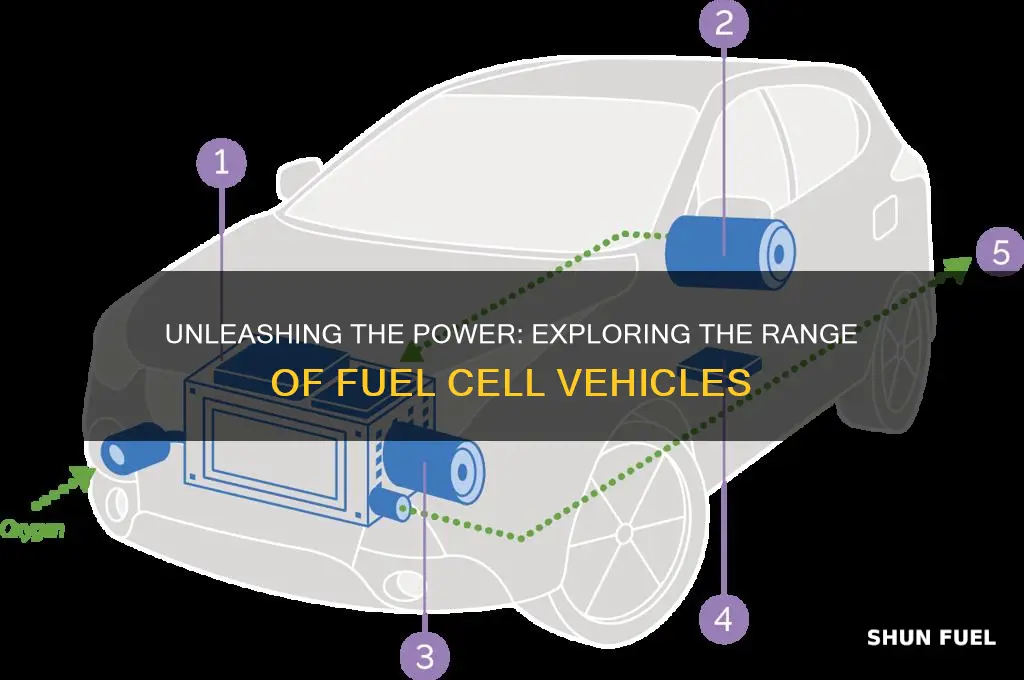
Fuel cell cars are an innovative alternative to traditional internal combustion engine vehicles, offering a cleaner and potentially more efficient way to travel. One of the key questions that potential buyers often ask is, How far can a fuel cell car go on a single charge? The answer to this question depends on several factors, including the specific model of the car, the capacity of its fuel cell, and the efficiency of its energy storage system. In this article, we will explore the range of fuel cell cars, discussing the technological advancements that have allowed these vehicles to travel longer distances and the factors that still influence their overall range.
What You'll Learn
- Fuel Cell Efficiency: How efficiently can fuel cells convert hydrogen into electricity
- Energy Storage: What role does energy storage play in fuel cell car range
- Hydrogen Availability: Is hydrogen readily available for refueling fuel cell cars
- Infrastructure Development: How does infrastructure impact fuel cell car range
- Environmental Impact: What is the environmental impact of fuel cell car usage

Fuel Cell Efficiency: How efficiently can fuel cells convert hydrogen into electricity?
Fuel cell efficiency is a critical aspect of understanding the performance and range of fuel cell vehicles. It refers to the effectiveness of the fuel cell system in converting the chemical energy of hydrogen into electrical energy, which then powers the vehicle's electric motor. The efficiency of this process is a key factor in determining how far a fuel cell car can travel on a single tank of hydrogen.
The efficiency of a fuel cell is primarily influenced by several factors. Firstly, the type of fuel cell technology used plays a significant role. Proton-exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) are commonly used in automotive applications due to their high power density and relatively low operating temperatures. These cells typically have an efficiency of around 40-60%, with some advanced designs reaching up to 70%. This means that a significant portion of the hydrogen's energy is converted into useful electrical power.
