The adoption of fuel cell technology in the automotive industry is a rapidly growing trend, but how widespread is its use? In recent years, the number of cars utilizing fuel cells has significantly increased, with many manufacturers investing in this innovative technology. Fuel cell vehicles, which produce electricity through a chemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen, offer a cleaner and more efficient alternative to traditional internal combustion engines. This paragraph will explore the current state of fuel cell car adoption, examining the factors driving their popularity and the challenges that remain in their widespread integration into the global automotive market.
What You'll Learn
- Fuel Cell Technology: Hydrogen fuel cells power cars, offering zero emissions
- Fuel Cell Adoption: Electric vehicles (EVs) are rapidly replacing fuel cell cars
- Fuel Cell Range: Fuel cell cars have a limited range compared to EVs
- Fuel Cell Cost: High production costs hinder widespread fuel cell car adoption
- Fuel Cell Infrastructure: The lack of hydrogen refueling stations limits fuel cell car use

Fuel Cell Technology: Hydrogen fuel cells power cars, offering zero emissions
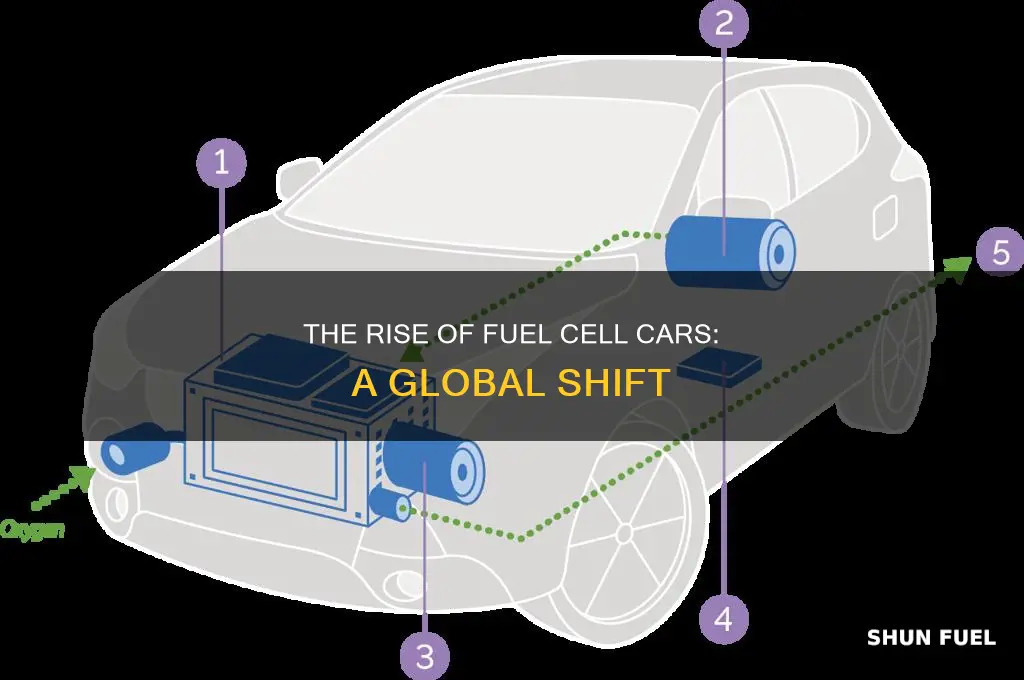
Fuel cell technology is an innovative and sustainable solution that has the potential to revolutionize the automotive industry. Hydrogen fuel cells, in particular, are gaining traction as a clean and efficient power source for vehicles, offering a promising alternative to traditional internal combustion engines. These cells provide a unique advantage by converting chemical energy directly into electricity through a reaction between hydrogen and oxygen, resulting in zero emissions of harmful pollutants.
The concept of using hydrogen as a fuel for transportation is not entirely new, but recent advancements in fuel cell technology have made it more practical and accessible. Fuel cells have been utilized in various applications, including stationary power generation, but their integration into the automotive sector has been a significant breakthrough. This technology enables cars to run on hydrogen, a renewable and abundant resource, without producing harmful exhaust gases.
