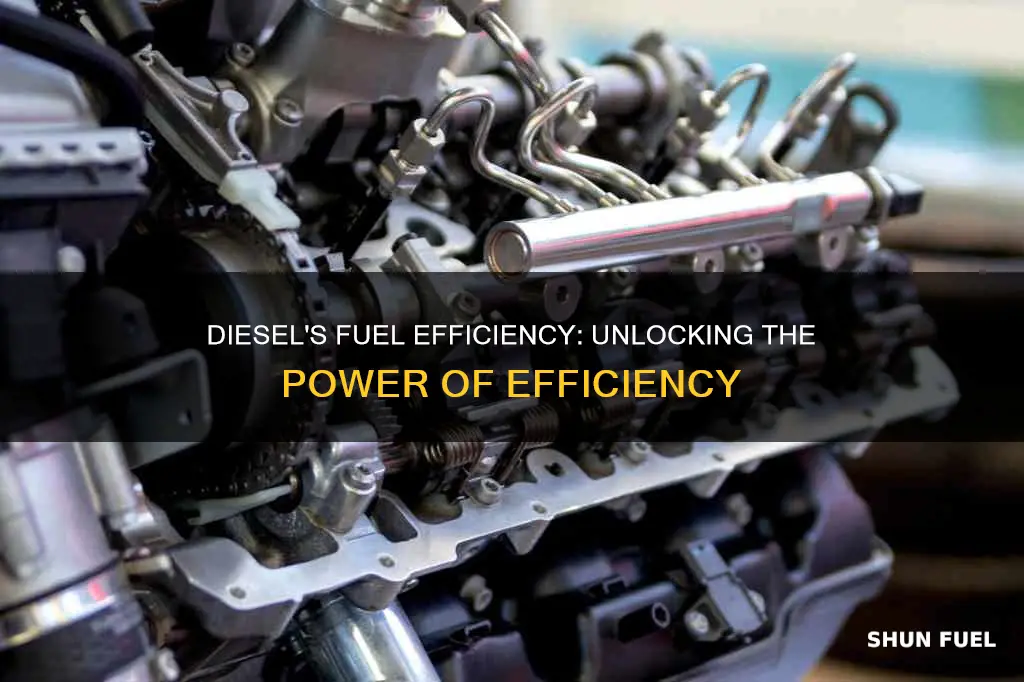
Diesel cars have long been associated with superior fuel efficiency compared to their gasoline counterparts. This efficiency is primarily due to the diesel engine's ability to compress air and inject fuel more efficiently, resulting in a higher energy output per unit of fuel. The higher compression ratio of diesel engines allows for a more complete combustion process, which means less fuel is wasted as unburned hydrocarbons. Additionally, diesel engines can operate at lower temperatures, reducing heat loss and further improving fuel efficiency. These factors, combined with the denser energy content of diesel fuel, contribute to the higher fuel economy that diesel cars are known for.
Characteristics of Diesel Car Fuel Efficiency
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Engine Type | Common-rail direct injection diesel engine |
| Fuel Injection | High-pressure common-rail system |
| Turbocharging | Often equipped with turbochargers for forced induction |
| Compression Ratio | Typically higher than gasoline engines (e.g., 18:1) |
| Engine Size | Usually smaller displacement compared to gasoline counterparts |
| Fuel | Diesel fuel, which has a higher energy density |
| Engine Management | Advanced electronic control units for precise fuel injection and timing |
| Turbo Lag | Reduced turbo lag due to advanced turbocharger technology |
| Emission Standards | Adherence to strict emission regulations (e.g., Euro 6) |
| Efficiency Improvements | Continuous advancements in engine design and technology |
| Real-World Performance | Improved fuel economy in real-world driving conditions |
| Weight | Often lighter due to use of aluminum and high-strength steel |
| Aerodynamics | Optimized body shapes for reduced drag |
| Tire Technology | Specialized tires for improved rolling resistance |
| Driver Behavior | Encouragement of efficient driving habits |
| Regenerative Braking | Some models feature regenerative braking systems |
| Hybrid Systems | Availability of diesel-electric hybrid variants |
What You'll Learn
- Engine Design: Diesel engines have a higher compression ratio, allowing for more efficient combustion
- Fuel Injection: Precise fuel injection systems optimize fuel-air mixture, reducing waste and improving mileage
- Turbocharging: Turbochargers provide extra power without increasing engine size, enhancing fuel economy
- Lower Emissions: Modern diesel engines meet strict emission standards, proving efficiency and environmental friendliness
- Engine Weight: Lighter engines contribute to better fuel efficiency by reducing overall vehicle weight

Engine Design: Diesel engines have a higher compression ratio, allowing for more efficient combustion
The superior fuel efficiency of diesel engines is largely attributed to their engine design, particularly the higher compression ratio. This design feature plays a pivotal role in enhancing the combustion process, which is fundamental to the engine's performance.
