Hydrogen fuel for cars is a promising alternative to traditional fossil fuels, and its production is a fascinating process. The creation of hydrogen fuel involves several methods, including steam methane reforming, which is the most common industrial process. This process starts with natural gas, where methane is reacted with steam at high temperatures to produce hydrogen and carbon monoxide. Another method is electrolysis, where water is split into hydrogen and oxygen using electricity, often from renewable sources. Additionally, hydrogen can be produced from biomass through a process called biomass gasification, which involves heating organic materials in a low-oxygen environment to produce a gas that can be further processed to extract hydrogen. These diverse production methods showcase the versatility of hydrogen fuel and its potential as a clean energy source for vehicles.
What You'll Learn
- Hydrogen Production Methods: Electrolysis, steam methane reforming, and biomass gasification are common processes
- Electrolysis: Water is split into hydrogen and oxygen using electricity, a clean and renewable method
- Steam Methane Reforming: Natural gas is reacted with steam to produce hydrogen and carbon dioxide
- Biomass Gasification: Organic materials are heated to produce a gas mixture containing hydrogen
- Carbon Capture and Storage: Technologies to capture and store carbon dioxide emissions during hydrogen production

Hydrogen Production Methods: Electrolysis, steam methane reforming, and biomass gasification are common processes
Hydrogen fuel for cars is produced through various methods, each with its own unique process and advantages. One of the most common and environmentally friendly ways to generate hydrogen is through electrolysis. This process involves passing an electric current through water, which splits the water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen. The key to successful electrolysis is the use of an efficient and cost-effective electrolyte, typically a solution of sulfuric acid or a solid polymer. The electric current causes a chemical reaction, releasing hydrogen gas on one side of the electrolyte and oxygen gas on the other. This method is highly sustainable as it relies on renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power, to generate the electricity.
Another widely adopted technique for hydrogen production is steam methane reforming. This process starts with natural gas, primarily composed of methane, and reacts it with steam at high temperatures and pressures. The reaction produces hydrogen and carbon monoxide, along with a small amount of carbon dioxide. The hydrogen is then separated from the carbon monoxide and other byproducts through a process called shift conversion, which removes any remaining carbon monoxide and adjusts the hydrogen-to-carbon monoxide ratio. This method is highly efficient and has been used for decades in the industrial sector, making it a reliable and established process for hydrogen generation.
Biomass gasification is an emerging technique that offers a more sustainable approach to hydrogen production. This process involves heating biomass, such as agricultural waste or dedicated energy crops, in a low-oxygen environment. The heat and lack of oxygen cause the biomass to undergo thermal decomposition, resulting in the production of hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and other gases. The gasification process can be carried out in various ways, including fixed-bed, fluidized bed, and entrained flow gasifiers. The hydrogen-rich gas, known as syngas, can then be processed further to remove impurities and increase hydrogen concentration. This method is particularly attractive due to its potential to utilize waste materials and reduce the environmental impact of hydrogen production.
Each of these hydrogen production methods has its own set of advantages and challenges. Electrolysis is environmentally friendly but may face challenges in terms of energy efficiency and cost, especially when using conventional power sources. Steam methane reforming is efficient and well-established but relies on fossil fuels, which raises concerns about sustainability. Biomass gasification offers a renewable and waste-reducing approach but requires careful feedstock selection and process optimization to ensure high-purity hydrogen production. The choice of method often depends on factors such as availability of resources, infrastructure, and environmental considerations.
In summary, hydrogen fuel for cars is produced through electrolysis, steam methane reforming, and biomass gasification. Electrolysis splits water into hydrogen and oxygen, offering a sustainable option. Steam methane reforming, a traditional process, generates hydrogen from natural gas. Biomass gasification, an emerging technique, utilizes waste materials to produce hydrogen-rich gas. Each method has its merits, and the selection of the most suitable process depends on various factors, ensuring a cleaner and more sustainable future for hydrogen-powered vehicles.
Winter Fuel Allowance: Can Care Home Residents Claim?
