Electric cars are revolutionizing the automotive industry, but do they use hydrogen fuel cells? This question delves into the intersection of two cutting-edge technologies: electric vehicles (EVs) and hydrogen fuel cell technology. While EVs primarily rely on batteries to power their electric motors, some innovative models are exploring the integration of hydrogen fuel cells to enhance their performance and efficiency. This exploration opens up new possibilities for sustainable transportation, blending the benefits of electric power with the energy density of hydrogen.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Technology | Hydrogen fuel cells are not used in electric cars. Electric cars are powered by electric motors and batteries. |
| Energy Source | Electric cars are typically powered by batteries charged from the electrical grid, while some models use hydrogen fuel cells (but this is less common). |
| Efficiency | Hydrogen fuel cells are generally more efficient than internal combustion engines, but the overall efficiency of electric cars is still influenced by the power generation and transmission processes. |
| Range | Electric cars with hydrogen fuel cells can have a longer range compared to battery-only electric cars, but the range is still limited by the fuel cell's capacity and the availability of hydrogen refueling stations. |
| Environmental Impact | Electric cars, especially those with battery-only powertrains, have lower environmental impacts compared to traditional internal combustion engine vehicles. Hydrogen fuel cells, when powered by renewable electricity, can be a clean energy source, but the production and distribution of hydrogen can have environmental consequences. |
| Infrastructure | Hydrogen refueling stations are less common than charging stations for electric cars, which can limit the practicality of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles. |
| Cost | The cost of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles is generally higher than that of battery-electric cars due to the technology's complexity and the need for specialized infrastructure. |
| Market Availability | Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles are less common in the market compared to battery-electric cars, and their adoption is still growing. |
| Performance | Electric cars with hydrogen fuel cells can offer quick refueling times and high power output, making them suitable for certain applications. |
| Research and Development | Significant research is ongoing to improve the efficiency, cost, and infrastructure for hydrogen fuel cell vehicles. |
What You'll Learn
- Electric Cars vs. Hydrogen Fuel Cells: Electric cars use batteries, while hydrogen fuel cells power some electric vehicles
- Hydrogen Fuel Cell Technology: Hydrogen fuel cells convert hydrogen and oxygen into electricity, offering a clean energy source
- Electric Vehicle Powertrains: Electric cars use electric motors and batteries, not hydrogen fuel cells, for propulsion
- Hydrogen Storage and Safety: Storing hydrogen safely is a challenge for fuel cell vehicles, impacting their practicality
- Environmental Impact: Hydrogen fuel cells produce zero emissions, but hydrogen production can have environmental consequences

Electric Cars vs. Hydrogen Fuel Cells: Electric cars use batteries, while hydrogen fuel cells power some electric vehicles
The comparison between electric cars and hydrogen fuel cell vehicles is an important aspect of the broader debate on sustainable transportation. While both technologies aim to reduce reliance on fossil fuels, they operate on different principles and have distinct advantages and limitations.
Electric cars, as the name suggests, primarily rely on electric batteries as their power source. These batteries store electrical energy, which is then used to power the vehicle's electric motor. The key advantage of this system is the immediate availability of power, allowing for quick acceleration and smooth driving. Electric cars are known for their efficiency and low environmental impact, especially when charged using renewable energy sources. The technology has advanced significantly, with modern electric vehicles offering impressive range, rapid charging capabilities, and a vast network of charging stations, making them a practical and popular choice for many drivers.
On the other hand, hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (FCVs) use a different approach. These cars convert hydrogen gas into electricity through a chemical reaction in a fuel cell, which then powers the electric motor. Hydrogen FCVs offer several unique benefits. They provide rapid refueling, similar to conventional gasoline vehicles, and produce zero direct emissions, making them environmentally friendly. However, the infrastructure for hydrogen refueling stations is still developing, and the production and distribution of hydrogen gas also present challenges in terms of sustainability and cost.
The debate often revolves around the efficiency and environmental impact of each system. Electric cars, with their direct use of batteries, have a simpler power train, which can lead to higher efficiency. Hydrogen FCVs, while producing zero tailpipe emissions, face challenges in the entire lifecycle of hydrogen production, transportation, and utilization, which can impact their overall environmental benefits.
In summary, electric cars and hydrogen fuel cell vehicles represent two distinct paths towards a more sustainable transportation future. Electric cars offer convenience, efficiency, and a well-established infrastructure, while hydrogen FCVs provide rapid refueling and zero emissions. The choice between the two depends on various factors, including local infrastructure, environmental considerations, and personal preferences, ultimately contributing to the ongoing evolution of the automotive industry.
