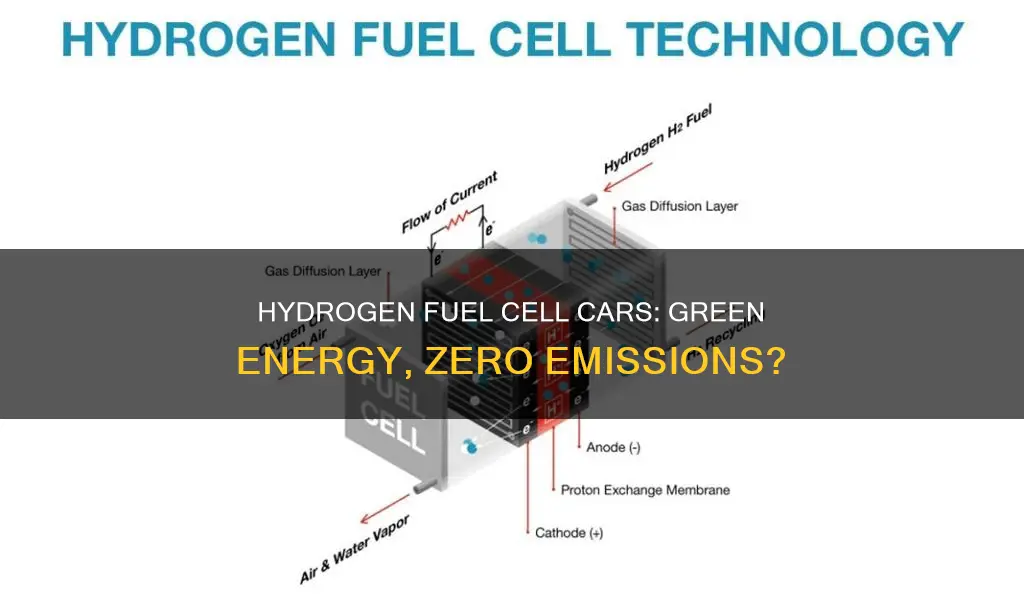
Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles have gained attention as a potential solution to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change. However, there is a common misconception that these cars emit carbon dioxide (CO2) during operation. In reality, hydrogen fuel cell cars produce only water vapor and warm air as byproducts, making them a clean and sustainable transportation option. This paragraph aims to clarify the environmental benefits of hydrogen fuel cell technology and address the misconception surrounding CO2 emissions.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Carbon Dioxide Emissions | Zero direct emissions from the vehicle itself. However, the process of producing hydrogen can result in CO2 emissions, depending on the method used. |
| Greenhouse Gas Impact | Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles are considered zero-emission vehicles, as they produce no direct greenhouse gas emissions during operation. |
| Air Quality | No harmful pollutants are released, making them environmentally friendly and beneficial for air quality. |
| Energy Efficiency | High efficiency in converting chemical energy to electrical energy, resulting in less energy waste. |
| Range | Similar to conventional electric vehicles, offering a range of around 300-400 miles on a single fill-up. |
| Refueling Time | Quick refueling process, typically taking less than 10 minutes, similar to gasoline vehicles. |
| Infrastructure | Requires a network of hydrogen fueling stations, which is still developing in many regions. |
| Cost | Currently, hydrogen fuel cell vehicles are more expensive than their electric counterparts due to the cost of hydrogen production and infrastructure. |
| Environmental Impact of Hydrogen Production | The environmental impact varies depending on the hydrogen production method. Electrolysis using renewable energy sources is the most sustainable. |
| Energy Source | Hydrogen is derived from various sources, including natural gas, coal, and water electrolysis, with the latter being the most sustainable. |
What You'll Learn
- Hydrogen Fuel Cell Efficiency: Energy Conversion and Carbon Emissions
- Carbon Footprint of Hydrogen Production: Electrolysis and Fossil Fuels
- Greenhouse Gas Impact: Hydrogen Fuel Cells vs. Internal Combustion Engines
- Carbon Dioxide Emissions Testing: Vehicle Performance and Environmental Impact
- Renewable Energy Integration: Hydrogen Fuel Cells and Carbon Neutrality

Hydrogen Fuel Cell Efficiency: Energy Conversion and Carbon Emissions
The efficiency of hydrogen fuel cell technology is a critical aspect of its environmental impact, particularly regarding carbon emissions. Hydrogen fuel cells, as the name suggests, generate electricity through a chemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen, producing water as the only byproduct. This process is highly efficient, converting a significant portion of the chemical energy in hydrogen into electrical energy.