In the context of engine design, the compression ratio refers to the volume of the combustion chamber when the piston is at the bottom of its stroke, divided by the volume when the piston is at the top. A higher compression ratio means that the air-fuel mixture is compressed more tightly before ignition, leading to a more efficient combustion process. This is a key advantage of diesel engines over their gasoline counterparts.
The higher compression ratio in diesel engines is a direct result of the engine's design. Diesel engines are typically designed with a larger displacement, which means the engine's cylinders are larger, accommodating more air and fuel. This larger volume allows for a higher compression ratio, as the piston has more space to compress the air-fuel mixture before it is ignited. The increased compression ratio facilitates a more complete and efficient combustion process, where the air-fuel mixture is burned more thoroughly, resulting in higher energy output and, consequently, better fuel efficiency.
This design feature is a critical factor in the overall efficiency of diesel engines. It enables diesel engines to achieve higher power outputs while consuming less fuel, which is why diesel vehicles often have better fuel economy than their gasoline equivalents. The higher compression ratio not only contributes to the engine's efficiency but also plays a role in reducing emissions, as a more complete combustion process can lead to lower levels of harmful pollutants.
In summary, the higher compression ratio in diesel engine design is a key factor in their superior fuel efficiency. This design feature enables more efficient combustion, leading to better performance and lower fuel consumption, which are significant advantages for diesel vehicles.
Fuel Efficiency: Unveiling the 1500cc Car's Mileage Secrets
You may want to see also

Fuel Injection: Precise fuel injection systems optimize fuel-air mixture, reducing waste and improving mileage
The efficiency of diesel engines is often attributed to the precise and sophisticated fuel injection technology employed in these vehicles. This technology plays a pivotal role in optimizing the fuel-air mixture, which is fundamental to achieving higher fuel efficiency.
Fuel injection systems in diesel engines are designed to deliver fuel directly into the combustion chamber, ensuring a precise and controlled process. Unlike older carburetors, which mixed fuel and air in a separate chamber, fuel injectors spray the fuel directly into the engine's intake manifold or directly into the cylinders. This direct injection method allows for a more accurate and consistent fuel-air mixture, which is crucial for efficient combustion. By precisely metering the fuel, these systems can ensure that the right amount of fuel is injected at the optimal time, creating a leaner mixture that burns more efficiently.
The precision of fuel injection is key to reducing waste and improving mileage. When the fuel-air mixture is optimized, it results in a more complete combustion process. This means that more of the fuel is burned efficiently, leaving less unburned fuel as waste. As a result, diesel engines can achieve higher mileage compared to their gasoline counterparts. The technology ensures that the engine operates at its most efficient level, maximizing power output while minimizing fuel consumption.
Furthermore, the direct injection method allows for better control over the combustion process. This control enables the engine to run at a slightly leaner mixture, which can lead to improved fuel economy. The engine's computer can adjust the fuel injection timing and quantity to maintain optimal performance while adapting to varying driving conditions and loads. This adaptability is a significant advantage of diesel engines, as it contributes to their overall efficiency and performance.
In summary, precise fuel injection systems are a critical factor in the superior fuel efficiency of diesel cars. By optimizing the fuel-air mixture, these systems ensure efficient combustion, reduce waste, and improve mileage. The direct injection method, coupled with advanced control systems, allows diesel engines to deliver exceptional performance while consuming less fuel, making them an attractive choice for environmentally conscious drivers.