Fossil Fuel Energy: A Sustainable Future for Cars?
You may want to see also

Hydrogen Fuel Cell Technology: Hydrogen fuel cells convert hydrogen and oxygen into electricity, offering a clean energy source
The concept of hydrogen fuel cells is an intriguing one, especially in the context of electric vehicles (EVs) and sustainable energy solutions. While electric cars have gained significant popularity for their zero-emission capabilities, the idea of using hydrogen fuel cells to power them presents an alternative approach to achieving clean transportation.
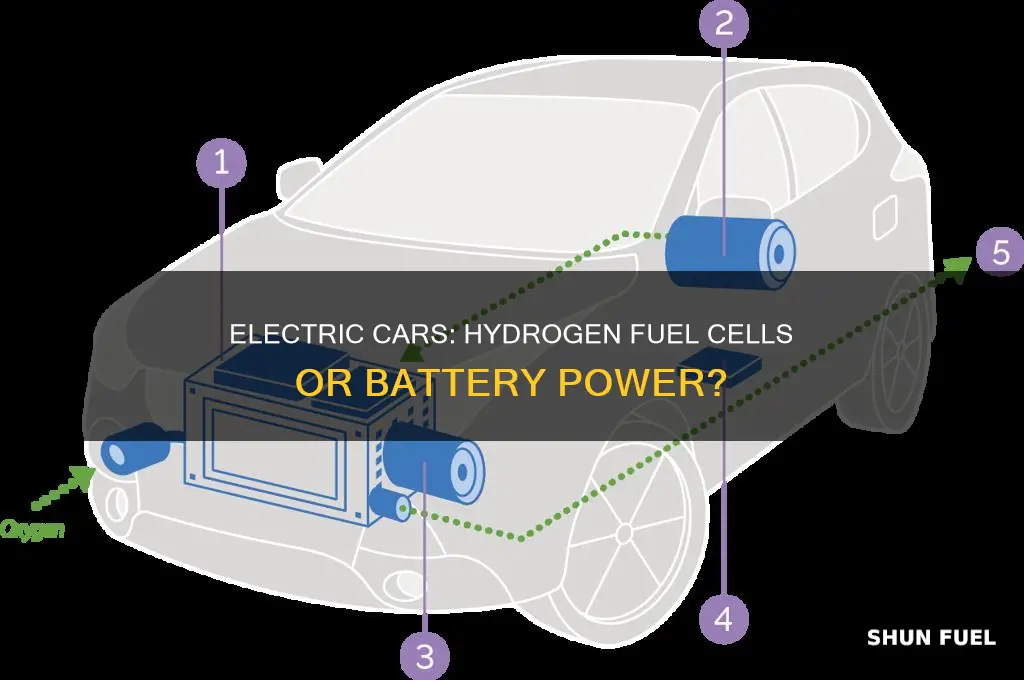
Hydrogen fuel cell technology is a fascinating process that enables the conversion of chemical energy into electrical energy. At its core, a fuel cell consists of two electrodes, an anode and a cathode, separated by an electrolyte. When hydrogen gas is supplied to the anode, it undergoes a reaction, releasing electrons and forming protons. These electrons are then directed through an external circuit, generating electricity, while the protons move through the electrolyte. Simultaneously, oxygen from the air is supplied to the cathode, where it combines with the protons and electrons to form water, thus completing the reaction. This entire process is highly efficient and produces only water and heat as byproducts, making it an environmentally friendly energy source.
In the context of electric cars, hydrogen fuel cells offer a promising solution to address the limitations of traditional battery-powered EVs. While electric cars have made significant strides in reducing carbon emissions, the availability of charging infrastructure and the time required for charging can be drawbacks. Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles, on the other hand, provide a rapid refueling experience similar to that of conventional gasoline cars. When hydrogen is introduced into the fuel cell, it initiates the electrochemical reaction, producing electricity to power the vehicle's electric motor. This technology has the potential to revolutionize the EV market by offering a more convenient and efficient alternative to traditional battery-based electric cars.
The beauty of hydrogen fuel cell technology lies in its ability to produce electricity through a clean and efficient process. Unlike internal combustion engines, fuel cells do not burn hydrogen; instead, they facilitate a chemical reaction that generates electricity. This makes hydrogen fuel cells a more environmentally friendly option, especially when compared to the combustion of fossil fuels. Additionally, the energy density of hydrogen is significantly higher than that of batteries, allowing for longer driving ranges and faster refueling times.
