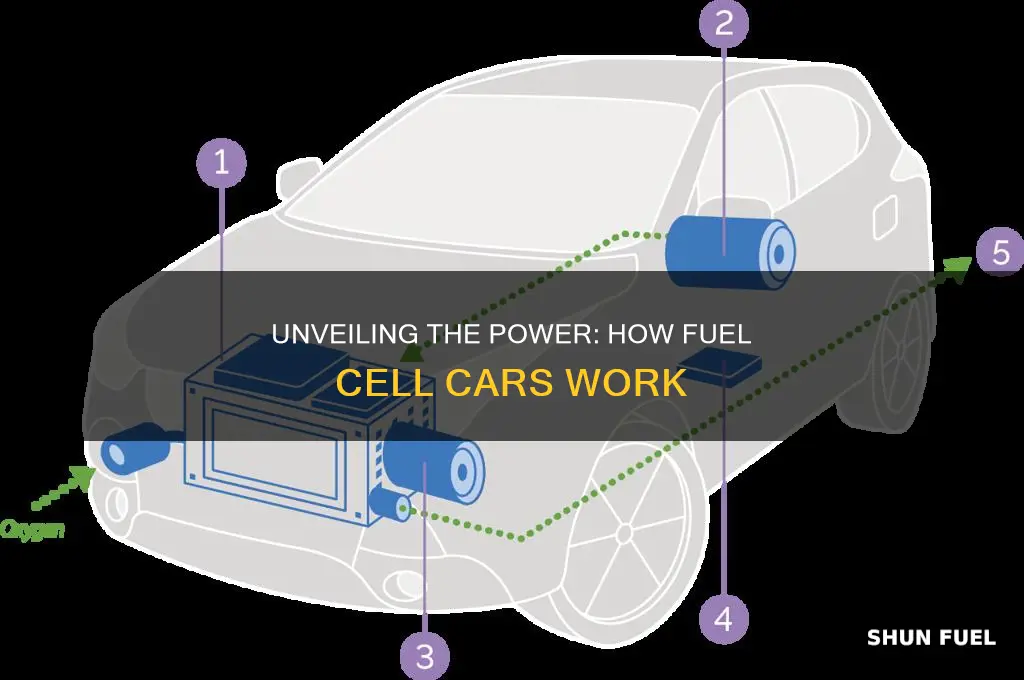
Fuel cell-powered cars are an innovative alternative to traditional internal combustion engine vehicles, offering a cleaner and more efficient way to drive. These cars utilize a unique process that involves converting chemical energy from a fuel, typically hydrogen, into electricity through a reaction with oxygen in the air. This electricity then powers an electric motor, which drives the vehicle's wheels. The key advantage of this technology is its ability to produce electricity through a chemical reaction, eliminating the need for frequent refueling and reducing emissions significantly. This paragraph introduces the concept of fuel cell technology and its potential to revolutionize the automotive industry.
How Fuel Cell-Powered Cars Work: Characteristics and Values
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Power Source | Hydrogen gas |
| Energy Conversion | Electrochemical reaction |
| Emission | Only water vapor and warm air |
| Efficiency | Up to 60% (higher than internal combustion engines) |
| Performance | Similar to conventional cars |
| Refueling Time | Similar to gasoline/diesel cars (3-5 minutes) |
| Range | Up to 300 miles (depending on fuel cell type and size) |
| Fuel Cell Type | Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM) fuel cells are most common |
| Storage | Hydrogen tanks (usually high-pressure) |
| Advantages | Zero tailpipe emissions, high efficiency, rapid refueling, renewable energy potential |
| Disadvantages | High initial cost, limited hydrogen infrastructure, hydrogen production and storage challenges |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, especially with renewable hydrogen production |
| Future Potential | Growing interest and investment in fuel cell technology, potential for widespread adoption |
What You'll Learn
- Power Generation: Fuel cells convert chemical energy from hydrogen and oxygen into electricity via electrochemical reactions
- Electric Motor: The electricity drives an electric motor, which powers the car's wheels
- Hydrogen Storage: Hydrogen is stored in high-pressure tanks or as a metal hydride compound
- Emission-Free Operation: Exhaust only produces water vapor and warm air, making fuel cell cars environmentally friendly
- Regenerative Braking: Some fuel cell vehicles use regenerative braking to recharge the battery and improve efficiency

Power Generation: Fuel cells convert chemical energy from hydrogen and oxygen into electricity via electrochemical reactions
Fuel cells are a fascinating technology that offers a clean and efficient way to power vehicles, and their operation revolves around the conversion of chemical energy into electrical power. This process begins with the fuel cell stack, which is the heart of the fuel cell system. Within the stack, a series of electrochemical reactions take place, utilizing the chemical energy stored in hydrogen and oxygen.
