Hydrogen has emerged as a promising alternative fuel for the automotive industry, offering a cleaner and potentially more efficient energy source compared to traditional gasoline or diesel. As a fuel, hydrogen can be utilized in fuel cell vehicles, where it undergoes a chemical reaction with oxygen from the air, producing electricity to power the car's electric motor. This process results in only water as a byproduct, making it an environmentally friendly option. The use of hydrogen as a fuel for cars involves the storage and delivery of compressed hydrogen gas, which can be supplied to vehicles through fueling stations. This innovative approach to powering automobiles has the potential to significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions and contribute to a more sustainable transportation system.
What You'll Learn
- Hydrogen Production: Sustainable methods like electrolysis using renewable energy are key to green hydrogen production
- Storage and Distribution: Developing efficient, safe storage and distribution systems is crucial for hydrogen fuel infrastructure
- Fuel Cell Technology: Hydrogen fuel cells convert hydrogen into electricity, powering electric vehicles with zero emissions
- Vehicle Design: Engineers optimize vehicle design for hydrogen fuel tanks, engines, and safety systems
- Infrastructure Expansion: Building hydrogen refueling stations and integrating with existing fuel distribution networks is essential for widespread adoption

Hydrogen Production: Sustainable methods like electrolysis using renewable energy are key to green hydrogen production
The production of hydrogen, especially when derived from sustainable methods, is a crucial aspect of developing hydrogen as a viable fuel for vehicles. One of the most promising and environmentally friendly approaches to hydrogen production is through the process of electrolysis, which can be powered by renewable energy sources. This method, often referred to as 'green hydrogen,' offers a clean and sustainable alternative to traditional hydrogen production techniques.
Electrolysis involves passing an electric current through water, typically in the presence of a catalyst, to split the water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen. The key to making this process sustainable is the use of renewable energy sources to power the electrolysis. By utilizing electricity generated from solar, wind, or hydroelectric power, the carbon footprint of hydrogen production can be significantly reduced, if not eliminated. This is in stark contrast to traditional hydrogen production methods, which often rely on fossil fuels and result in substantial greenhouse gas emissions.
The technology for renewable energy-powered electrolysis has advanced significantly in recent years, making it more efficient and cost-effective. Modern electrolysis systems can achieve high hydrogen production rates while maintaining a low energy consumption ratio. This is particularly important for the automotive industry, where the efficiency and scalability of hydrogen production methods are critical to the widespread adoption of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles.
In addition to its environmental benefits, green hydrogen production through electrolysis offers several advantages for the automotive sector. Firstly, the high purity of hydrogen produced through this method ensures that it is free from contaminants, which is essential for the efficient operation of fuel cells. Secondly, the flexibility of renewable energy sources allows for the decentralized production of hydrogen, enabling the establishment of local hydrogen refueling stations, which can be particularly beneficial for the distribution and infrastructure development required by hydrogen-powered vehicles.
The transition to sustainable hydrogen production methods, such as renewable energy-powered electrolysis, is a vital step in the development of a hydrogen economy. It not only addresses the environmental concerns associated with traditional hydrogen production but also paves the way for a more sustainable and efficient transportation system. As the world seeks to reduce its reliance on fossil fuels and combat climate change, the role of green hydrogen in the automotive industry becomes increasingly significant.
Fuel Pump Refueling: Essential or Overkill?
You may want to see also

Storage and Distribution: Developing efficient, safe storage and distribution systems is crucial for hydrogen fuel infrastructure
The widespread adoption of hydrogen as a fuel for vehicles relies heavily on the development of robust storage and distribution systems. Hydrogen's unique properties, such as its high energy density and low volume, present both opportunities and challenges when it comes to infrastructure. Efficient and safe storage is essential to ensure that hydrogen can be transported and supplied to refueling stations, making it accessible to the public.
One of the primary methods for storing hydrogen is in compressed gas tanks. These tanks are designed to hold hydrogen at high pressures, typically ranging from 350 to 700 bars (5,000 to 10,000 psi). The pressure is carefully regulated to maintain a stable and safe environment. For instance, the 700-bar standard is widely used in the automotive industry, allowing for a higher energy density and more compact storage compared to lower-pressure systems. However, the high pressure requires specialized materials and manufacturing processes to ensure the structural integrity of the tanks.
Another storage approach is through cryogenic storage, where hydrogen is cooled to extremely low temperatures, close to absolute zero (-253°C or -423°F). This method significantly reduces the volume of hydrogen, making it more suitable for long-distance transportation and large-scale storage. Cryogenic tanks are often used in industrial settings and can store hydrogen in a liquid state, providing a high energy density. However, this process is energy-intensive and requires advanced insulation materials to maintain the low temperature.
Distribution networks for hydrogen fuel also need to be carefully designed. Hydrogen can be transported via pipelines, similar to natural gas, but the infrastructure must be adapted to handle the unique properties of hydrogen. Pipelines need to be constructed with materials that can withstand the corrosive nature of hydrogen and ensure a tight seal to prevent leaks. Additionally, the distribution system should incorporate safety measures, such as leak detection and emergency shutdown mechanisms, to mitigate potential risks associated with hydrogen transportation.
Furthermore, the development of hydrogen refueling stations is critical to the overall infrastructure. These stations need to be strategically located along major transportation routes to provide convenient access for vehicle owners. The refueling process must be efficient and safe, requiring specialized equipment and trained personnel to manage the high-pressure hydrogen supply. The design and placement of these stations should consider factors like traffic flow, land availability, and proximity to existing fueling infrastructure.
In summary, the storage and distribution of hydrogen for automotive fuel applications require a comprehensive approach. It involves the development of advanced storage solutions, such as high-pressure tanks and cryogenic systems, each with its own set of advantages and challenges. Efficient distribution networks, including pipelines and refueling stations, must be established to ensure a reliable supply of hydrogen to vehicle owners. By addressing these infrastructure needs, the transition to hydrogen-powered vehicles can become more feasible and widely accepted.
Can Your Car Still Run on Bad Fuel?
You may want to see also