However, it is important to note that the widespread adoption of hydrogen fuel cell technology in electric cars faces several challenges. The infrastructure for hydrogen production, storage, and distribution is still developing, and building a comprehensive network of hydrogen refueling stations is crucial for the technology's success. Furthermore, the cost of hydrogen fuel cells and the materials required for their construction need to become more affordable and accessible to make them a viable option for mass-market electric vehicles. Despite these challenges, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on improving the efficiency, durability, and scalability of hydrogen fuel cell technology, making it a promising candidate for the future of clean transportation.
Can You Fuel a Car While It's Running? Unlocking the Mystery
You may want to see also

Electric Vehicle Powertrains: Electric cars use electric motors and batteries, not hydrogen fuel cells, for propulsion
Electric vehicles (EVs) have revolutionized the automotive industry, offering an eco-friendly and efficient alternative to traditional internal combustion engines. One common misconception is that electric cars utilize hydrogen fuel cells for propulsion, which is not the case. Let's clarify the power source behind these vehicles and how they actually work.
Electric cars, as the name suggests, run on electricity, and their propulsion system is quite different from that of hydrogen-powered vehicles. The primary component of an electric vehicle's powertrain is the electric motor, which is responsible for converting electrical energy into mechanical energy to drive the wheels. These motors are highly efficient and provide instant torque, resulting in smooth acceleration. The power source for these motors is the battery pack, typically a lithium-ion battery, which stores electrical energy and supplies it to the motor when needed.
When an electric car is driven, the battery pack powers the electric motor, which in turn rotates the wheels. This process is simple and direct, with no involvement of hydrogen fuel cells. Hydrogen fuel cells, often associated with another technology called fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs), are not used in conventional electric cars. FCEVs use a different approach, where hydrogen gas is reacted with oxygen in the air to produce electricity through a fuel cell, which then powers the electric motor. However, this technology is distinct from the electric powertrains found in standard electric cars.
The misconception might arise from the fact that both electric and hydrogen fuel cell vehicles aim to reduce environmental impact and provide clean transportation. However, electric cars have gained popularity due to their simplicity, high efficiency, and the extensive charging infrastructure available. The use of electric motors and batteries allows for rapid charging, making EVs more convenient for daily use compared to the time-consuming process of refueling hydrogen vehicles.
In summary, electric cars rely on electric motors and batteries for propulsion, offering a sustainable and efficient driving experience. The technology behind electric powertrains is well-established and widely adopted, making it a popular choice for environmentally conscious consumers. While hydrogen fuel cell technology has its place in the automotive industry, it is not the power source for the electric cars we commonly see on the roads today.
Understanding Fuel Injection: Can You DIY Your Car's Injection System?
You may want to see also

Hydrogen Storage and Safety: Storing hydrogen safely is a challenge for fuel cell vehicles, impacting their practicality
The concept of electric cars powered by hydrogen fuel cells is an intriguing one, offering a potential solution to the environmental concerns surrounding traditional internal combustion engines. However, the practical implementation of this technology faces a significant hurdle: hydrogen storage and safety. Storing hydrogen safely and efficiently is a complex challenge that impacts the overall practicality of fuel cell vehicles.
One of the primary concerns with hydrogen storage is its high energy density. Hydrogen has a much higher energy density compared to conventional fuels like gasoline or diesel. While this is advantageous for energy storage, it also poses a safety risk. Hydrogen is a highly flammable gas, and any leak or malfunction in the storage system could lead to dangerous situations. To address this, researchers and engineers are exploring various storage methods, including compressed gas tanks, liquid hydrogen tanks, and metal hydride storage. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages, and finding a balance between energy density, safety, and practicality is crucial.
Compressed hydrogen gas tanks, similar to those used in some current fuel cell vehicles, offer high energy density but require specialized materials to withstand the pressure. These tanks must be designed to prevent leaks and ensure that any potential hazards are minimized. Liquid hydrogen storage, on the other hand, provides a higher energy density but presents challenges in terms of handling and infrastructure. It requires cryogenic temperatures to maintain the liquid state, making storage and transportation more complex and costly.
