency, power, and performance. When using a fuel system cleaner, follow the manufacturer's instructions carefully. Typically, you'll add the cleaner to the fuel tank or run it through the fuel system according to the product's guidelines. This process can help prevent blockages and ensure optimal fuel flow.
Regular Inspections: It is essential to inspect your fuel system regularly for any signs of contamination or damage. Look for signs of corrosion, leaks, or blockages in the fuel lines. Check for any visible debris or contaminants in the fuel tank and consider using a fuel stabilizer to prevent the growth of harmful microorganisms. By identifying and addressing issues early on, you can avoid costly repairs and maintain a healthy fuel system.
By following these maintenance practices, you can ensure that your fuel pump and filter remain clean and free of blockages, promoting optimal engine performance and longevity. Remember, regular care and attention to your fuel system can save you from potential engine issues and keep your vehicle running smoothly.
Fuel Line Removal Guide: Mercedes-Benz E350 Fuel Fail 92
You may want to see also

Return Line Material: Choose the right material for durability and compatibility
When it comes to selecting the appropriate material for a fuel regulator return line, several factors come into play to ensure optimal performance and longevity. The primary consideration is the compatibility of the material with the fuel being used, as different fuels have varying chemical compositions and properties. For instance, gasoline and diesel have distinct characteristics that require specific material choices to prevent degradation and ensure reliable operation.
One crucial aspect is the resistance of the return line material to the fuel's chemical properties. Some fuels contain additives or have higher levels of moisture, which can lead to corrosion or degradation of certain materials over time. For example, using a return line made of standard steel for a fuel containing high levels of ethanol may result in corrosion, affecting the line's integrity and performance. Therefore, it is essential to choose materials that offer excellent resistance to the specific fuel being used.
Additionally, the operating temperature of the fuel system plays a significant role in material selection. Different materials have varying temperature tolerances, and extreme temperatures can cause expansion or contraction, potentially leading to leaks or damage. For high-temperature applications, materials like stainless steel or aluminum alloys with superior heat resistance are preferred. Conversely, for low-temperature environments, materials that remain flexible and resistant to cracking are ideal.
Flexibility and bendability are other important considerations, especially in fuel systems where the return line may need to accommodate various angles and bends. Materials like rubber or flexible plastics can provide the necessary flexibility to navigate through tight spaces without compromising the line's integrity. However, it is crucial to ensure that these flexible materials are also resistant to fuel degradation and can withstand the system's operating conditions.
Lastly, the overall durability of the return line material is vital for long-term performance. The chosen material should be able to withstand mechanical stress, vibrations, and potential impacts without deteriorating or becoming susceptible to damage. Reinforced rubber or composite materials with high tensile strength can offer the required durability, ensuring the return line remains intact and functional over extended periods.
Understanding Fuel Impulse Lines: Their Role in Engine Performance
You may want to see also

Pressure Regulation: Ensure the return line maintains optimal fuel pressure
The fuel return line plays a critical role in maintaining the correct fuel pressure within the system, ensuring optimal engine performance and longevity. Proper pressure regulation is essential to prevent issues such as engine misfires, reduced power, and potential damage to the fuel system. Here's a detailed guide on how to ensure the return line maintains optimal fuel pressure:
Understanding the Fuel Return Line:
The return line is a crucial component in the fuel system, connecting the fuel pump to the fuel tank and the fuel regulator. Its primary function is to allow fuel to flow back to the tank after it has been pressurized by the pump and regulated by the regulator. This process ensures that the engine receives the precise amount of fuel required for efficient combustion.
Pressure Regulation Techniques:
- Check for Clogs: Start by inspecting the return line for any blockages or clogs. Over time, debris, contaminants, or even air bubbles can accumulate in the line, disrupting the fuel flow and pressure. Use a fuel filter to trap contaminants and regularly inspect the line for any signs of damage or obstruction.
- Maintain Proper Fuel Filter: A clean and well-maintained fuel filter is essential for optimal pressure regulation. Clogged filters can restrict fuel flow, leading to increased pressure drop. Regularly replace the fuel filter according to the manufacturer's recommendations to ensure the return line functions efficiently.
- Inspect for Leaks: Leaks in the return line can cause fuel to spill back into the tank, resulting in low pressure at the regulator. Inspect the line for any signs of damage, cracks, or loose connections. Ensure all fittings and connections are tight and secure to prevent fuel loss and maintain the desired pressure.
- Monitor Pressure: Use a fuel pressure gauge to regularly check the pressure in the return line. The ideal pressure can vary depending on the engine and vehicle specifications. If the pressure is too high, it may indicate a malfunctioning pump or regulator. Conversely, low pressure could suggest a clogged line or filter. Adjustments to the fuel system may be necessary to achieve the optimal pressure range.
- Adjust Fuel Pump Settings: In some cases, you may need to adjust the fuel pump settings to ensure the return line operates within the desired pressure range. This might involve calibrating the pump's output or using a pressure regulator valve to control the flow. Consult the vehicle's manual or seek professional advice for specific instructions on adjusting the fuel pump.
By implementing these pressure regulation techniques, you can ensure that the fuel return line functions optimally, providing the correct fuel pressure to the engine. Regular maintenance and monitoring of the fuel system will contribute to improved performance, fuel efficiency, and the overall longevity of the vehicle.
Honda Motorcycle Fuel Tank Line Disconnection: A Step-by-Step Guide
You may want to see also

