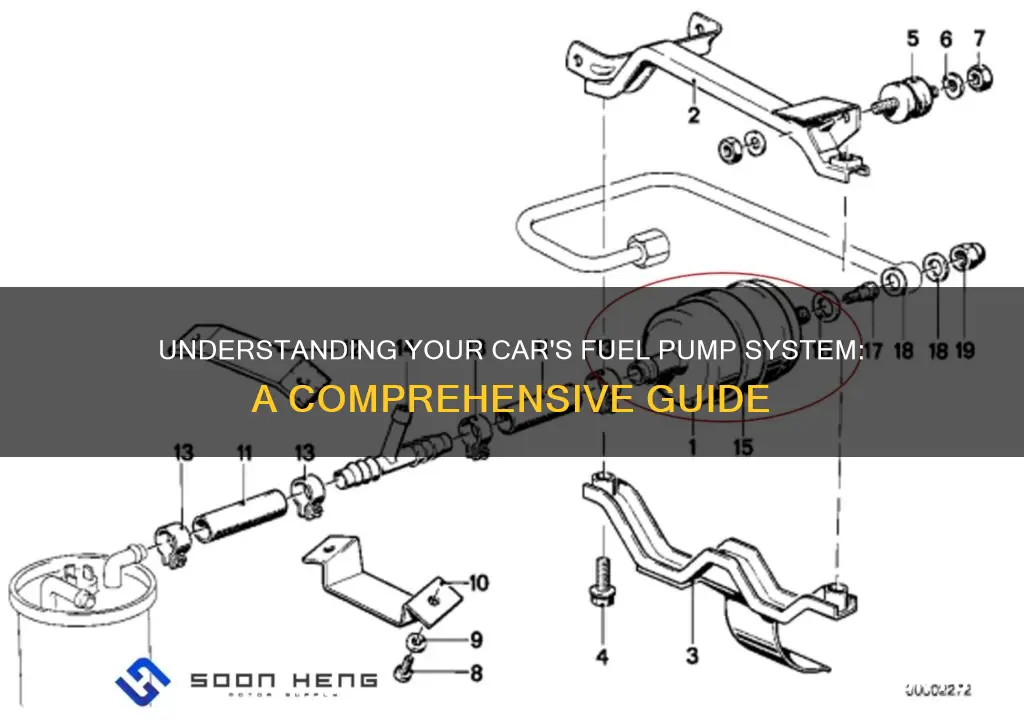
Fuel pumps are an essential component of a car's fuel system, responsible for delivering fuel from the tank to the engine. Understanding the number of fuel pumps in a car is crucial for maintenance and troubleshooting. In this paragraph, we will explore the typical configurations of fuel pumps in different car models and discuss the factors that determine the number of pumps required for optimal performance.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Number of Fuel Pumps | Typically 1 or 2 |
| Location | Usually in the fuel tank or engine compartment |
| Function | Deliver fuel from the tank to the engine |
| Types | Mechanical, electric, or both |
| Failure Modes | Clogging, electrical issues, wear and tear |
| Maintenance | Regular checks and replacements |
| Common Issues | Pump failure, pressure loss, fuel leaks |
| Impact | Engine performance, fuel efficiency, and starting difficulties |
What You'll Learn
- Fuel Pump Location: Identify the car's fuel pump's exact location
- Fuel Pump Count: Determine how many fuel pumps are in the engine
- Fuel Pump Types: Understand the different types of fuel pumps used
- Fuel Pump Function: Explain the role of fuel pumps in the car's engine
- Fuel Pump Maintenance: Learn how to maintain and service fuel pumps

Fuel Pump Location: Identify the car's fuel pump's exact location
The fuel pump in a car is a critical component responsible for delivering fuel from the tank to the engine. The exact location of the fuel pump can vary depending on the make and model of the vehicle. It is essential to identify the precise spot to ensure proper maintenance and troubleshooting.
