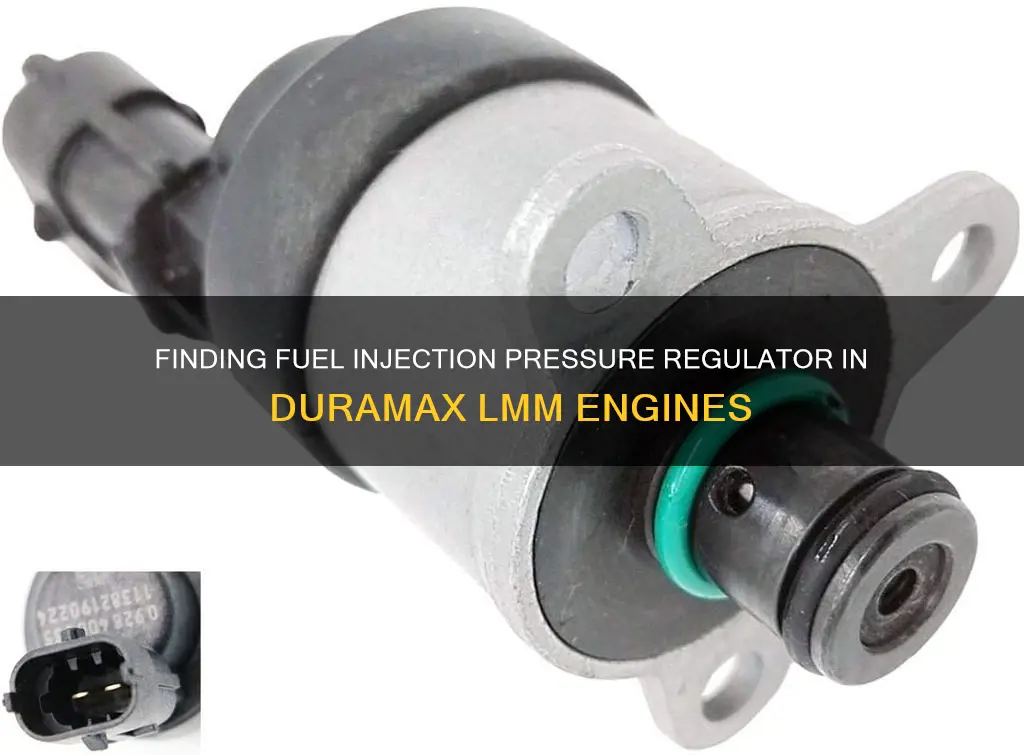
The fuel pressure regulator is located on the CP3/CP4 injection pump in a 2008 LMM Duramax. It can be serviced without removing the pump. The fuel pressure regulator controls the amount of fuel that goes through, so if it is faulty, you may experience hard starts, injector knocking, or smoking.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Vehicle compatibility | 2006-2010 GM 6.6L LMM LBZ Duramax Diesel |
| Interchange Part # | MPROP - 97384667 / PR444 / 6.6 DIESEL, 097384667, 904575, 904-575, LBZ FCA, LMM FCA, FCA, PR444 |
| Location | On the CP3/CP4 injection pump |
What You'll Learn

Fuel pressure regulator location
The fuel pressure regulator is located on the CP3/CP4 injection pump. It can be serviced without removing the pump.
The fuel pressure regulator is not easily accessible and requires the removal of several sensors to reach it. The hardest part of the process is getting the last bolt on the bottom of the regulator. A Torx screwdriver and a pipe wrench can be used to remove the screws, but be careful not to shatter the handle.
The fuel pressure regulator is vital to your truck's power, efficiency, and longevity. If you are experiencing hard starts, injector knocking, or smoking, you may need to replace the fuel pressure regulator.
Troubleshooting Car Crank Issues: Fuel Pump Pressure
You may want to see also