The power generation process starts with the injection of pure hydrogen gas into the fuel cell. This hydrogen is then directed onto the anode (negative electrode) of the cell. Here, the hydrogen molecules undergo a reaction, losing their electrons, which are then transported through an external circuit, creating an electric current. This reaction can be simplified as: 2H₂ → 4H⁺ + 4e⁻. The electrons, having traveled through the circuit, return to the cathode (positive electrode) via the external circuit, completing the electrical circuit.
Simultaneously, oxygen from the air is supplied to the cathode. Here, the oxygen molecules react with the electrons and protons (H⁺ ions) that have been transported from the anode. This reaction forms water, completing the electrochemical process. The overall reaction at the cathode is: O₂ + 4H⁺ + 4e⁻ → 2H₂O.
The key to this power generation lies in the electrochemical reactions, which are driven by the difference in electrical potential between the anode and cathode. This potential difference is created by the internal resistance of the fuel cell and the external circuit. As the reactions proceed, a continuous flow of electrons through the circuit generates electricity, which can then be used to power the vehicle's electrical systems and drive the electric motor.
It's important to note that fuel cells produce electricity directly through these reactions, eliminating the need for traditional combustion processes. This results in a more efficient and environmentally friendly power source compared to internal combustion engines. The chemical energy stored in hydrogen is thus converted into electrical energy, providing a sustainable and clean power source for fuel cell-powered vehicles.
Fuel Injector Power: Can You Damage Your Car?
You may want to see also

Electric Motor: The electricity drives an electric motor, which powers the car's wheels
The electric motor is a crucial component in fuel cell-powered vehicles, playing a pivotal role in converting electrical energy into mechanical motion to propel the car forward. When the electricity generated by the fuel cell is supplied to the electric motor, a series of intricate processes unfolds. This motor is typically designed to be highly efficient, ensuring that the electrical energy is effectively transformed into kinetic energy to drive the vehicle's wheels.
The operation of the electric motor is a complex interplay of electromagnetic principles. It consists of a rotor and a stator, both of which are essential for its functionality. The rotor, often made of lightweight materials, rotates within the stator, which is a stationary component. When the electric current passes through the motor's windings, it creates a magnetic field that interacts with the rotor's magnetic field, resulting in rotational motion. This rotation is then transferred to the car's wheels via a system of gears and driveshafts, enabling the vehicle to move.
The efficiency of the electric motor is a critical factor in the overall performance of the fuel cell-powered car. Engineers strive to optimize the motor's design to minimize energy losses during the conversion process. This includes selecting appropriate materials for the rotor and stator, ensuring proper cooling systems to manage heat dissipation, and employing advanced control algorithms to regulate the motor's speed and torque. By maximizing efficiency, the motor can deliver the required power to the wheels while minimizing energy wastage.
Furthermore, the electric motor's performance is closely tied to the vehicle's driving experience. A well-designed motor provides smooth and responsive acceleration, ensuring that the car responds promptly to the driver's commands. The motor's ability to deliver torque at various speeds contributes to the overall driving dynamics, making fuel cell-powered vehicles known for their quick acceleration and seamless power delivery.