Can Fuel Freeze in Your Car? Winter Fuel Safety Tips
You may want to see also

Turbocharging: Turbochargers provide extra power without increasing engine size, enhancing fuel economy
Turbocharging is a key factor in the improved fuel efficiency of diesel engines. Turbochargers are devices that increase the power output of an engine without the need for a larger engine displacement. This technology has been a cornerstone of diesel engine design for decades, and its benefits are particularly evident in the context of fuel economy.
When an engine is turbocharged, it essentially gains an additional power source. The turbocharger compresses the air-fuel mixture before it enters the engine's cylinders, allowing for a more efficient combustion process. This compression is achieved by forcing air into the engine at a higher pressure, which then enables the engine to produce more power for a given volume of fuel. As a result, the engine can deliver higher torque and power outputs while maintaining a smaller overall size. This is a significant advantage over naturally aspirated engines, which require larger displacements to achieve similar performance levels.
The efficiency boost provided by turbochargers is especially beneficial for diesel engines, which are naturally known for their torque and low-end power. By utilizing a turbocharger, diesel engines can maintain their renowned torque characteristics while also improving their power-to-weight ratio. This means that diesel vehicles can offer strong acceleration and responsive performance without compromising on fuel efficiency. The turbocharger's ability to provide extra power without a significant increase in engine size is a critical aspect of why diesel cars often achieve better fuel economy compared to their gasoline counterparts.
In practical terms, this translates to diesel vehicles being able to travel longer distances on a single tank of fuel. Turbocharging allows for a more efficient use of fuel, as the engine can extract more power from a smaller amount of fuel. This is particularly advantageous for long-distance travel, where fuel efficiency can significantly impact the overall cost of ownership. Additionally, the improved power delivery from turbochargers means that diesel engines can maintain their efficiency across a wide range of speeds and loads, further enhancing their reputation for fuel economy.
The design and calibration of turbochargers are crucial to optimizing this process. Engineers must carefully select the appropriate turbocharger size and configuration to match the engine's requirements. This ensures that the turbocharger provides the necessary boost without causing excessive lag or reducing the engine's responsiveness. Modern diesel engines often feature advanced turbocharger systems that offer precise control over boost levels, further refining the balance between power and fuel efficiency.
Mastering the Art of Key Banging: Fuel-Injected Car Edition
You may want to see also

Lower Emissions: Modern diesel engines meet strict emission standards, proving efficiency and environmental friendliness
Modern diesel engines have made significant strides in terms of emissions, addressing the environmental concerns that once plagued the diesel engine. This is primarily due to the stringent emission standards that diesel engines now have to meet. These standards, set by regulatory bodies such as the European Union's Euro 6 and the United States' EPA Tier 3, have pushed engine manufacturers to develop technologies that reduce harmful emissions while maintaining efficiency.
One of the key advancements is the introduction of selective catalytic reduction (SCR) systems. SCR is a post-treatment technology that reduces nitrogen oxides (NOx), a harmful pollutant, by injecting a solution of urea (also known as diesel exhaust fluid, DEF) into the exhaust stream. This urea reacts with the NOx in the presence of a catalyst, converting it into harmless nitrogen and water vapor. This technology is now standard in most modern diesel engines, ensuring that NOx emissions are significantly lower, even at high loads and temperatures.
Additionally, diesel engines have improved their combustion processes. Modern diesel engines use advanced injection systems that precisely control the timing and amount of fuel injected into the engine. This precision ensures that fuel is burned more efficiently, with less unburned fuel ending up in the exhaust. As a result, the engine produces fewer carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrocarbon (HC) emissions, which are both harmful to the environment and contribute to smog formation.
The design of modern diesel engines has also played a crucial role in reducing emissions. Engineers have optimized the engine's geometry and flow characteristics to promote efficient combustion. This includes the use of advanced piston designs, such as the use of high-strength materials and improved cooling systems, which help maintain optimal engine temperatures and reduce the formation of harmful emissions.