In most modern cars, the fuel pump is typically located inside the fuel tank. This design keeps the pump submerged in fuel, which helps prevent contamination and ensures a consistent fuel supply. The fuel tank is usually positioned at the rear of the vehicle, often near the bottom, to allow for better weight distribution and stability. For example, in many compact cars, the fuel pump can be found in the center of the tank, while in some larger vehicles, it might be positioned on the side or even at the rear of the tank.
To locate the fuel pump, you can start by opening the fuel tank. This process may require removing the gas cap and lifting the fuel filler door, which is often a plastic or metal flap. Once the tank is accessible, you should see the fuel pump, which is usually a small, rectangular or cylindrical component. It is often connected to the fuel lines and may have a small filter attached. It's important to note that the fuel pump is a delicate part, and handling it with care is essential to avoid any damage.
In some cases, the fuel pump might be located outside the fuel tank. This can happen in certain engine designs or older vehicle models. For instance, in some sports cars or high-performance vehicles, the fuel pump can be found in the engine compartment, often mounted near the front of the engine. Identifying the exact spot in these cases may require consulting the vehicle's service manual or seeking professional assistance.
Identifying the fuel pump's location is crucial for various reasons. It allows for easy access during maintenance tasks such as replacing or repairing the pump. Additionally, knowing the exact spot can help in troubleshooting fuel-related issues, as it enables mechanics to isolate and inspect the pump for any problems. Proper maintenance and timely repairs can ensure the fuel system's reliability and overall vehicle performance.
Hemp's Green Revolution: Can We Power Cars with Nature's Gold?
You may want to see also

Fuel Pump Count: Determine how many fuel pumps are in the engine
The number of fuel pumps in a car's engine can vary depending on the vehicle's make, model, and year. Generally, most cars have one or two fuel pumps, but some high-performance or larger vehicles might have more. Understanding the fuel pump configuration is essential for maintenance and troubleshooting purposes. Here's a step-by-step guide to help you determine the number of fuel pumps in your car's engine:
- Visual Inspection: Start by visually inspecting your car's engine bay. Locate the fuel tank and the associated fuel lines. Look for any visible fuel pumps, which are typically located near the fuel tank. Count the number of pumps you can see. This visual inspection can give you an initial idea of the fuel pump count.
- Engine Diagram: Refer to your car's engine manual or workshop guide. These resources often provide detailed diagrams of the engine's components, including the fuel system. Look for illustrations that show the fuel pump(s) and their connections. The diagram should indicate the exact number and location of the fuel pumps. If you have access to a service manual specific to your vehicle's make and model, it will be an invaluable resource for this step.
- Check the Fuel Pump Relay: The fuel pump relay is an electrical component that controls the power supply to the fuel pumps. It is usually located near the engine or in the fuse box. Open the hood and locate the relay. Check the manufacturer's specifications or consult the vehicle's wiring diagram to determine if there is more than one fuel pump relay. If there are multiple relays, it could indicate the presence of additional fuel pumps.
- Engine Disassembly (Advanced Method): If the above methods do not provide a clear answer, you might need to disassemble the engine to gain a better view. This step is more complex and should only be attempted by experienced mechanics or car enthusiasts. Carefully remove the engine cover and inspect the fuel injectors or carburetor (depending on the engine type). Count the number of fuel pump modules or components connected to the injectors or carburetor.
Remember, it's crucial to consult the vehicle's documentation and seek professional advice if you're unsure. The fuel pump system is a critical part of the car's operation, and any modifications or repairs should be done with proper knowledge and tools to ensure safety and optimal performance.
Flex Fuel: Can Your Car Handle the Switch?