In a fuel cell-powered vehicle, the hydrogen gas is fed into the cell, where it undergoes a chemical reaction with oxygen from the air. This process generates electricity, which then powers the car's electric motor. The only byproduct of this reaction is water vapor, making it an environmentally friendly alternative to conventional combustion engines. This zero-emission characteristic is a significant advantage, addressing the environmental concerns associated with traditional vehicles.
The efficiency of fuel cell technology is another compelling factor. These cells can convert a higher percentage of the hydrogen's energy into electricity compared to traditional engines. This increased efficiency translates to improved performance and a longer driving range for fuel cell vehicles. As a result, hydrogen fuel cell cars can offer a more sustainable and practical solution for daily transportation needs.
The adoption of fuel cell technology in the automotive industry is still growing, but it has the potential to significantly reduce the environmental impact of transportation. With ongoing research and development, the number of fuel cell vehicles on the road is expected to increase, contributing to a cleaner and more sustainable future. This technology paves the way for a new era of eco-friendly transportation, where hydrogen fuel cells play a pivotal role in powering vehicles with zero emissions.
Formula 1 Fuel: Powering the Ultimate Speed Machines
You may want to see also

Fuel Cell Adoption: Electric vehicles (EVs) are rapidly replacing fuel cell cars
The automotive industry is undergoing a significant transformation, with electric vehicles (EVs) gaining rapid popularity and market share. This shift is partly due to the advancements in battery technology, which have made EVs more efficient, affordable, and environmentally friendly compared to traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. As a result, the adoption of fuel cell vehicles, which were once seen as a promising alternative to EVs, is slowing down.
Fuel cells, which generate electricity through a chemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen, offer a clean and efficient way to power vehicles. However, despite their potential, fuel cell cars have faced several challenges that have hindered their widespread adoption. One of the primary issues is the lack of a robust hydrogen infrastructure. Hydrogen refueling stations are currently limited in number and availability, making it inconvenient for fuel cell vehicle owners to refuel. This is in stark contrast to the extensive charging networks for EVs, which have made electric driving more accessible and convenient.
Another factor contributing to the decline in fuel cell car sales is the performance and range limitations of these vehicles. While modern fuel cell cars can offer impressive range, they often fall short compared to the long-range capabilities of contemporary EVs. Additionally, the high cost of fuel cell systems and the limited availability of hydrogen fuel make it economically unviable for many consumers.
As a result of these challenges, the market for fuel cell cars is shrinking. Many automotive manufacturers are shifting their focus to EV technology, investing heavily in battery-powered vehicles. This strategic shift is driven by the increasing demand for sustainable transportation, government incentives, and the technological advancements that have made EVs more appealing to consumers.
In summary, the rapid rise of electric vehicles is overshadowing the adoption of fuel cell cars. The combination of a well-established charging infrastructure, longer range, and lower costs has made EVs the preferred choice for environmentally conscious consumers. While fuel cells have their merits, the current market dynamics suggest that the future of sustainable transportation lies in the widespread adoption of electric vehicles.
Why Turning Your Car Off While Filling Up Can Be a Bad Idea
You may want to see also

Fuel Cell Range: Fuel cell cars have a limited range compared to EVs
The range of fuel cell vehicles is a significant factor that sets them apart from electric vehicles (EVs). While EVs have made remarkable strides in improving their range, fuel cell cars still face challenges in terms of distance coverage. On average, fuel cell vehicles can travel between 250 to 400 miles on a single tank of hydrogen, which is significantly less than the range of many modern EVs. For instance, the Tesla Model S, a popular EV, boasts a range of over 400 miles on a single charge, while the Hyundai Nexo, a fuel cell SUV, can only manage around 300 miles on hydrogen. This disparity in range is primarily due to the efficiency and energy storage capabilities of the respective technologies.