Fuel pressure regulator replacement
The fuel pressure regulator is a device designed to maintain constant fuel pressure for proper fuel atomization. It is responsible for ensuring the fuel injectors disperse the right amount of fuel needed for combustion.
Symptoms of a Faulty Fuel Pressure Regulator:
A vehicle will begin to have a difficult start-up, making the starter engage for longer than normal. The engine may also begin to operate erratically and there may be instances where the engine simply cuts out during normal operation.
Replacing the Fuel Pressure Regulator:
- Park your vehicle on a flat, hard surface and ensure that the transmission is in park (for automatics) or in 1st gear (for manuals).
- Secure the front tires with wheel chocks and engage the parking brake to lock the rear tires from moving.
- Install a nine-volt battery saver into your cigarette lighter to keep your computer live and your settings current.
- Disconnect the battery by taking the ground cable off the battery's negative post to disable the power going to the fuel pump.
- Remove the engine cover and any brackets that may be in the way of the fuel pressure regulator.
- If your engine has an intake that overlaps the fuel pressure regulator, remove the intake before proceeding.
- Find the Schrader valve, or test port, on the fuel rail. Put on safety glasses and protective clothing, then place a small drip pan under the rail and a towel over the port.
- Using a small flat screwdriver, open the valve by pushing on the Schrader valve to bleed off the pressure in the fuel rail.
- If there is no test port or Schrader valve, remove the supply fuel hose to the fuel rail using a drip pan and a fuel hose quick disconnect tool kit.
- Remove the vacuum line and mounting hardware from the fuel pressure regulator, then take the regulator off the fuel rail.
- Clean the fuel rail with a lint-free cloth and check the condition of the vacuum hose from the engine manifold to the fuel pressure regulator, replacing it if necessary.
- Install the new fuel pressure regulator onto the fuel rail, screwing in the mounting hardware finger-tight before tightening to 12 inch-pounds, then a 1/8 turn.
- Put on the vacuum hose and install any brackets or the intake that you had to remove, using new gaskets or o-rings to seal the intake to the engine.
- Put back the engine cover by snapping it into place.
- Reconnect the battery and remove the nine-volt battery saver from the cigarette lighter.
- Remove the wheel chocks from the rear wheels.
- Turn the ignition key on and listen for the fuel pump to activate, then turn off the ignition after the fuel pump stops making noise. Cycle the ignition key on and off 3 to 4 times to ensure the fuel rail is full and pressurized.
- Check for leaks using a combustible gas detector and sniff the air for any fuel odors.
- Drive the vehicle around the block, listening for any engine cylinders not firing correctly and feeling for any odd vibrations.
- Monitor the dashboard for the fuel level and for any engine light to appear. If the engine light comes on, further diagnosis of the fuel system may be required.
Removing the High-Pressure Fuel Pump in a BMW 760Li
You may want to see also

Fuel pressure regulator function
The fuel pressure regulator is a critical component of any vehicle, as it directly affects the performance and longevity of the engine. Its primary function is to maintain the correct fuel pressure for the injectors, ensuring they receive an adequate amount of fuel to function properly. This is especially important during rapid changes in fuel demand, such as when accelerating or driving uphill.
A fuel pressure regulator typically consists of a diaphragm and a bypass valve. The diaphragm has two sides, one exposed to the pressure from the fuel rail, and the other to the vacuum or boost pressure from the inlet tract. The regulator adjusts the fuel pressure against this air pressure or boost, allowing the fuel injector to maintain the ideal ratio between fuel and boost.
If the fuel pressure is too high, it can cause misfiring and increased emissions. On the other hand, low fuel pressure can result in poor vehicle performance, difficulty starting the engine, and even damage to the injectors. Therefore, the regulator plays a crucial role in ensuring the engine receives the right amount of fuel at the right pressure, optimising performance and fuel efficiency.
In terms of the 2008 LMM Duramax, the fuel injection pressure regulator is located in the centre, towards the front of the engine, on the CP3 injection pump. Replacing this regulator can be a challenging task, requiring the disconnection of various sensors and careful manoeuvring to access the bolts. However, doing so can significantly improve the vehicle's performance, throttle responsiveness, and fuel efficiency.
Checking Fuel Pressure: VW VR6 Guide
You may want to see also