You may want to see also

Fuel Pump Types: Understand the different types of fuel pumps used
The fuel pump is a critical component in a vehicle's fuel system, responsible for delivering fuel from the tank to the engine. Understanding the different types of fuel pumps can help car owners and mechanics make informed decisions when it comes to maintenance and repairs. Here's an overview of the various fuel pump types commonly found in cars:
Mechanical Fuel Pumps: This is the traditional type of fuel pump found in older vehicles. It operates using a diaphragm or a diaphragm and piston assembly. When the engine is running, the mechanical pump is activated by the engine's camshaft, which opens a valve, allowing fuel to flow from the tank to the engine. These pumps are known for their simplicity and reliability, but they may require more frequent maintenance due to their mechanical nature. Over time, diaphragms can wear out, and the pump may need to be replaced.
Electric Fuel Pumps: Modern cars often utilize electric fuel pumps, which are powered by a small electric motor. These pumps are more efficient and offer better performance compared to their mechanical counterparts. Electric pumps are typically located inside the fuel tank and are controlled by the engine control unit (ECU). The ECU sends a signal to the pump, turning it on when the engine is running and off when the vehicle is stationary. This type of pump ensures a consistent fuel supply and can handle higher fuel pressures, making it suitable for high-performance vehicles.
In-Tank vs. Out-of-Tank: Fuel pumps can be categorized as either in-tank or out-of-tank. In-tank pumps are located inside the fuel tank, which provides some protection from contaminants and temperature fluctuations. Out-of-tank pumps, on the other hand, are mounted outside the tank and are more common in older vehicles. The choice between the two depends on the vehicle's design and intended use.
High-Pressure vs. Low-Pressure: Another classification is based on the fuel pressure they can deliver. High-pressure pumps are designed to provide a higher fuel pressure, typically required by fuel-injected engines. These pumps ensure that the fuel is atomized properly for efficient combustion. Low-pressure pumps, as the name suggests, operate at lower pressures and are often used in older vehicles with carbureted engines.
Understanding the different fuel pump types is essential for diagnosing and resolving fuel-related issues in a vehicle. Each type has its advantages and is chosen based on the specific requirements of the engine and vehicle design. Regular maintenance and timely replacements can ensure optimal engine performance and longevity.
Understanding Your Car's Fuel Efficiency: A Comprehensive Guide
You may want to see also

Fuel Pump Function: Explain the role of fuel pumps in the car's engine
The fuel pump is a critical component in a car's engine system, responsible for delivering gasoline from the fuel tank to the engine's carburetor or fuel injection system. Its primary function is to ensure a consistent and controlled supply of fuel, which is essential for efficient combustion and optimal engine performance. Without a properly functioning fuel pump, the engine would not receive the required amount of fuel, leading to poor performance, reduced power, and potential engine damage.
In modern vehicles, there are typically two types of fuel pumps: mechanical and electric. Mechanical fuel pumps are driven by the engine's camshaft and are commonly found in older car models. These pumps are designed to provide a constant fuel flow rate, ensuring a steady supply of gasoline to the engine. On the other hand, electric fuel pumps are more prevalent in newer cars and are powered by a separate electric motor. This type of pump offers precise control over fuel pressure, allowing for better engine management and improved performance.
The role of the fuel pump is to maintain a specific fuel pressure within the engine's system. When the engine is running, the pump operates at a higher pressure to ensure a continuous fuel supply. During periods of low engine load or when the car is idling, the pump adjusts its pressure to provide just enough fuel for efficient combustion. This dynamic pressure regulation is crucial for maintaining optimal engine performance and fuel efficiency.
One of the key functions of the fuel pump is to prevent fuel vaporization, especially in warmer climates. As gasoline is a volatile substance, it can easily vaporize, leading to poor engine performance and increased emissions. The fuel pump ensures that the gasoline remains in a liquid state by delivering it at the right pressure and temperature. This process is particularly important in fuel injection systems, where precise fuel delivery is critical for accurate engine control.
In summary, the fuel pump plays a vital role in the proper functioning of a car's engine. It ensures a consistent fuel supply, regulates pressure, and prevents fuel vaporization, all of which contribute to efficient combustion and optimal engine performance. Whether it's a mechanical or electric pump, its proper maintenance and timely replacement are essential to keep the vehicle running smoothly and reliably.