Another factor affecting efficiency is the operating conditions. Fuel cells operate optimally within a specific temperature range, and deviations from this range can impact performance. For instance, lower temperatures can reduce the efficiency of the cell, affecting the overall range of the vehicle. Additionally, the pressure of the hydrogen fuel and the humidity of the membrane can also influence efficiency.
The efficiency of fuel cell systems can be further enhanced through various engineering optimizations. These include improvements in catalyst materials, membrane design, and overall system integration. Researchers and engineers are constantly working on developing new materials and designs to increase the efficiency of fuel cells, thereby extending the driving range of fuel cell vehicles.
In summary, fuel cell efficiency is a crucial consideration when assessing the range of fuel cell cars. With ongoing advancements in technology and engineering, the efficiency of fuel cells is expected to improve, leading to longer driving ranges and more viable alternatives to traditional internal combustion engine vehicles. This efficiency is a key enabler for the widespread adoption of hydrogen fuel cell technology in the automotive industry.
Fuel Injection: The Diesel Engine's Secret Weapon
You may want to see also

Energy Storage: What role does energy storage play in fuel cell car range?
Energy storage is a critical component in the development of fuel cell vehicles, addressing the primary challenge of limited range associated with these vehicles. Fuel cell cars, which generate electricity through the electrochemical reaction of hydrogen and oxygen, have the potential to offer zero-emission transportation. However, their range has been a significant barrier to widespread adoption. This is where energy storage systems come into play, enabling these vehicles to store and utilize energy more efficiently.
The role of energy storage in fuel cell cars is multifaceted. Firstly, it provides a means to store the electrical energy generated by the fuel cell. This stored energy can then be used to power the vehicle's electric motor, ensuring a continuous and reliable source of power. The efficiency of this process is crucial, as it directly impacts the overall range of the vehicle. Modern fuel cell vehicles often employ advanced storage solutions, such as lithium-ion batteries, to maximize energy retention and minimize energy loss during storage and usage.
Secondly, energy storage allows for the optimization of power delivery to the vehicle's systems. Fuel cells produce electricity at a steady rate, but the power required for acceleration or other high-demand situations can vary significantly. Energy storage systems act as a buffer, smoothing out these power fluctuations and ensuring that the vehicle's electric motor receives the necessary energy to maintain performance. This is particularly important in electric vehicles, where rapid acceleration and consistent power output are essential for a smooth driving experience.
Furthermore, energy storage contributes to the overall efficiency and longevity of fuel cell vehicles. By efficiently managing the energy flow, storage systems can reduce the stress on the fuel cell itself, improving its lifespan. This is a significant advantage, as fuel cell durability has been a concern in the automotive industry. Efficient energy storage also minimizes energy waste, ensuring that the vehicle's range is maximized with each fuel cell activation.
In summary, energy storage is integral to the advancement of fuel cell car technology, addressing the range limitation and improving overall performance. Through efficient storage and power management, these vehicles can offer a more practical and appealing alternative to traditional internal combustion engines. As research and development in this field continue, we can expect further enhancements in energy storage solutions, leading to longer ranges and more sustainable fuel cell vehicles.
Unveiling the Secrets: How Car Makers Boost Engine Fuel Efficiency
You may want to see also

Hydrogen Availability: Is hydrogen readily available for refueling fuel cell cars?
The availability of hydrogen for refueling fuel cell vehicles is a critical aspect of their practicality and widespread adoption. While fuel cell cars offer a promising alternative to traditional internal combustion engines, the infrastructure for hydrogen refueling is still developing.