Fuel Cell Technology: Hydrogen fuel cells convert hydrogen into electricity, powering electric vehicles with zero emissions
The concept of using hydrogen as a fuel for vehicles is an innovative approach to addressing the environmental challenges associated with traditional combustion engines. At the heart of this technology lies the fuel cell, a device that harnesses the power of chemical reactions to generate electricity, offering a clean and efficient alternative to conventional automotive power sources.
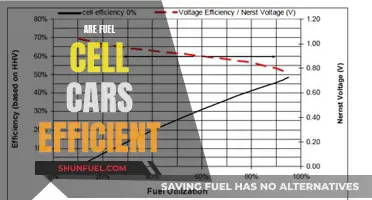
Fuel cell technology operates on a fundamental principle: the conversion of hydrogen gas into electricity through an electrochemical reaction. This process occurs within the fuel cell, which consists of two electrodes (anode and cathode) separated by an electrolyte. When hydrogen is supplied to the anode, it undergoes a reaction, releasing electrons and forming a positively charged hydrogen ion. These electrons are then directed through an external circuit, providing the electrical power needed to operate the vehicle. The hydrogen ions, meanwhile, migrate through the electrolyte to the cathode, where they react with oxygen from the air, producing water as the only byproduct. This entire process is both efficient and environmentally friendly, emitting no harmful pollutants.
The efficiency of hydrogen fuel cells is a key advantage. Unlike internal combustion engines, which can convert only about 20-30% of the energy in fuel to power, fuel cells can achieve efficiencies of up to 60%, making them a highly efficient energy conversion system. This high efficiency means that more of the energy stored in the hydrogen fuel is utilized to power the vehicle, resulting in reduced energy wastage and improved overall performance.
Furthermore, the environmental benefits of hydrogen fuel cells are significant. As mentioned, the only byproduct of the reaction is water, making hydrogen fuel cell vehicles zero-emission vehicles. This is a crucial advantage over conventional cars, which release harmful pollutants such as carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter, contributing to air pollution and climate change. By eliminating these emissions, hydrogen fuel cell technology offers a cleaner, greener alternative for transportation, helping to reduce the carbon footprint of the automotive industry.
In the context of electric vehicles (EVs), hydrogen fuel cells provide a unique solution. While traditional EVs use batteries as the primary energy storage, fuel cell EVs offer a different approach. The fuel cell generates electricity directly, eliminating the need for frequent charging and providing a longer range compared to battery-powered EVs. This is particularly advantageous for long-distance travel and heavy-duty applications, where the range and refueling time of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles can be more appealing to drivers.
In summary, hydrogen fuel cell technology presents a promising avenue for the future of automotive fuel. Its ability to convert hydrogen into electricity efficiently and with zero emissions makes it a viable option for powering electric vehicles. As the world seeks sustainable transportation solutions, hydrogen fuel cells offer a clean, efficient, and environmentally friendly alternative, contributing to a greener and more sustainable future for the automotive industry.
UK Car Fuel Tank Sizes: How Big is Yours?
You may want to see also

