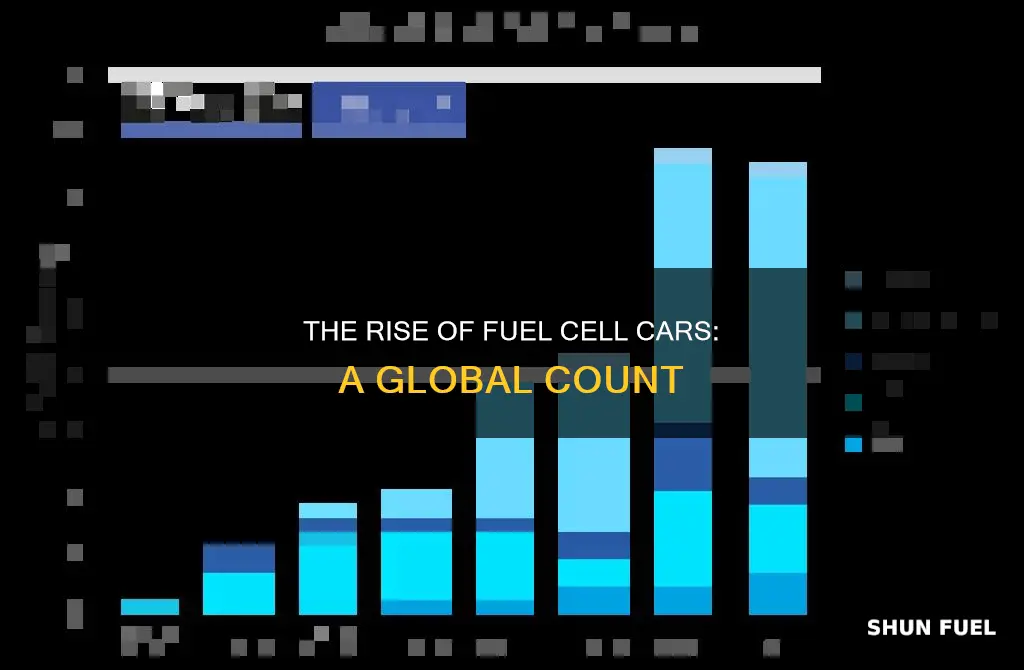
The number of fuel cell cars on the road is a topic of growing interest as the world shifts towards sustainable transportation. As of 2023, the global market for fuel cell vehicles is still in its infancy, with a relatively small number of cars available for purchase. However, this number is expected to grow significantly in the coming years as more manufacturers invest in fuel cell technology and governments offer incentives to promote the adoption of these vehicles. This paragraph will explore the current state of fuel cell cars and the factors influencing their market presence.
What You'll Learn
- Market Penetration: Number of fuel cell vehicles sold and registered globally
- Geographical Distribution: Regional adoption and sales of fuel cell cars
- Production Capacity: Manufacturing capabilities and output of fuel cell vehicles
- Government Incentives: Impact of subsidies and policies on fuel cell car sales
- Consumer Awareness: Public knowledge and interest in fuel cell technology

Market Penetration: Number of fuel cell vehicles sold and registered globally
The market penetration of fuel cell vehicles (FCVs) is a critical aspect of understanding the current status and potential of this emerging technology. As of 2023, the global market for fuel cell cars is still in its infancy, with a relatively small number of vehicles on the road compared to conventional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles.
According to recent data, the number of fuel cell vehicles sold and registered worldwide has been steadily increasing but remains a fraction of the overall automotive market. In 2022, global sales of FCVs reached approximately 10,000 units, a significant jump from the previous year's sales of around 7,000 units. This growth is primarily attributed to the increasing interest and support from governments and automotive manufacturers for hydrogen-powered vehicles. Countries like Japan, South Korea, and the United States have been at the forefront of this market, with Japan leading the way in terms of sales and infrastructure development.