Currently, the distribution and availability of hydrogen are limited compared to conventional fuels. Hydrogen refueling stations are not as common as gas stations, and their distribution varies significantly across different regions. This lack of widespread availability can be attributed to several factors. Firstly, the production of hydrogen, especially through electrolysis, is energy-intensive and currently relies heavily on renewable energy sources. As a result, the cost of producing and supplying hydrogen can be relatively high, making it more expensive than gasoline or diesel for refueling. Secondly, the infrastructure for storing and transporting hydrogen safely and efficiently is still evolving. High-pressure tanks and specialized pipelines are required to handle hydrogen, which adds complexity and cost to the refueling process.
Despite these challenges, efforts are underway to improve hydrogen availability. Governments and private companies are investing in the development of hydrogen refueling stations, particularly in areas with high demand for fuel cell vehicles. These stations are being established in strategic locations, such as along major highways and in urban centers, to provide convenient refueling options for drivers. Additionally, research and development are focused on improving hydrogen production methods, exploring alternative feedstocks, and reducing the energy requirements for electrolysis. These advancements aim to lower the cost of hydrogen production and make it more accessible for widespread use.
In the future, it is anticipated that hydrogen availability will improve significantly. As the technology matures and economies of scale are achieved, the cost of hydrogen production and distribution is expected to decrease. This, coupled with increasing public and private investments in hydrogen infrastructure, will make hydrogen refueling stations more prevalent and convenient.
In summary, while hydrogen availability is currently a limiting factor for the widespread adoption of fuel cell cars, ongoing efforts and investments are addressing this issue. The development of a robust hydrogen infrastructure, along with advancements in production methods, will play a crucial role in making fuel cell vehicles a viable and convenient transportation option for the general public.
Lincoln Town Car Fuel Filter: A 2001 Model's Essential Component
You may want to see also

Infrastructure Development: How does infrastructure impact fuel cell car range?
The range of fuel cell vehicles is a critical aspect of their adoption and success, and it is significantly influenced by the development and quality of infrastructure. Fuel cell cars, which produce electricity through a chemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen, offer a promising alternative to traditional internal combustion engines. However, their real-world range can vary widely depending on various factors, including the state of the infrastructure that supports them.
One of the primary ways infrastructure impacts fuel cell car range is through the availability and accessibility of hydrogen refueling stations. These stations are essential for providing the necessary hydrogen gas to power the fuel cell. The distribution and density of these stations can vary across regions, and their presence or absence can directly affect a fuel cell car's ability to travel long distances. In areas with well-developed hydrogen infrastructure, drivers can conveniently locate stations, ensuring they can refuel and maintain their journey. Conversely, regions with limited or no hydrogen infrastructure may force drivers to plan their trips carefully, potentially reducing their overall range.
The design and efficiency of hydrogen refueling stations also play a role. Modern stations are designed to minimize the time required for refueling, often taking just a few minutes. However, older or less efficient stations may take longer, impacting the overall driving experience and range. Additionally, the pressure and temperature of the hydrogen gas can vary, and stations equipped with advanced compression and cooling systems can provide higher-pressure hydrogen, allowing for faster refueling and potentially increasing the car's range.
Another critical aspect of infrastructure is the power grid and its ability to support the electricity demands of fuel cell vehicles. When fuel cell cars are not in use, they can act as mobile energy storage devices, feeding electricity back into the grid. This process, known as vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology, can help balance the grid and provide additional power during peak demand. However, the effectiveness of V2G depends on the grid's infrastructure, including its capacity to handle the bidirectional flow of electricity. Upgrading the power grid to accommodate V2G technology can significantly enhance the overall range and efficiency of fuel cell vehicles.
Furthermore, the development of infrastructure for hydrogen production and distribution is vital. Centralized hydrogen production facilities, often powered by renewable energy sources, can supply the necessary hydrogen for refueling stations. The efficiency and sustainability of these production methods can impact the overall cost and availability of hydrogen, thereby affecting the range of fuel cell cars. Investing in green hydrogen production, which uses renewable energy to generate hydrogen, can ensure a more environmentally friendly and sustainable fuel source for the long term.