In terms of energy conversion, hydrogen fuel cells offer a more efficient alternative to traditional internal combustion engines. While internal combustion engines convert only about 20-30% of the energy in gasoline or diesel into useful work, fuel cells can achieve efficiencies of up to 60%, and in some cases, even higher. This higher efficiency means that more of the energy stored in the hydrogen fuel is utilized, reducing the overall energy loss during the power generation process.
The environmental benefit of this efficiency is twofold. Firstly, it reduces the amount of energy required to power a vehicle, which can lead to lower overall energy consumption and reduced demand for energy resources. Secondly, and more importantly, the process of generating electricity through fuel cells does not produce carbon dioxide or other greenhouse gases, unlike the combustion of fossil fuels. This is a significant advantage over conventional vehicles, which emit CO2 and contribute to climate change.
However, it's essential to consider the entire lifecycle of hydrogen fuel cell technology. The production of hydrogen, especially if it is derived from natural gas through a process called steam methane reforming, can result in significant carbon emissions. This process, known as 'gray' hydrogen, can have a carbon footprint similar to or even higher than that of conventional vehicles. To truly reduce carbon emissions, the focus should be on using 'green' hydrogen, which is produced through renewable energy sources, such as wind or solar power, with minimal to no carbon emissions during production.
In summary, hydrogen fuel cell technology has the potential to significantly reduce carbon emissions and improve energy efficiency. However, the environmental benefits are highly dependent on the methods used to produce hydrogen. By adopting green hydrogen production, the technology can become a viable and sustainable solution for reducing carbon emissions in the transportation sector.
Electric vs. Fuel: Unveiling the Weight Difference
You may want to see also

Carbon Footprint of Hydrogen Production: Electrolysis and Fossil Fuels
The carbon footprint of hydrogen production is a critical aspect of understanding the environmental impact of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles. While hydrogen fuel cell cars themselves do not emit carbon dioxide during operation, the process of producing hydrogen can vary in its environmental impact, depending on the method and energy sources used.
Electrolysis is a common method for producing hydrogen, where water is split into hydrogen and oxygen using an electric current. This process can be powered by renewable energy sources like solar or wind power, which significantly reduces the carbon footprint. When renewable energy is used, the carbon emissions associated with hydrogen production are minimal, often considered carbon-neutral. However, if the electricity used for electrolysis comes from fossil fuel-based power plants, the carbon footprint increases. The burning of fossil fuels releases substantial amounts of carbon dioxide, and this emission is directly linked to the production of hydrogen through electrolysis.
The carbon footprint of hydrogen production through electrolysis is influenced by the efficiency of the process and the energy mix used. Advanced electrolysis technologies can improve efficiency, reducing the overall energy consumption and, consequently, the carbon emissions. Additionally, the use of carbon capture and storage (CCS) techniques can further minimize the environmental impact by capturing and storing carbon dioxide emissions from fossil fuel-based power plants.
In contrast, the production of hydrogen through steam methane reforming, a process often associated with fossil fuels, has a higher carbon footprint. This method involves reacting methane with steam to produce hydrogen and carbon monoxide. The reaction releases carbon dioxide as a byproduct, and the overall process is energy-intensive, often relying on fossil fuel combustion. As a result, this method contributes significantly to greenhouse gas emissions, making it less environmentally friendly compared to electrolysis powered by renewable sources.