Furthermore, the integration of electronic control units (ECUs) has allowed for real-time monitoring and adjustment of engine parameters. These ECUs can optimize fuel injection, timing, and other variables to ensure that the engine operates at its most efficient and environmentally friendly state. This level of control is particularly important in meeting the strict emission standards, as it enables the engine to adapt to various driving conditions and maintain low emissions throughout its operation.
Gumout Fuel Cleaner: Safe for E85 Engines?
You may want to see also

Engine Weight: Lighter engines contribute to better fuel efficiency by reducing overall vehicle weight
The concept of engine weight and its impact on fuel efficiency is a fascinating aspect of automotive engineering. When it comes to diesel cars, one of the key reasons for their superior fuel economy is the design and construction of their engines. Lighter engines play a crucial role in achieving better fuel efficiency, and this is how:
In the pursuit of improved fuel efficiency, engineers have focused on reducing the weight of the engine without compromising its performance. Lighter engines contribute to a significant advantage in the overall weight distribution of the vehicle. By utilizing advanced materials and innovative manufacturing techniques, engineers can create engines that are both powerful and lightweight. This reduction in engine weight directly translates to a decrease in the overall weight of the vehicle, which is a critical factor in fuel efficiency.
The benefits of a lighter engine extend beyond just the weight reduction. Lighter components mean that the engine requires less energy to operate, resulting in improved fuel efficiency. This is particularly noticeable during acceleration and when driving at higher speeds. With a lighter engine, the vehicle can achieve better performance while consuming less fuel, making it an environmentally friendly choice.
Furthermore, the design and construction of a lightweight engine involve careful consideration of various components. For instance, the use of lightweight materials like aluminum alloys or advanced composites can replace traditional heavy metals. These materials offer excellent strength-to-weight ratios, ensuring that the engine remains robust and durable while being significantly lighter. This meticulous approach to engine design is a testament to the dedication of automotive manufacturers to pushing the boundaries of fuel efficiency.
In summary, the weight of the engine is a critical factor in the overall fuel efficiency of diesel cars. Lighter engines contribute to reduced vehicle weight, improved performance, and better fuel consumption. Through the use of advanced materials and engineering techniques, manufacturers are able to create powerful yet lightweight engines, making diesel vehicles an attractive option for those seeking both performance and fuel economy. This aspect of diesel car design showcases the continuous innovation in the automotive industry to meet the evolving needs of environmentally conscious consumers.
Faulty Fuel Pump Relay: Performance Impact and Solutions
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Diesel engines operate on the principle of compression ignition, where fuel is injected into a highly compressed air-fuel mixture, causing it to ignite without a spark plug. This process results in a more complete combustion of the fuel, leading to higher energy efficiency. The compression ratio in diesel engines is typically higher, allowing for better fuel-air mixture control and more efficient power generation.
Diesel fuel injection systems are designed to precisely control the amount of fuel injected into the engine. This precision ensures that the air-fuel mixture is optimally balanced, promoting efficient combustion. The system calculates the required fuel based on engine load, speed, and temperature, delivering the right amount of energy to the engine at any given time, thus improving overall fuel efficiency.
Yes, diesel engines often produce more low-end torque compared to gasoline engines. This torque advantage allows diesel cars to accelerate smoothly and efficiently, especially at lower RPMs. The higher torque output means the engine doesn't need to rev as high to achieve the same power, resulting in improved fuel efficiency. Additionally, diesel engines' ability to provide strong torque across a wide RPM range contributes to their overall efficiency.
The weight of a diesel engine can be a consideration, but it is not the primary factor. Modern diesel engines are designed to be lightweight and compact while maintaining strength and durability. Lighter engines can improve fuel efficiency by reducing the overall weight of the vehicle, which has a direct impact on fuel consumption. However, engine design, materials, and manufacturing processes play a more significant role in achieving efficiency.
Diesel Particulate Filters are emission control devices that trap soot and other particulate matter from the exhaust, improving air quality. While DPFs do not directly impact fuel efficiency, they help maintain the engine's performance and efficiency over time. By keeping the engine clean, DPFs ensure that the combustion process remains efficient, and the engine operates optimally, which can indirectly contribute to better fuel economy.