The majority of these fuel cell cars are concentrated in specific regions, with Asia-Pacific accounting for a substantial portion of the global market. Japan, in particular, has seen a surge in FCV sales, with its domestic market witnessing a significant increase in the number of registered fuel cell vehicles. This can be partly attributed to the country's aggressive push towards hydrogen technology and the establishment of a comprehensive hydrogen fuel infrastructure. South Korea and China are also making notable strides in this sector, with government incentives and investments driving the adoption of fuel cell vehicles.
Despite the growth, it is essential to note that the number of fuel cell cars on the road is still relatively low compared to the global vehicle population. As of 2022, the global fleet of FCVs accounted for less than 0.1% of the total passenger vehicles in operation. This low market penetration can be attributed to several factors, including high production costs, limited refueling infrastructure, and consumer skepticism about the technology's reliability and convenience.
However, industry experts predict that this trend will change in the coming years. With ongoing technological advancements, cost reductions, and increased government support, the number of fuel cell vehicles sold and registered globally is expected to grow exponentially. The development of more efficient and cost-effective fuel cell systems, along with the expansion of hydrogen refueling stations, will play a crucial role in accelerating the market penetration of FCVs. Additionally, the growing environmental concerns and the push towards decarbonization are likely to further drive the adoption of fuel cell technology in the transportation sector.
Funny Cars vs. Top Fuel Dragsters: Who's Faster?
You may want to see also

Geographical Distribution: Regional adoption and sales of fuel cell cars
The geographical distribution of fuel cell cars varies significantly across the globe, with certain regions embracing this technology more than others. As of 2023, the majority of fuel cell vehicles are concentrated in a few key markets, primarily in Europe and Asia.
In Europe, countries like Germany, Norway, and Sweden have been at the forefront of fuel cell car adoption. Germany, for instance, has a substantial number of fuel cell cars on its roads, largely due to government incentives and a supportive infrastructure. Norway, known for its ambitious environmental goals, has seen remarkable success in this sector. The country's comprehensive charging network, combined with tax incentives, has encouraged consumers to opt for fuel cell vehicles. As a result, Norway boasts one of the highest per-capita rates of fuel cell car ownership in the world.
Asian markets, particularly Japan and South Korea, also contribute significantly to the global fuel cell car population. Japan, a pioneer in the development of fuel cell technology, has a substantial number of fuel cell cars in operation, especially in urban areas. The country's commitment to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and its technological prowess have driven this adoption. South Korea, too, has made strides in this area, with a growing number of fuel cell cars on its roads, especially in the capital city of Seoul.
In the United States, the adoption of fuel cell cars is more localized, with a few states leading the way. California, for example, has been a major proponent of fuel cell technology, offering incentives and building a robust charging infrastructure. This has resulted in a notable presence of fuel cell cars in the state, particularly in metropolitan areas. However, the overall number of fuel cell cars in the U.S. remains relatively low compared to the global leaders.
The regional adoption of fuel cell cars is influenced by various factors, including government policies, environmental regulations, and the availability of supporting infrastructure. Regions with favorable policies and a strong focus on sustainability tend to have higher adoption rates. Additionally, the presence of a robust charging network and the availability of hydrogen refueling stations play a crucial role in encouraging consumers to choose fuel cell vehicles over traditional alternatives.
While the number of fuel cell cars on the road is still relatively small compared to conventional vehicles, the trend of increasing adoption is evident. As more regions recognize the benefits of fuel cell technology, including its environmental advantages and long-term sustainability, the geographical distribution of these vehicles is likely to become more diverse and widespread.
Fuel Filter Failure: When Your Car Suddenly Cuts Off
You may want to see also

Production Capacity: Manufacturing capabilities and output of fuel cell vehicles
The production capacity of fuel cell vehicles (FCVs) has been a critical aspect of the industry's growth and development. As of 2023, the global market for FCVs is still in its early stages, with a relatively small number of vehicles on the road compared to traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) cars. However, the manufacturing capabilities and output of these vehicles are rapidly expanding.