Metal hydride storage is another approach, where hydrogen is absorbed into a metal matrix. This method offers a safer storage option as it operates at lower pressures and temperatures. However, the efficiency of metal hydride storage is lower compared to compressed gas tanks, and the process of absorbing and releasing hydrogen can be slower. Researchers are actively working on improving the efficiency and speed of metal hydride storage to make it a more viable option.
Ensuring the safety of hydrogen storage systems is paramount. This includes implementing robust safety mechanisms, such as pressure relief valves, leak detection systems, and advanced materials that can withstand potential hazards. Additionally, educating the public about the safe handling and use of hydrogen-powered vehicles is essential to gain widespread acceptance and trust. The development of comprehensive safety standards and regulations will also play a crucial role in making fuel cell vehicles a safe and practical reality.
In summary, while hydrogen fuel cells offer a promising alternative to traditional combustion engines, the safe and efficient storage of hydrogen remains a critical challenge. Overcoming this hurdle will require continued research, innovation, and collaboration among engineers, scientists, and policymakers to ensure that fuel cell vehicles can become a viable and widely accepted solution for sustainable transportation.
The Ultimate Guide to Fuel Tankering: Is It Worth It?
You may want to see also

Environmental Impact: Hydrogen fuel cells produce zero emissions, but hydrogen production can have environmental consequences
The concept of electric cars powered by hydrogen fuel cells is an intriguing one, offering a potential solution to the environmental challenges associated with traditional internal combustion engines. While hydrogen fuel cells themselves produce zero emissions, the process of generating hydrogen for these cells can have significant environmental implications.
Hydrogen production primarily involves two methods: steam methane reforming and electrolysis. Steam methane reforming, the most common process, involves reacting methane with steam to produce hydrogen and carbon monoxide. This method is highly efficient but also has a substantial carbon footprint due to the large amount of natural gas used and the associated greenhouse gas emissions. The process releases carbon dioxide, a potent contributor to global warming, and requires significant energy input, often derived from fossil fuels.
Electrolysis, on the other hand, offers a cleaner alternative. It involves using electricity to split water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen. However, the environmental benefit of this method depends on the source of the electricity. If the electricity is generated from renewable sources like wind or solar, the overall carbon footprint is significantly reduced. Yet, if the electricity is produced from non-renewable sources, such as coal or natural gas, the environmental impact can be similar to that of steam methane reforming.
The environmental consequences of hydrogen production extend beyond greenhouse gas emissions. The extraction and processing of natural gas, a key feedstock for steam methane reforming, can lead to habitat destruction and water pollution. Additionally, the large-scale infrastructure required for hydrogen production and distribution can have significant land use impacts.
In summary, while hydrogen fuel cells in electric cars offer a promising path towards reducing vehicle emissions, the environmental impact of hydrogen production cannot be overlooked. The choice of production method and energy sources is critical in determining the overall sustainability of this technology. As the world seeks to transition to cleaner energy systems, it is essential to consider the entire lifecycle of hydrogen production and its potential environmental consequences.
Smoke Signals: Fuel Filter's Role in Car Emissions
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
No, electric cars do not use hydrogen fuel cells. Electric vehicles (EVs) are powered by electric motors that run on electricity stored in batteries. Hydrogen fuel cells are a different technology used in vehicles like the Toyota Mirai, which is a specific type of electric car that utilizes hydrogen as its primary energy source.
Electric cars operate by converting chemical energy from batteries into electrical energy, which then powers the electric motor. The batteries are typically charged by plugging the car into an electrical outlet or a charging station. This process allows electric vehicles to run on electricity, reducing their reliance on fossil fuels and minimizing direct emissions.
Yes, there are a few electric cars that incorporate hydrogen fuel cell technology. These vehicles, like the aforementioned Toyota Mirai, produce electricity through a chemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen, emitting only water as a byproduct. This makes them zero-emission vehicles, but they are less common compared to traditional battery-electric cars.
A hydrogen fuel cell is a device that generates electricity through a reaction between hydrogen and oxygen, producing water and electricity. It provides power to the vehicle's electric motor. On the other hand, a conventional battery stores electrical energy and directly powers the motor. Hydrogen fuel cells offer a different approach to achieving zero-emission transportation.
Absolutely! The automotive industry is witnessing a transition towards more sustainable transportation, and both electric cars and hydrogen fuel cell vehicles have their unique advantages. Electric cars are more prevalent and offer a wider range of models, while hydrogen fuel cell vehicles provide an alternative for those seeking zero-emission mobility with a different technology. This diversity caters to various consumer preferences and market demands.