The limited range of fuel cell cars is primarily attributed to the energy density of hydrogen and the efficiency of fuel cell systems. Hydrogen, being a highly flammable gas, requires a larger and heavier fuel tank to store the same amount of energy as a lithium-ion battery in an EV. As a result, fuel cell vehicles tend to be bulkier and heavier, which can impact their overall performance and efficiency. Additionally, the current state of hydrogen infrastructure is not as extensive as that of charging stations for EVs, making it less convenient for long-distance travel.
Despite the range limitation, fuel cell technology offers several advantages. It provides rapid refueling, typically taking just a few minutes, compared to the longer charging times of EVs. This makes fuel cell cars more suitable for certain applications, such as fleet vehicles or commercial transportation, where quick turnaround times are essential. However, for personal use, especially for those living in areas with limited hydrogen refueling stations, the range of fuel cell cars may still be a significant consideration.
To address the range issue, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on improving fuel cell efficiency and exploring alternative hydrogen storage methods. Some innovations include advanced fuel cell designs, improved catalysts, and the use of compressed hydrogen gas or liquid hydrogen, which can potentially increase energy density. Additionally, the integration of fuel cells with other power sources, such as batteries, is being explored to create hybrid systems that can extend the range of fuel cell vehicles.
In summary, while fuel cell cars offer rapid refueling and other benefits, their range remains a critical factor compared to EVs. The limited distance they can cover on a single tank of hydrogen is a result of technological constraints and infrastructure limitations. Ongoing advancements in fuel cell technology and hydrogen storage methods aim to enhance the range and overall appeal of fuel cell vehicles, making them more competitive in the market.
Automatic vs Manual: Fuel Efficiency Debate
You may want to see also

Fuel Cell Cost: High production costs hinder widespread fuel cell car adoption
The high production costs of fuel cell vehicles present a significant barrier to their widespread adoption and integration into the automotive industry. Fuel cells, which convert chemical energy from hydrogen into electricity to power a vehicle, offer a promising alternative to traditional internal combustion engines. However, the manufacturing process of these cells and the associated components is complex and expensive.
One of the primary reasons for the high production costs is the specialized nature of the materials and components required. Fuel cells demand advanced materials such as platinum catalysts, rare earth metals, and carbon-based components, which are not only scarce but also expensive. For instance, platinum, a critical element in fuel cell design, is used as a catalyst to facilitate the electrochemical reaction. Its cost, however, is substantial, and the amount required for a single fuel cell stack can be significant, contributing to the overall production expense.
Additionally, the manufacturing process itself is intricate and energy-intensive. Fuel cell production involves multiple steps, including the preparation of raw materials, the assembly of cell stacks, and the integration of various subsystems. Each step requires precise control and specialized equipment, which adds to the overall cost. The complexity of the manufacturing process often results in higher labor costs and increased operational expenses, further contributing to the high production prices.
The high production costs have a direct impact on the marketability of fuel cell vehicles. As a result, they are often priced significantly higher than their conventional counterparts, making them less accessible to the general public. This price disparity can deter potential buyers, especially those who are price-sensitive, from considering fuel cell vehicles as a viable option. Consequently, the limited market appeal hampers the potential for widespread adoption and the realization of the environmental benefits that fuel cell technology could offer.
To address this challenge, researchers and engineers are exploring ways to reduce production costs through innovative manufacturing techniques and material substitutions. The development of more efficient and cost-effective production methods is crucial for making fuel cell vehicles competitive in the market. This includes optimizing the use of materials, streamlining the manufacturing process, and potentially exploring alternative energy sources or storage solutions that could reduce the overall cost of fuel cell systems.
Dirty Oil: The Hidden Fuel-Waster in Your Engine
You may want to see also

Fuel Cell Infrastructure: The lack of hydrogen refueling stations limits fuel cell car use
The widespread adoption of fuel cell vehicles is significantly hindered by the inadequate infrastructure for hydrogen refueling stations. While fuel cell cars offer a promising alternative to traditional internal combustion engines, their potential remains untapped due to the limited availability of hydrogen refueling stations. This critical issue poses a significant barrier to the growth of the fuel cell vehicle market.