You may want to see also

Electrolysis: Water is split into hydrogen and oxygen using electricity, a clean and renewable method
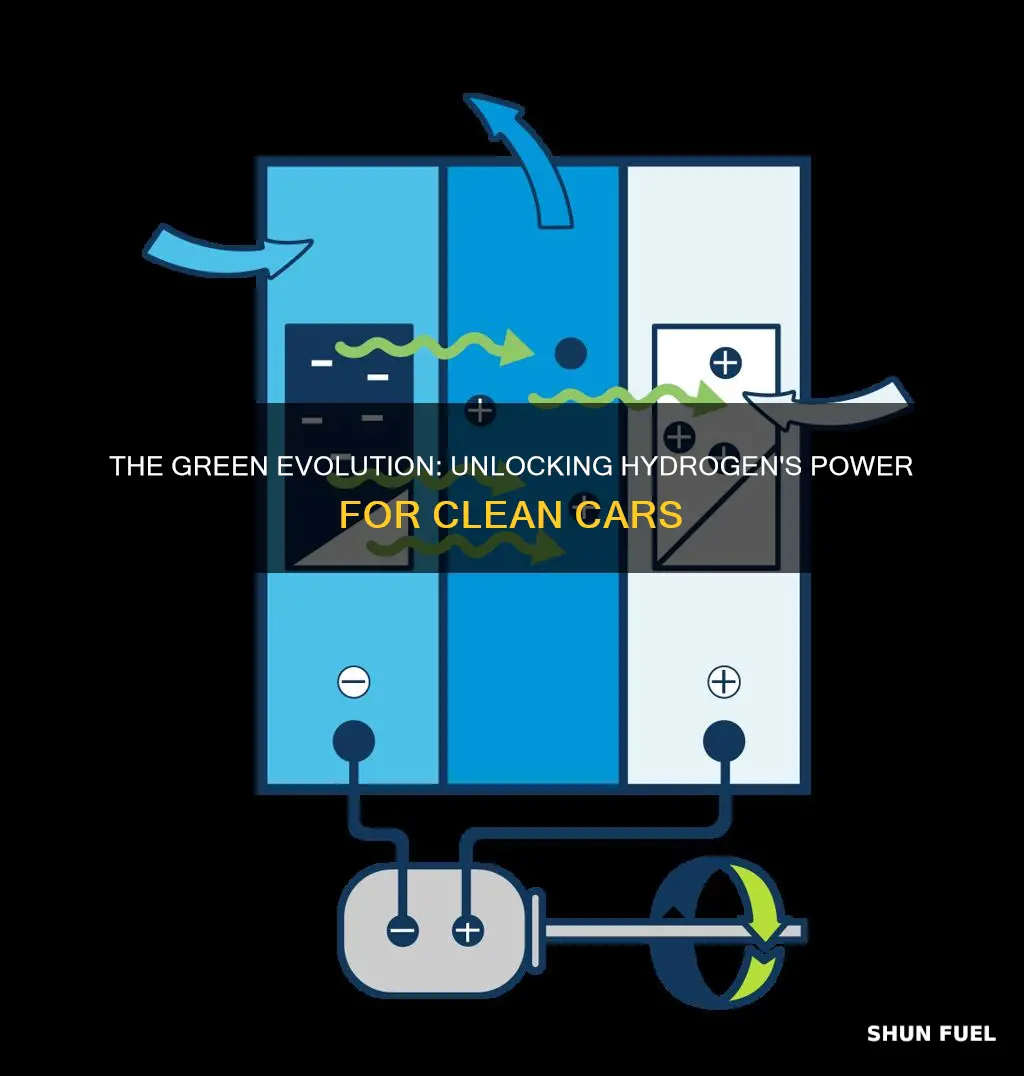
Electrolysis is a fascinating process that forms the basis of hydrogen fuel production, offering a clean and renewable approach to generating hydrogen gas. This method involves the use of electricity to split water molecules (H2O) into their constituent elements: hydrogen (H2) and oxygen (O2). The process is both efficient and environmentally friendly, making it an attractive option for sustainable hydrogen production.
The electrolysis process begins with the setup of an electrolyzer, a device specifically designed for this purpose. The electrolyzer consists of an anode and a cathode immersed in water, with an electrolyte solution, typically an alkaline or acidic substance, in between. When an electric current is applied, it passes through the water, causing a chemical reaction. At the anode, water molecules lose electrons and split into oxygen and hydroxide ions. Simultaneously, at the cathode, hydrogen ions from the water combine with electrons to form hydrogen gas.
The key advantage of electrolysis is its ability to produce hydrogen gas without emitting greenhouse gases or pollutants, making it a green energy source. The electricity used can be sourced from renewable energy, such as solar or wind power, further reducing the environmental impact. This renewable energy integration ensures that the entire process is sustainable and contributes to a cleaner energy future.