In summary, the carbon footprint of hydrogen production is a complex issue. Electrolysis powered by renewable energy sources offers a low-carbon or carbon-neutral alternative, while methods relying on fossil fuels can have a substantial environmental impact. The choice of production method and energy sources is crucial in determining the overall sustainability of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles. Understanding these factors is essential for developing and implementing clean and efficient hydrogen production technologies.
Hydrogen Fuel Cells: The Green Revolution on the Road?
You may want to see also

Greenhouse Gas Impact: Hydrogen Fuel Cells vs. Internal Combustion Engines
The debate surrounding the environmental impact of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles often centers on their emissions, particularly in comparison to traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. One common misconception is that hydrogen fuel cell cars emit carbon dioxide (CO2), a greenhouse gas, as a byproduct of their operation. However, the reality is quite different.
Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles produce electricity through a chemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen, resulting in the primary emission of water vapor and warm air. This process is highly efficient and produces no direct emissions of CO2 or other harmful pollutants. In contrast, internal combustion engines burn fossil fuels, releasing CO2 and other greenhouse gases as a byproduct, contributing significantly to air pollution and climate change.
The environmental benefits of hydrogen fuel cells become even more apparent when considering the entire lifecycle of the vehicle. The production and transportation of hydrogen, as well as the manufacturing of fuel cell components, can have environmental impacts, but these are generally offset by the zero-emission nature of the vehicle during operation. In contrast, the extraction, refining, and combustion of fossil fuels for ICE vehicles contribute to a much higher level of greenhouse gas emissions over their lifecycle.
Furthermore, the potential for hydrogen to be produced through renewable energy sources, such as wind or solar power, adds another layer of environmental benefit. When hydrogen is generated using renewable energy, the entire lifecycle of the fuel cell vehicle becomes carbon-neutral, meaning the energy used to power the vehicle does not contribute to net greenhouse gas emissions.
In summary, hydrogen fuel cell cars do not emit carbon dioxide during operation, making them a cleaner alternative to internal combustion engine vehicles. While there are considerations regarding the production and distribution of hydrogen, the overall environmental impact of fuel cell vehicles is significantly lower, especially when compared to the lifecycle emissions of ICE vehicles. This technology has the potential to play a crucial role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating climate change.
Electric Revolution: Unveiling the Green vs. Fuel Debate
You may want to see also

Carbon Dioxide Emissions Testing: Vehicle Performance and Environmental Impact
The question of whether hydrogen fuel cell cars emit carbon dioxide is an important one, especially in the context of environmental sustainability and vehicle performance. Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (HFCVs) are gaining traction as a potential solution to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and improve air quality. However, it's crucial to understand their entire lifecycle, including the emissions they produce during operation and the potential environmental impact.
Hydrogen fuel cell cars, as the name suggests, use hydrogen gas as their primary fuel source. When hydrogen reacts with oxygen in the fuel cell, it produces electricity, which powers the vehicle's electric motor. The only byproduct of this reaction is water vapor, which is emitted as steam from the car's exhaust. This process is highly efficient and does not directly emit carbon dioxide or other harmful pollutants.
However, the environmental impact of hydrogen fuel cell cars can be influenced by the source of hydrogen. Hydrogen can be produced through various methods, including electrolysis of water, natural gas reforming, and biomass gasification. Each method has its own set of emissions and environmental considerations. For instance, if the hydrogen is produced through electrolysis using renewable energy sources, the overall carbon footprint of the vehicle is significantly reduced. In contrast, if hydrogen is derived from natural gas, the process can result in methane emissions, which are a potent greenhouse gas.
To assess the true environmental impact, a comprehensive testing and evaluation process is necessary. This includes analyzing the entire lifecycle of the vehicle, from hydrogen production to fuel cell operation and vehicle disposal. Testing should focus on measuring the direct emissions during operation, as well as the indirect emissions associated with hydrogen production and infrastructure. By conducting these tests, researchers can determine the net carbon dioxide emissions and provide valuable insights into the vehicle's performance and environmental benefits.