Several factors contribute to the current production capacity of FCVs. Firstly, the technology is still relatively new, and the infrastructure for mass production is not yet fully established. Many automotive manufacturers are investing in research and development to optimize the production processes and reduce costs. This includes improving the efficiency of fuel cell stacks, developing more cost-effective hydrogen storage systems, and enhancing the overall vehicle design. As a result, the production rates of FCVs have been steadily increasing, with some manufacturers reporting significant growth in their output.
For instance, Toyota, one of the early adopters of fuel cell technology, has been producing the Mirai FCV since 2014. In 2022, Toyota announced an increase in production capacity, aiming to produce 30,000 units of the Mirai by 2030. This significant boost in production is a direct response to the growing demand for sustainable transportation options and the company's commitment to reducing its carbon footprint. Similarly, other automotive giants like Hyundai, Honda, and Mercedes-Benz have also expanded their FCV production capabilities, with plans to increase their output in the coming years.
Despite the growth, the overall production volume of FCVs remains relatively low compared to the millions of ICE cars produced annually. This is primarily due to the higher costs associated with fuel cell technology, which are often attributed to the small-scale production and limited economies of scale. However, as the technology matures and production processes become more efficient, the cost of FCVs is expected to decrease, making them more accessible to a wider market.
In summary, the production capacity of fuel cell vehicles is improving, driven by technological advancements and increased investment from automotive manufacturers. While the current output is still relatively small, the industry is witnessing a rapid expansion, which will be crucial in establishing FCVs as a viable and sustainable transportation option in the future. As the market demand for clean energy vehicles continues to grow, the production capabilities will play a pivotal role in meeting the increasing demand for fuel cell cars.
Car Fuel Gauge Accuracy: A Deep Dive into Reliability
You may want to see also

Government Incentives: Impact of subsidies and policies on fuel cell car sales
The adoption of fuel cell vehicles has been significantly influenced by government incentives and policies, which have played a crucial role in promoting the technology and accelerating its integration into the automotive market. One of the primary mechanisms through which governments have encouraged the sale of fuel cell cars is through subsidies and financial incentives. These incentives often take the form of direct grants, tax credits, or rebates provided to consumers or manufacturers. For instance, many countries offer substantial tax credits for the purchase of fuel cell vehicles, which can significantly reduce the upfront cost for consumers, making these cars more affordable and attractive. These subsidies not only benefit individual buyers but also contribute to the overall competitiveness of fuel cell technology in the market.
In addition to financial incentives, governments have implemented various policies to support the infrastructure development necessary for fuel cell car adoption. This includes investing in hydrogen refueling stations, which are essential for the widespread use of fuel cell vehicles. By establishing a network of these stations, governments ensure that fuel cell car owners have convenient access to the necessary fuel, addressing a significant range anxiety concern associated with early electric vehicle (EV) adoption. Furthermore, policies promoting the use of renewable energy sources for hydrogen production can further enhance the environmental credentials of fuel cell cars, making them an even more appealing option for environmentally conscious consumers.
The impact of these government initiatives is evident in the sales figures of fuel cell cars. In regions with robust incentives and supportive policies, the market for fuel cell vehicles has experienced significant growth. For example, countries with well-established hydrogen refueling infrastructure and substantial subsidies have witnessed a rapid increase in fuel cell car sales. This trend is particularly notable in markets where traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles are being phased out, as governments aim to accelerate the transition to cleaner transportation options. As a result, the number of fuel cell cars on the road has been steadily rising, contributing to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly transportation ecosystem.
However, the effectiveness of these incentives and policies is not solely dependent on financial support. Regulatory frameworks and standards also play a pivotal role in shaping the market for fuel cell vehicles. Governments can mandate the inclusion of fuel cell cars in public transportation fleets, encourage their use in taxi services, or provide preferential treatment in government procurement processes. Such policies not only stimulate sales but also demonstrate the viability and reliability of fuel cell technology in real-world applications. Moreover, long-term policy stability is essential to provide manufacturers and investors with the confidence needed to commit resources to fuel cell vehicle development and production.