During electrolysis, the efficiency of hydrogen production is influenced by various factors. These include the type of electrolyte, the temperature of the water, and the applied voltage. Researchers and engineers are continually optimizing these parameters to enhance the overall efficiency of the process. For instance, using a more efficient electrolyte or adjusting the voltage can lead to higher hydrogen production rates while minimizing energy consumption.
Electrolysis has gained significant attention as a potential solution to the growing demand for clean energy alternatives. Its ability to produce hydrogen fuel in a sustainable manner aligns with global efforts to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and combat climate change. As technology advances, electrolysis is expected to play a crucial role in the development of hydrogen-based transportation and energy storage systems, offering a promising path towards a more sustainable and environmentally conscious future.
Hydrogen Fuel Cell Car: DIY Guide to Building Your Own Power Source
You may want to see also

Steam Methane Reforming: Natural gas is reacted with steam to produce hydrogen and carbon dioxide
Steam methane reforming is a crucial process in the production of hydrogen fuel for vehicles, offering a reliable and efficient method to extract hydrogen from natural gas. This process involves a chemical reaction where natural gas, primarily composed of methane, is combined with steam under high temperatures and specific conditions. The reaction is facilitated by a catalyst, often made of nickel, which speeds up the process without being consumed in the reaction itself.
In this process, methane (CH4) and steam (H2O) react to form hydrogen (H2) and carbon dioxide (CO2). The balanced chemical equation for this reaction is:
CH4 + H2O → CO2 + 3H2
Here, one mole of methane reacts with one mole of steam to produce one mole of carbon dioxide and three moles of hydrogen gas. The reaction is exothermic, meaning it releases heat, which is why high temperatures are required to initiate and sustain the process. Typically, the reaction occurs at temperatures ranging from 700°C to 900°C (1292°F to 1652°F), and the pressure is often maintained at around 20-30 bar (20-30 MPa).
The steam methane reformer is the key equipment used in this process. It consists of a reactor, where the reaction takes place, and a heat exchanger to supply the necessary heat. The reformer is designed to handle the high temperatures and pressures involved in the reaction. The hydrogen produced is then typically cooled and compressed to remove any remaining carbon dioxide and to meet the storage and transportation requirements for fuel.
This method of hydrogen production is widely used in the industry due to its high efficiency and the availability of natural gas as a feedstock. It is a mature technology, with a long history of successful application in various industries, including the production of hydrogen for ammonia synthesis and the chemical industry. The process also generates carbon dioxide as a byproduct, which can be captured and stored or utilized for other purposes, contributing to a more sustainable approach to hydrogen production.
Jet Fuel: A Viable Alternative for Car Engines?
You may want to see also

Biomass Gasification: Organic materials are heated to produce a gas mixture containing hydrogen
Biomass gasification is a fascinating process that plays a crucial role in the production of hydrogen fuel for vehicles. This method involves the conversion of organic materials, such as agricultural residues, wood chips, and even certain types of waste, into a valuable energy source. The process begins with the careful selection and preparation of the feedstock, ensuring it meets the required specifications for gasification.
In the gasification process, organic materials are subjected to extremely high temperatures, often ranging from 700°C to 1,100°C (1,292°F to 2,012°F). This intense heat causes the organic matter to undergo a series of chemical reactions. Through the application of controlled oxygen, the organic feedstock undergoes pyrolysis, where it is broken down into a solid residue (char), a gaseous product (syngas), and a liquid product (bio-oil). The syngas, a mixture of carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrogen (H2), is a key component in the production of hydrogen fuel.
The syngas is then cooled and processed to separate the hydrogen from other gases. This is typically achieved through a process called 'shift reaction,' where carbon monoxide is converted to carbon dioxide (CO2) and additional hydrogen. The resulting hydrogen-rich gas can be further purified to meet the standards required for vehicle fuel. This purification process ensures that the hydrogen produced is of high quality and suitable for use in fuel cells or internal combustion engines.
One of the significant advantages of biomass gasification is its ability to utilize a wide range of organic materials. This includes agricultural waste, such as corn stover and wheat straw, as well as dedicated energy crops like switchgrass and poplar trees. By employing these readily available resources, the process becomes more sustainable and environmentally friendly. Additionally, the gasification process can be integrated into existing agricultural systems, providing a valuable byproduct in the form of biochar, which can enhance soil quality.