In summary, hydrogen fuel cell cars have the potential to significantly reduce carbon dioxide emissions compared to conventional internal combustion engine vehicles. However, the overall environmental impact depends on the source of hydrogen and the efficiency of the production and distribution processes. Through rigorous testing and evaluation, we can better understand the performance and environmental advantages of hydrogen fuel cell technology, ensuring its role in a sustainable future.
Fuel Injection: Do Carts Need Fuel Pumps?
You may want to see also

Renewable Energy Integration: Hydrogen Fuel Cells and Carbon Neutrality
The integration of hydrogen fuel cells into renewable energy systems is a pivotal strategy in the pursuit of carbon neutrality, offering a pathway to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate climate change. Hydrogen fuel cells, when powered by renewable energy sources, provide a clean and efficient means of generating electricity, with water and heat as the only byproducts. This technology is particularly significant in the transportation sector, where it can serve as a viable alternative to conventional internal combustion engines, thereby reducing carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions.
The process begins with the generation of hydrogen through renewable energy sources such as wind, solar, or hydroelectric power. These methods of hydrogen production are crucial as they ensure that the fuel is derived from clean, sustainable sources, minimizing the environmental impact. Once produced, the hydrogen is utilized in fuel cells, which convert the chemical energy of hydrogen into electricity through a reaction with oxygen, resulting in the formation of water. This process is highly efficient and produces no direct emissions of CO2 or other harmful pollutants.
The environmental benefits of hydrogen fuel cells are substantial. By replacing fossil fuels in transportation, fuel cell vehicles can significantly reduce CO2 emissions, contributing to the overall goal of carbon neutrality. For instance, a hydrogen fuel cell car powered by renewable electricity can achieve zero tailpipe emissions, making it an environmentally friendly option. This is particularly important in urban areas where air quality is a critical concern. Moreover, the use of hydrogen fuel cells in public transportation, such as buses and trains, can further enhance the reduction of carbon emissions on a larger scale.
However, the transition to hydrogen fuel cells and renewable energy integration faces several challenges. One significant obstacle is the infrastructure required for hydrogen production, storage, and distribution. Developing a comprehensive network of hydrogen refueling stations is essential to support the widespread adoption of fuel cell vehicles. Additionally, the cost of hydrogen production and the technology required for efficient storage and transportation need to be addressed to make it economically viable.
Despite these challenges, the potential of hydrogen fuel cells in achieving carbon neutrality is immense. As the world seeks to transition towards a more sustainable future, the integration of renewable energy sources with hydrogen fuel cell technology can play a pivotal role. It offers a pathway to reduce reliance on fossil fuels, decrease greenhouse gas emissions, and improve air quality. With continued research, investment, and policy support, hydrogen fuel cells can become a cornerstone of a low-carbon economy, contributing to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly world.
Uncover Your Car's Fuel Capacity: A Comprehensive Guide
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
No, they do not. Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles are considered a clean and sustainable transportation option because they produce only water and heat as byproducts, with no direct emission of carbon dioxide or other harmful pollutants.
Hydrogen fuel cells generate electricity through an electrochemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen. This process involves the conversion of chemical energy into electrical energy, which then powers the vehicle's electric motor.
While the vehicles themselves do not emit carbon dioxide, the production of hydrogen can have some environmental impact. The most common method of hydrogen production is through steam methane reforming, which can result in greenhouse gas emissions if not managed sustainably. However, efforts are being made to develop carbon-neutral hydrogen production methods, such as electrolysis powered by renewable energy sources.
Absolutely. Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles have the potential to significantly reduce carbon emissions compared to conventional internal combustion engine cars. As the world aims to transition towards a low-carbon economy, hydrogen fuel cell technology offers a promising alternative, especially for heavy-duty vehicles and long-distance transportation.