In summary, government incentives and policies have been instrumental in driving the adoption of fuel cell cars. Financial subsidies, infrastructure development, and supportive regulations have collectively contributed to the increasing presence of fuel cell vehicles on the road. As the world seeks to reduce its carbon footprint and transition towards sustainable transportation, the role of governments in fostering the growth of fuel cell technology will remain pivotal. Continued investment and policy support are necessary to further accelerate the market penetration of fuel cell cars and ensure a greener future for the automotive industry.
Maximize Savings: The Fuel Economy Factor in Car Purchases
You may want to see also

Consumer Awareness: Public knowledge and interest in fuel cell technology
The concept of fuel cell technology has been gaining traction in the automotive industry, but its public awareness and consumer interest remain relatively low compared to more conventional vehicle technologies. Fuel cells, which convert chemical energy from hydrogen into electricity to power electric motors, offer a promising alternative to internal combustion engines. However, the public's understanding and enthusiasm for this technology are crucial for its widespread adoption.
Consumer awareness of fuel cell technology is essential for several reasons. Firstly, it can help educate the public about the environmental benefits of fuel cell vehicles. These cars produce zero tailpipe emissions, reducing air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. By raising awareness, consumers can be informed about the positive environmental impact, which is a significant selling point for many eco-conscious individuals. Secondly, understanding fuel cell technology can address misconceptions and myths surrounding it. Many people might associate fuel cells with hydrogen bombs or complex scientific concepts, leading to skepticism. Educating the public can clarify these misunderstandings and present fuel cell technology as a safe and efficient alternative.
The current public knowledge about fuel cell cars is limited, and this lack of awareness presents a challenge. Most consumers are unfamiliar with the technology, its advantages, and its potential impact on the automotive industry. This ignorance can hinder the market's growth, as potential buyers might opt for more conventional vehicles due to a lack of information. To increase interest, car manufacturers and environmental advocates should collaborate to develop educational campaigns and initiatives. These efforts could include showcasing fuel cell vehicles at public events, providing test drives, and offering detailed information through various media platforms.
Social media and online forums have become powerful tools for spreading information and generating interest. Creating online content that explains the basics of fuel cell technology, its benefits, and its real-world applications can attract a wider audience. Additionally, sharing success stories and case studies of fuel cell vehicle owners can inspire others to consider this technology. For instance, highlighting the performance, reliability, and long-term cost savings of fuel cell cars can appeal to environmentally conscious and technologically inclined consumers.
In summary, raising public awareness and interest in fuel cell technology is vital for its successful integration into the automotive market. By educating consumers about the environmental benefits, addressing misconceptions, and utilizing various communication channels, the industry can foster a more informed and engaged audience. This, in turn, will contribute to the growth of fuel cell vehicle sales and accelerate the transition towards cleaner and more sustainable transportation options.
Car Insurance Coverage: Contaminated Fuel and Your Policy
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
As of 2023, there are approximately 1,000 fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs) on the road worldwide. This number includes passenger cars, buses, and commercial vehicles.
Japan leads the way with the most fuel cell cars on the road, primarily due to the government's incentives and support for hydrogen infrastructure. As of 2022, Japan had over 500 FCEVs, with Toyota and Honda being the main manufacturers.
Yes, several fuel cell cars are available for consumers in the US market. The most notable examples include the Toyota Mirai, Honda Clarity Fuel Cell, and the Hyundai ix35 Fuel Cell. These vehicles are primarily found in California due to the state's zero-emission vehicle regulations.
The adoption of fuel cell cars has been relatively slow compared to other electric vehicle technologies. In the early 2000s, there was significant interest and investment, but production volumes have been lower than expected. However, recent years have seen a growing interest, with more manufacturers introducing fuel cell models and governments offering incentives to encourage adoption.
One of the primary challenges is the lack of a robust hydrogen refueling infrastructure. Building a network of hydrogen stations is crucial for the widespread use of FCEVs. Additionally, the high cost of fuel cell systems and the limited range compared to some battery-electric vehicles can be deterrents for potential buyers.