In summary, biomass gasification is a promising technology for producing hydrogen fuel from organic materials. It offers a sustainable and efficient approach to generating clean energy. With further research and development, this process could potentially contribute significantly to the global transition towards renewable and environmentally friendly transportation fuels.
Hemp Fuel: The Green Alternative for Your Car?
You may want to see also

Carbon Capture and Storage: Technologies to capture and store carbon dioxide emissions during hydrogen production
The process of producing hydrogen fuel for vehicles involves various methods, and one critical aspect is addressing the environmental impact, particularly the carbon emissions associated with hydrogen production. Carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies play a pivotal role in mitigating these emissions, ensuring a more sustainable approach to hydrogen generation.
CCS is a process that aims to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by capturing carbon dioxide (CO2) from industrial sources, such as those involved in hydrogen production, and then storing it underground or utilizing it in other ways. In the context of hydrogen fuel, the primary focus is on capturing CO2 emissions during the production process, especially from methods like steam methane reforming, which is a common technique for generating hydrogen. This reforming process involves reacting methane with steam to produce hydrogen and CO2 as a byproduct.
One of the key technologies employed in carbon capture is absorption, where CO2 is captured using specialized solvents or sorbents. These materials have a high affinity for CO2 and can effectively separate it from the gas stream. Amine-based solvents, for instance, are commonly used in industrial-scale CCS systems. When CO2 comes into contact with these solvents, it forms a stable compound, allowing for its removal from the process stream. This captured CO2 can then be compressed and transported for storage or further utilization.
Another approach is membrane separation, which utilizes semi-permeable membranes to selectively transport CO2. These membranes have specific pores that allow CO2 molecules to pass through while blocking others. This method is particularly useful for capturing CO2 from gas streams with varying compositions. Membrane technology can be employed in both pre-combustion and post-combustion scenarios, making it versatile for different hydrogen production processes.
Storage is a critical component of CCS, ensuring that captured CO2 is safely and permanently contained. One common storage method is geological sequestration, where CO2 is injected into deep underground formations, such as depleted oil and gas reservoirs or saline aquifers. These geological formations provide a secure and long-term storage solution, minimizing the risk of CO2 release into the atmosphere. Additionally, CO2 can be utilized for enhanced oil recovery, where it is injected into oil reservoirs to increase the extraction of trapped oil.
In summary, carbon capture and storage technologies are essential for the sustainable production of hydrogen fuel. By implementing absorption, membrane separation, and appropriate storage methods, it becomes feasible to capture and manage CO2 emissions during hydrogen generation, contributing to a cleaner and more environmentally friendly energy sector. These technologies are vital in the transition towards a low-carbon economy, where hydrogen fuel can play a significant role in transportation and energy generation.
Tire Choice: Unlocking Fuel Savings with the Right Rubber
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Hydrogen fuel for vehicles is primarily produced through a process called steam methane reforming. This process involves reacting natural gas (methane) with steam at high temperatures to produce hydrogen and carbon dioxide. The reaction is typically carried out in a specialized reactor, and the resulting hydrogen is then compressed and stored for use in fuel cell vehicles.
Yes, hydrogen can be produced from renewable sources, making it a more sustainable option. Electrolysis of water using electricity from renewable sources like solar or wind power is a common method. During electrolysis, water molecules are split into hydrogen and oxygen, providing a clean and green source of hydrogen fuel.
To meet the stringent requirements of the automotive industry, hydrogen fuel must be highly purified. The production process often involves multiple stages of purification, including pressure swing adsorption (PSA) and membrane separation. These methods remove impurities and ensure that the hydrogen is of the required purity for safe and efficient use in fuel cell vehicles.
Absolutely! Other methods include biomass gasification, where organic materials are heated to produce a gas mixture containing hydrogen, and biological processes that utilize microorganisms to generate hydrogen from organic matter. These alternative methods offer potential for decentralized hydrogen production and contribute to the diversity of hydrogen fuel generation techniques.
Scaling up hydrogen fuel production for mass market adoption presents several challenges. These include the need for large-scale infrastructure, such as production plants and distribution networks, to supply hydrogen to refueling stations. Additionally, ensuring a consistent supply of renewable energy sources for electrolysis and managing the energy-intensive nature of certain production methods are crucial aspects that require further development and optimization.