Clamping and Routing: Secure and route the line to avoid damage
When dealing with the fuel regulator return line, proper clamping and routing are crucial to ensure the system's longevity and optimal performance. This process involves securing the line to prevent damage and maintaining a clean, organized route throughout the engine bay. Here's a step-by-step guide to achieving this:
Start by identifying the fuel regulator return line, which is typically a flexible hose or tube that connects the fuel pump to the engine's intake system. Locate the clamps that hold this line in place and ensure they are in good condition. Old or damaged clamps can lead to fuel leaks and potential engine issues. Replace any faulty clamps with new ones designed for the specific fuel line. Clamps should be tight enough to secure the line but not so tight that they cause damage or restrict flow.
Once the clamps are in place, it's time to route the line carefully. Begin at the fuel pump and follow the line's natural path towards the engine. Avoid sharp bends or kinks, as these can restrict fuel flow and potentially damage the line over time. Instead, use bends and loops that allow for smooth, continuous movement. Route the line away from hot engine components and sharp edges to prevent heat damage and physical harm. Consider using protective sleeves or shields to cover the line where it passes over sharp edges or near heat sources.
As you route the line, ensure it is not twisted or cramped, as this can lead to fuel aeration and reduced performance. Keep the line as straight and flat as possible to maintain optimal fuel flow. If the line needs to cross other components, use appropriate tie-downs or brackets to secure it without causing strain or damage. Proper routing also involves leaving enough slack to allow for engine movement without the line becoming taut or tight.
Finally, double-check all connections and ensure the line is securely clamped at various points along its length. This prevents the line from coming loose during engine operation and potential fuel loss. Regularly inspect the line for any signs of wear, damage, or leaks, especially after periods of high mileage or extreme operating conditions. By following these clamping and routing practices, you can ensure the fuel regulator return line remains intact and functions efficiently.
Teguar ClampD: A Fuel Line Alternative?
You may want to see also

Testing and Inspection: Regularly check for leaks and proper function
When it comes to maintaining the fuel system of your vehicle, regular testing and inspection of the fuel regulator return line are crucial. This component plays a vital role in ensuring that the engine receives the correct amount of fuel for optimal performance. Here's a detailed guide on how to approach this task:
Start by locating the fuel regulator return line, which is typically a small diameter hose or pipe that connects the fuel pump to the engine. It is essential to inspect this line for any signs of damage, cracks, or leaks. Use a bright flashlight to examine the line for any visible issues. Look for any bends or kinks that might have occurred during installation or previous repairs. Ensure that all connections are secure and free from corrosion. If you notice any damage, it is best to replace the return line to prevent potential fuel leaks.
The primary purpose of testing for leaks is to identify any potential issues before they cause significant problems. Use a soapy water solution to carefully inspect the return line for leaks. Apply the solution along the entire length of the line, paying close attention to connections and bends. If you notice any bubbles forming, it indicates a leak. Leaks can lead to fuel wastage, reduced engine performance, and potential safety hazards. Address any leaks promptly by tightening connections or replacing the affected section of the line.
In addition to visual inspections, it is beneficial to perform a functional test of the fuel regulator return line. This can be done by temporarily disconnecting the line and observing the fuel pressure gauge or sensor. If the gauge or sensor shows a significant drop in pressure when the line is disconnected, it suggests a potential issue with the return line or the fuel pump. Re-attach the line and check for any abnormal pressure fluctuations. Proper fuel pressure is critical for engine operation, and any deviations should be addressed immediately.
Regular maintenance and testing can help prevent unexpected breakdowns and ensure your vehicle's fuel system operates efficiently. By following these inspection procedures, you can identify and rectify issues with the fuel regulator return line, ultimately contributing to the overall reliability and performance of your engine. Remember, proper maintenance is key to keeping your vehicle in optimal condition.
Honda Small Engine Fuel Line: Understanding the Fuel System
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The fuel regulator return line is a crucial component in a vehicle's fuel system, designed to ensure optimal fuel pressure and flow. It connects the fuel regulator to the fuel tank, allowing excess fuel to return to the tank when the regulator reduces the pressure to the engine.
A leaking return line can cause fuel wastage and potential engine performance issues. Signs of a leak include fuel odors in the cabin, fuel stains around the vehicle, and a noticeable drop in fuel level despite regular use. If you suspect a leak, inspect the line for any cracks, corrosion, or damage, and consider consulting a professional mechanic for a thorough inspection.
While some minor fuel system repairs can be tackled by DIY enthusiasts, replacing the return line requires specific knowledge and tools. It is essential to understand the vehicle's fuel system layout and have access to the necessary replacement parts. If you are unsure or uncomfortable with the task, it is best to consult a qualified mechanic to ensure the job is done safely and correctly.
Regular maintenance can help prolong the life of the return line. It is recommended to check the line for any signs of damage or corrosion during routine vehicle inspections. Keeping the fuel tank and lines clean by using fuel system cleaner can also prevent buildup and ensure proper fuel flow. Additionally, using the correct type of fuel and maintaining the vehicle's overall health can contribute to the longevity of the fuel system components.
Ignoring a damaged or leaking return line can lead to several issues. These may include reduced engine performance, increased fuel consumption, and potential engine damage due to improper fuel pressure. Over time, the engine may struggle to start or may experience rough idling. It is essential to address any fuel system problems promptly to avoid costly repairs and ensure the vehicle's reliability.