In summary, infrastructure development plays a pivotal role in determining the range and practicality of fuel cell cars. The availability and efficiency of hydrogen refueling stations, the state of the power grid, and the methods of hydrogen production and distribution all contribute to the overall driving experience. As the technology advances and infrastructure improves, fuel cell vehicles can become more accessible and appealing to a wider range of consumers, potentially revolutionizing the automotive industry and reducing our reliance on fossil fuels.
Turbocharged Engine Maintenance: Can Fuel Injector Cleaner Be Used?
You may want to see also

Environmental Impact: What is the environmental impact of fuel cell car usage?
The environmental impact of fuel cell vehicles is a crucial aspect to consider when evaluating their sustainability and potential benefits. Unlike traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) cars, fuel cell vehicles produce zero tailpipe emissions, which significantly reduces their environmental footprint. This is primarily due to the process of generating electricity through the electrochemical reaction of hydrogen and oxygen, resulting in the only byproduct being water vapor and a small amount of heat. This clean energy production method makes fuel cell cars an attractive alternative to conventional vehicles, especially in the context of reducing greenhouse gas emissions and improving air quality.
However, the environmental benefits of fuel cell cars extend beyond their direct emissions. The production and transportation of hydrogen, the fuel for these vehicles, can have varying environmental consequences. If the hydrogen is produced through renewable energy sources, such as electrolysis powered by solar or wind energy, the overall carbon footprint of the fuel cell car is minimized. This is because the energy used to generate hydrogen is clean and sustainable, making the entire fuel cycle environmentally friendly.
On the other hand, if hydrogen production relies on fossil fuels, the environmental impact becomes more complex. The extraction and processing of fossil fuels for hydrogen generation can lead to habitat destruction and contribute to air and water pollution. Additionally, the transportation of hydrogen, especially over long distances, may require energy-intensive compression and cooling processes, potentially increasing the overall carbon emissions. Therefore, the sustainability of fuel cell cars is closely tied to the methods and sources used for hydrogen production and distribution.
Despite these considerations, fuel cell vehicles offer a promising path towards reducing our reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating climate change. Their ability to produce electricity through a clean and efficient process makes them a key component in the transition to a more sustainable transportation system. As technology advances and infrastructure for hydrogen refueling stations expands, the environmental impact of fuel cell cars is likely to become even more favorable, especially when coupled with the widespread adoption of renewable energy sources.
In summary, the environmental impact of fuel cell car usage is primarily positive due to their zero-emission nature. However, the sustainability of this technology depends on the methods used for hydrogen production and distribution. By utilizing renewable energy sources for hydrogen generation, fuel cell cars can significantly contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and improving environmental conditions, making them a valuable tool in the fight against climate change.
Power Boost: How a New Fuel Pump Revives Your Car's Performance
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The range of a fuel cell electric vehicle (FCEV) can vary depending on several factors, including the specific model, fuel cell technology, battery capacity, and driving conditions. On average, FCEVs can travel between 250 to 400 miles (400 to 644 kilometers) on a full tank of hydrogen. Some advanced models have achieved even longer ranges, with some capable of going over 500 miles (805 kilometers) on a single charge.
The range is primarily influenced by the fuel cell's efficiency, the size and capacity of the hydrogen storage tank, and the vehicle's overall design and aerodynamics. Larger fuel cells and higher-pressure hydrogen tanks can increase the range. Additionally, factors like driving speed, weather conditions, and the use of accessories also impact the distance an FCEV can cover.
Yes, fuel cell cars have the potential to offer comparable or even superior range to traditional electric vehicles (EVs). While early FCEV models had limited ranges, recent advancements in technology have significantly improved their performance. With the ability to refuel quickly and the potential for longer ranges, fuel cell cars could provide an attractive alternative for those seeking extended travel without the long charging times associated with some EVs.