Vehicle Design: Engineers optimize vehicle design for hydrogen fuel tanks, engines, and safety systems
Engineers play a pivotal role in optimizing vehicle design for hydrogen fuel systems, ensuring that the transition to hydrogen-powered cars is both feasible and safe. The primary challenge lies in the unique properties of hydrogen, which requires specialized design considerations for fuel tanks, engines, and safety mechanisms.
Fuel Tanks:
Designing hydrogen fuel tanks is a critical aspect of vehicle engineering. Engineers must address the high compressibility and low density of hydrogen compared to conventional fuels. This means that tanks need to be designed to store hydrogen at high pressures, typically around 350-700 bar, to achieve practical driving ranges. The tank's material and structure are crucial; engineers often opt for lightweight, high-strength materials like carbon fiber composites to minimize vehicle weight while ensuring structural integrity. The tank's design also needs to consider factors such as thermal management to prevent hydrogen embrittlement and ensure the overall safety of the vehicle.
Engines and Powertrains:
Hydrogen fuel cell engines present a different set of design requirements. These engines convert chemical energy from hydrogen and oxygen into electricity, powering the vehicle. Engineers aim to optimize the fuel cell's efficiency, ensuring that the conversion process is as energy-efficient as possible. The design involves intricate heat management systems to maintain optimal operating temperatures and prevent performance degradation. Additionally, engineers focus on developing compact and lightweight powertrains, as hydrogen fuel cell systems can be more bulky than traditional internal combustion engines. This requires careful integration of the fuel cell, electric motor, and other components to minimize space and weight.
Safety Systems:
Safety is paramount in hydrogen vehicle design. Engineers implement advanced safety features to mitigate the unique risks associated with hydrogen. This includes sophisticated pressure regulation and release systems in fuel tanks to prevent overpressure and potential explosions. Fire-resistant materials and designs are employed to minimize the risk of combustion. Furthermore, engineers develop precise detection and monitoring systems to identify leaks or abnormal conditions, ensuring rapid response and safe operation. The vehicle's overall structure may also be designed to provide a protective barrier around the fuel system, enhancing safety in the event of an accident.
In summary, vehicle design for hydrogen fuel systems demands a meticulous approach, considering the unique properties of hydrogen and the specific requirements of fuel cells. Engineers strive to create efficient, safe, and practical solutions, addressing challenges related to storage, power generation, and safety. This meticulous design process is crucial for the successful integration of hydrogen technology into the automotive industry.
Boats vs. Cars: Fuel Efficiency Showdown
You may want to see also

Infrastructure Expansion: Building hydrogen refueling stations and integrating with existing fuel distribution networks is essential for widespread adoption
The widespread adoption of hydrogen as a fuel for vehicles relies heavily on the development of a robust infrastructure network, particularly in the form of hydrogen refueling stations. These stations are the vital link between hydrogen production and the end-user, providing the necessary fuel for vehicles to operate. The current challenge lies in the limited availability of these stations, which is a significant barrier to the widespread use of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles.
To address this issue, a comprehensive strategy for infrastructure expansion is required. This involves a multi-faceted approach, including the construction of new refueling stations and the integration of hydrogen infrastructure with existing fuel distribution networks. By doing so, we can ensure that hydrogen fuel becomes a more accessible and convenient option for vehicle owners.
Building hydrogen refueling stations is a critical step in this process. These stations need to be strategically located to serve a wide range of vehicle owners, including those in urban areas and along major transportation routes. The design and construction of these stations should consider factors such as energy efficiency, safety, and environmental impact. Modern refueling stations can be designed to be compact and efficient, utilizing advanced technologies to minimize the space required and reduce the overall environmental footprint.
Integrating hydrogen refueling infrastructure with existing fuel distribution networks is another crucial aspect. This integration allows for the seamless transition of hydrogen fuel into the current energy ecosystem. It involves collaboration between hydrogen producers, fuel cell vehicle manufacturers, and energy companies to establish a standardized system for fuel delivery and distribution. By connecting hydrogen refueling stations to existing pipelines, storage facilities, and transportation networks, we can ensure a steady supply of hydrogen fuel to support the growing number of fuel cell vehicles on the road.
Furthermore, the integration process should focus on interoperability and compatibility. This includes adopting common standards for hydrogen compression, storage, and dispensing, as well as ensuring that fueling processes are efficient and user-friendly. By aligning with existing fuel distribution networks, the infrastructure expansion strategy can leverage the established logistics and supply chain management systems, making hydrogen fuel more readily available to consumers.
In summary, the expansion of hydrogen refueling stations and the integration with existing fuel distribution networks are vital components in the journey towards widespread hydrogen fuel adoption for cars. This infrastructure development will not only provide the necessary fuel supply but also ensure convenience and accessibility for vehicle owners, ultimately contributing to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly transportation sector.
Marine Fuel in Cars: What You Need to Know
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles offer several benefits. Firstly, they produce zero tailpipe emissions, only releasing water vapor and warm air, making them environmentally friendly. Secondly, hydrogen cars can provide a longer driving range compared to battery-electric vehicles, addressing the range anxiety often associated with electric cars. Additionally, hydrogen refueling is relatively quick, similar to gasoline or diesel refueling, making it convenient for drivers.
A hydrogen fuel cell vehicle operates by converting the chemical energy of hydrogen into electricity through a process called electrochemical reaction. The hydrogen gas is supplied to the fuel cell, where it reacts with oxygen from the air in the presence of a catalyst. This reaction produces electricity, which powers the electric motor, driving the wheels. The only byproduct is water, which is released as steam through the car's exhaust.
The infrastructure for hydrogen refueling is still developing, but it is gradually expanding. You can locate hydrogen stations through various means. Many countries have websites or apps that provide real-time data on hydrogen refueling stations, allowing you to plan your trips accordingly. Additionally, some car manufacturers offer location-based services that can guide you to nearby hydrogen refueling points. It's advisable to check with local authorities or hydrogen fuel providers to stay updated on the availability of fueling stations in your area.