F1 Fuel Capacity: Unlocking the Secrets of Speed
You may want to see also

Fuel Pump Maintenance: Learn how to maintain and service fuel pumps
The number of fuel pumps in a car can vary depending on the make and model, but typically, there is one primary fuel pump located near the engine, responsible for delivering fuel from the tank to the engine's fuel injectors or carburetor. Some vehicles, especially those with larger engines or higher performance requirements, may have an additional secondary fuel pump, often found in the fuel tank itself, which provides additional pressure or flow when needed. Understanding the location and function of these pumps is essential for proper maintenance.
Regular maintenance of the fuel pump is crucial to ensure optimal engine performance and longevity. Over time, fuel pumps can experience wear and tear, leading to reduced efficiency or even failure. Here's a step-by-step guide to help you maintain and service your fuel pump:
- Inspect the Fuel Pump and Lines: Start by visually inspecting the fuel pump and its associated lines. Check for any signs of damage, corrosion, or leaks. Look for cracks, rust, or debris that might indicate wear. Ensure that all connections are secure and free from corrosion. If you notice any issues, it's best to replace the pump and lines to prevent further complications.
- Check Fuel Filter: The fuel filter plays a vital role in maintaining the health of the fuel pump. Over time, contaminants and debris can accumulate in the filter, restricting fuel flow. Regularly inspect and replace the fuel filter as recommended by the vehicle manufacturer. Clogged filters can strain the fuel pump, leading to reduced performance.
- Maintain Engine Oil and Air Quality: Keep the engine oil clean and change it at the recommended intervals. Engine oil can become contaminated with fuel and debris, affecting the pump's performance. Additionally, ensure your vehicle's air filter is clean and free of dust and dirt. A restricted air supply can lead to increased fuel consumption and potential pump strain.
- Use the Right Fuel: Using the correct grade of fuel as specified by the manufacturer is essential. Different fuels have varying properties, and using the wrong type can impact the pump's performance and longevity. Always refer to your vehicle's manual for fuel recommendations.
- Address Engine Issues Promptly: Engine problems, such as misfires or rough idling, can put additional stress on the fuel pump. If you notice any engine-related issues, have them diagnosed and repaired promptly. Regular engine maintenance, including tune-ups, can help prevent such problems and ensure the fuel pump operates efficiently.
- Consider Pump Replacement: If your vehicle is older or has high mileage, consider replacing the fuel pump as part of routine maintenance. Over time, pumps can develop internal leaks or wear out, leading to reduced fuel pressure. Replacing the pump can prevent fuel delivery issues and ensure your engine runs smoothly.
By following these maintenance steps, you can keep your fuel pump in good condition, ensuring reliable fuel delivery to your engine. Regular care and attention to the fuel system will contribute to the overall performance and longevity of your vehicle. Remember, proper maintenance can save you from potential breakdowns and costly repairs in the long run.
Unlocking the Mystery: Can You Put True Fuel in Any Car?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The number of fuel pumps in a car can vary depending on the make and model, as well as the engine configuration. Most modern cars have one or two fuel pumps. Some vehicles, especially those with larger engines or higher performance requirements, may have more than two fuel pumps to ensure adequate fuel supply and efficient operation.
Fuel pumps are usually located in the fuel tank or close to it. In some cases, they might be mounted on the engine bay or even integrated into the fuel injection system. The exact location can vary based on the vehicle's design.
A fuel pump's primary role is to deliver fuel from the tank to the engine's carburetor or fuel injection system. It ensures a continuous supply of fuel at the required pressure to enable efficient combustion and power generation.
Yes, many cars can operate with just one fuel pump. However, having two fuel pumps provides redundancy and can improve performance, especially in high-demand situations or when the engine is running at full load.
The number of fuel pumps doesn't directly impact fuel efficiency. However, a well-maintained and properly functioning fuel pump system ensures that the engine receives the correct amount of fuel, which can indirectly contribute to better fuel economy.