Hydrogen refueling stations are essential for the practical use of fuel cell vehicles. These stations provide the necessary hydrogen gas, which is then used to power the fuel cell, generating electricity to propel the vehicle. However, the current network of hydrogen refueling stations is sparse and unevenly distributed, particularly in urban areas. This lack of infrastructure means that fuel cell car owners often face challenges in finding a nearby station to refuel, limiting their ability to travel long distances without running out of hydrogen.
The construction of hydrogen refueling stations is a complex and costly endeavor. It requires specialized equipment, high-pressure gas storage, and safety measures to handle hydrogen, which is a highly flammable and reactive gas. As a result, the establishment of these stations is a significant investment, often requiring collaboration between governments, energy companies, and vehicle manufacturers. Despite the potential benefits, the financial and logistical challenges have led to a slow pace of development, leaving many regions without adequate hydrogen infrastructure.
Furthermore, the expansion of hydrogen refueling stations is crucial for the development of a comprehensive fuel cell vehicle ecosystem. Without a robust network of stations, the market for fuel cell cars remains niche and limited to early adopters. This lack of infrastructure also hinders the development of a sustainable business model for hydrogen fuel suppliers and station operators, creating a vicious cycle that slows down the necessary growth of the industry.
Addressing this challenge requires a multi-faceted approach. Governments play a pivotal role in incentivizing the construction of hydrogen refueling stations by offering financial support and creating favorable policies. Collaboration between various stakeholders, including energy companies, vehicle manufacturers, and infrastructure developers, is essential to streamline the process and reduce costs. Additionally, research and development efforts should focus on improving the efficiency and safety of hydrogen refueling stations, making them more accessible and appealing to both businesses and consumers.
In conclusion, the absence of a robust hydrogen refueling infrastructure is a critical factor limiting the widespread adoption of fuel cell vehicles. To accelerate the transition to a cleaner and more sustainable transportation system, it is imperative to prioritize the development of hydrogen refueling stations, ensuring that the necessary infrastructure is in place to support the growing number of fuel cell cars on the road.
Fuel Filters: Do New Cars Still Need Them?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
As of 2023, there are approximately 1,000 fuel cell vehicles (FCVs) in operation worldwide. This number includes passenger cars, buses, and commercial vehicles. The majority of these vehicles are in use in countries like Japan, South Korea, and the United States, where governments and automotive manufacturers have invested in fuel cell technology.
The primary reasons for the relatively small number of fuel cell cars are technology maturity, infrastructure, and cost. Fuel cell technology has been in development for decades, and while it has shown great promise, it is still in the early stages of commercialization. Building a comprehensive fueling infrastructure for hydrogen, the fuel used in fuel cells, is a significant challenge and requires substantial investment. Additionally, the cost of fuel cell systems and the overall vehicle price is currently higher compared to conventional internal combustion engine vehicles.
Yes, many automotive manufacturers and governments are working towards expanding the use of fuel cell technology. Several carmakers have announced plans to launch new fuel cell vehicle models in the coming years. Governments are also providing incentives and subsidies to encourage the adoption of FCVs, including tax credits, grants, and the development of hydrogen refueling stations. These efforts aim to accelerate the transition to a more sustainable transportation system.
Fuel cell cars offer several advantages, including zero direct emissions, high energy efficiency, and a quiet, smooth driving experience. They produce electricity through a chemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen, emitting only water vapor and warm air. This makes fuel cell vehicles an environmentally friendly alternative to conventional cars. Additionally, fuel cell cars can refuel quickly, similar to gasoline or diesel vehicles, and have a long driving range.
Fuel cell vehicles and battery electric vehicles represent two different approaches to sustainable transportation. BEVs are powered by electric motors and batteries, storing electrical energy and converting it directly into motion. While BEVs have a larger market presence and are rapidly growing, fuel cell cars offer unique advantages. FCVs can be refueled quickly and have a longer driving range, making them suitable for long-distance travel. However, BEVs have the advantage of a well-established charging infrastructure and lower fuel costs in many regions.