In summary, the electric motor serves as the bridge between the electrical energy produced by the fuel cell and the mechanical force required to move the vehicle. Its intricate design and efficient operation are vital to the success of fuel cell-powered cars, offering a sustainable and environmentally friendly mode of transportation.
Fuel Door Placement: A Global Standard for Car Safety and Convenience
You may want to see also

Hydrogen Storage: Hydrogen is stored in high-pressure tanks or as a metal hydride compound
The storage of hydrogen is a critical component in the operation of fuel cell-powered vehicles, as it directly impacts the car's range and performance. Hydrogen storage systems are designed to efficiently hold the gas in a form that can be safely utilized by the fuel cell stack. There are two primary methods for storing hydrogen in these vehicles: high-pressure tanks and metal hydride compounds.
High-pressure tanks are a common and mature technology in the automotive industry. These tanks are typically made of lightweight, strong materials such as aluminum or carbon fiber composites. The hydrogen is compressed to a very high pressure, often exceeding 5000 pounds per square inch (psi), which allows for a relatively compact storage space. This method provides a high energy density, enabling longer driving ranges. However, the high pressure and potential hazards associated with hydrogen storage require careful design and safety measures to prevent leaks and ensure the vehicle's integrity.
An alternative approach is to store hydrogen as a metal hydride compound. This method involves bonding hydrogen atoms with a metal, usually a transition metal, to form a stable compound. The most common metal hydride used is sodium alanate (NaAlH4). This compound can store a significant amount of hydrogen in a relatively safe and low-pressure environment. When the fuel cell requires hydrogen, the metal hydride is heated, causing the hydrogen to be released. This process is reversible, allowing for the recycling of the metal hydride compound. Metal hydride storage systems offer the advantage of lower operating temperatures and pressures compared to high-pressure tanks, reducing safety concerns.
The choice between these storage methods depends on various factors, including vehicle design, driving range requirements, and safety considerations. High-pressure tanks are often favored for their high energy density and established infrastructure, making them a popular choice for fuel cell vehicles. On the other hand, metal hydride storage provides a safer and more flexible storage solution, especially for smaller vehicles or those with limited space.
In both cases, the efficiency and safety of hydrogen storage are crucial for the widespread adoption of fuel cell-powered cars. Researchers and engineers are continually working on improving storage technologies to address challenges such as cost, weight, and safety, ensuring that hydrogen-powered vehicles become a viable and sustainable transportation option.
E10 Fuel: Can Your Car Handle It?
You may want to see also

Emission-Free Operation: Exhaust only produces water vapor and warm air, making fuel cell cars environmentally friendly
Fuel cell-powered cars are a groundbreaking innovation in the automotive industry, offering a sustainable and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional internal combustion engines. One of the most remarkable aspects of these vehicles is their emission-free operation, which sets them apart from conventional cars. When you start a fuel cell car, the only byproduct of the energy conversion process is water vapor and warm air, making it a truly clean and green mode of transportation.
At the heart of this emission-free operation is the fuel cell, a device that converts chemical energy from a fuel source, typically hydrogen, into electrical energy through a process called electrochemical reaction. This reaction occurs in the fuel cell stack, where hydrogen gas and oxygen from the air are combined to produce electricity, with water and heat as the only byproducts. The absence of combustion means that there is no release of harmful pollutants like carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides, or particulate matter, which are common in traditional vehicle exhaust.
The process begins when the driver engages the accelerator, triggering the fuel cell to generate electricity. This electricity powers the electric motor, which drives the wheels and propels the vehicle forward. The only emission from the exhaust pipe is the warm air and water vapor that result from the electrochemical reaction. This is in stark contrast to conventional cars, where the exhaust system releases a range of pollutants, contributing to air pollution and environmental degradation.
The environmental benefits of fuel cell cars are significant. By eliminating the need for combustion, these vehicles reduce air pollution, improve local air quality, and contribute to a healthier environment. The absence of harmful emissions also means that fuel cell cars are quieter, making urban driving more pleasant and reducing noise pollution. Furthermore, the use of hydrogen as a fuel source offers a potential long-term solution to reducing our reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating the environmental impact of the transportation sector.
In summary, fuel cell-powered cars achieve emission-free operation by utilizing the electrochemical reaction of hydrogen and oxygen, resulting in the production of electricity and the release of only water vapor and warm air. This technology not only reduces air pollution but also contributes to a more sustainable and environmentally conscious future for the automotive industry. As the world seeks cleaner and greener transportation options, fuel cell cars are poised to play a pivotal role in shaping a more sustainable future.
Unleash Your Car's Potential: Can Vpower Fuel Boost Performance?
You may want to see also

Regenerative Braking: Some fuel cell vehicles use regenerative braking to recharge the battery and improve efficiency
Regenerative braking is a fascinating technology that plays a crucial role in enhancing the efficiency of fuel cell vehicles. When a fuel cell car is in motion, the electric motor acts as a generator, converting the vehicle's kinetic energy back into electrical energy during deceleration or braking. This process is known as regenerative braking, and it is a key feature in many fuel cell-powered automobiles.
As the driver applies the brakes, the electric motor switches to generator mode, capturing the kinetic energy that would otherwise be wasted as heat. This energy is then directed back into the vehicle's battery pack, effectively recharging it. The regenerative braking system works in conjunction with the fuel cell system, ensuring that the excess energy generated during braking is utilized efficiently. By converting kinetic energy to electrical energy, the car can extend its range and reduce the overall energy consumption.
The beauty of regenerative braking lies in its ability to improve the vehicle's overall efficiency. When a traditional internal combustion engine brakes, it wastes a significant amount of energy as heat, which is lost from the system. In contrast, fuel cell vehicles with regenerative braking systems can recover a substantial portion of this energy, leading to increased efficiency and reduced fuel consumption. This technology is particularly advantageous for city driving, where frequent stops and starts are common, as it helps to optimize energy usage in these stop-and-go scenarios.
The regenerative braking system's effectiveness is closely tied to the vehicle's overall design and the efficiency of the fuel cell stack. The captured energy is then stored in the battery, which powers the electric motor and other electrical components of the car. This stored energy can be utilized when needed, ensuring a consistent and efficient power supply. As a result, fuel cell vehicles with regenerative braking offer a more sustainable and environmentally friendly driving experience.
In summary, regenerative braking is a vital component of fuel cell-powered vehicles, enabling them to recharge their batteries and improve overall efficiency. This technology harnesses the kinetic energy that would otherwise be lost during braking and converts it into a valuable resource for the vehicle's operation. By implementing regenerative braking, fuel cell cars can extend their range, reduce fuel consumption, and provide a more sustainable transportation solution.
Top Fuel Power: Tubes or No Tubes?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Fuel cell-powered vehicles use a process called electrochemical reaction to produce electricity. This is achieved by combining hydrogen gas with oxygen from the air in the presence of a catalyst, typically platinum. The reaction produces electricity, water, and heat as byproducts.
The fuel cell stack is the heart of the fuel cell system. It consists of multiple fuel cells arranged in a series, each containing an anode, cathode, and an electrolyte membrane. The stack converts chemical energy from the fuel into electrical energy through a series of redox reactions.
Unlike traditional internal combustion engines, fuel cell cars don't store energy in the form of a large battery. Instead, they use the fuel cell to generate electricity on-demand. The excess electricity produced can be used to power accessories or, in some cases, be stored in a smaller battery for additional range.
Fuel cell-powered cars offer several benefits. They produce zero tailpipe emissions, reducing air pollution and greenhouse gases. The vehicles can refuel quickly, similar to conventional cars, and have a longer range than battery-electric vehicles. Additionally, fuel cells are highly efficient, converting over 60% of the chemical energy in hydrogen to electricity.
Hydrogen fuel is typically stored in high-pressure tanks on board the vehicle. The fuel cell system manages the supply of hydrogen, ensuring a steady flow to the stack for efficient operation. Some cars also use advanced storage systems, like metal hydride or carbon-based materials, to store hydrogen in a safer and more compact manner.