Fuel pressure regulator issues
The fuel pressure regulator in a 2008 LMM Duramax regulates the pressure of the fuel that goes into the injectors. It is located in the fuel rail, which is in the valley, very centre towards the front.
A bad fuel pressure regulator can cause a host of issues, including:
- Engine performance problems: A loss of fuel pressure can cause hard-starting, rough running, stalling, and a lack of power.
- Check engine light: The car's engine computer detects issues that could lead to increased emissions and illuminates the check engine light.
- Black smoke from the tailpipe: A faulty regulator can cause the engine to run rich, resulting in black smoke emissions.
- Fuel in the regulator's vacuum line: A ruptured diaphragm inside the regulator can allow fuel to be drawn into the vacuum line and the engine's intake manifold.
- No-start condition: A faulty regulator may not deliver enough pressure to the fuel injectors, resulting in insufficient fuel and the engine not starting.
Some Duramax owners have reported issues with their fuel pressure regulator, causing problems such as surging at idle, low acceleration power, and rough idling. Replacing the fuel pressure regulator can improve throttle responsiveness and smoothen the idle.
Fuel Pressure Maintenance Tips for 1998 Rangers
You may want to see also

Fuel pressure regulator maintenance
Location and Replacement Process:
The fuel pressure regulator in the 2008 LMM Duramax is located on the CP3 pump, which is situated in the valley, towards the front and center of the engine. Replacing it involves disconnecting various sensors and removing bolts, specifically the last bolt on the bottom of the FPR, which can be challenging to access. Some people choose to rig an Allen key or use a Torx screwdriver and pipe wrench for this bolt. It is also recommended to use a magnet to hold the bit in place and extract the screws.
Symptoms of a Faulty Regulator:
A faulty fuel pressure regulator can cause a range of issues, including:
- Hard starting or no start: The regulator cannot maintain the necessary system pressure for the injectors to spray fuel properly during startup.
- Stalling: Similar to hard-starting issues, the regulator can't maintain sufficient fuel pressure during low-speed operation, leading to stalling after idling for some time.
- Hesitation under acceleration: Improper fuel pressure causes lean fuel conditions, misfires, and interrupted combustion, resulting in hesitation and lack of power.
- Decreased fuel efficiency: Malfunctioning regulators lead to incorrect fuel pressure, causing the engine to run inefficiently and waste fuel.
- Check engine light: Fault codes related to fuel rail pressure sensor range/performance, high or low fuel rail pressure, and fuel delivery errors will be stored, triggering the check engine light.
- Rough idling: The regulator cannot distribute fuel evenly, leading to engine shaking, RPM fluctuations, and occasional sputtering or misfiring.
- Backfiring: Extra fuel enters the exhaust and spontaneously combusts, resulting in loud pops or bangs from the tailpipe.
- Problems starting when hot: The regulator struggles to control escalating fuel pressure as the engine heats up, leading to issues with restarting a heat-soaked engine.
- Accelerating problems: Delayed throttle response, misfiring, surging sensation, and knocking while accelerating are all related to fuel mixture issues caused by unstable fuel pressure.
- Failed emissions test: Faulty regulators can cause excessive polluting, leading to failed emissions tests due to high hydrocarbon, carbon monoxide, or nitric oxide levels.
- Fuel smells: Intermittent fuel odours inside the vehicle or around the fuel rail can indicate leaks from the regulator.
- External fuel leaks: The most severe symptom; fuel leaks from the regulator housing can pose a significant safety hazard and require immediate attention.
Testing and Diagnosis:
To test the fuel pressure regulator, connect a fuel pressure gauge and disconnect the vacuum hose while the engine is running. If the fuel system pressure does not increase by 8-10 psi, the regulator is likely defective and needs replacement. It is also important to check the vacuum hose connection for any signs of fuel, as this indicates a broken diaphragm inside the regulator.
Replacement Cost:
The cost of replacing the fuel pressure regulator includes parts and labour. The regulator assembly itself typically costs between $100 and $300. Labour charges can range from $100 to $300, depending on the complexity of the job. Therefore, the total replacement cost can be expected to fall between $200 and $500 or more.
Maintenance Tips:
While there is no set schedule for replacing the fuel pressure regulator, regular maintenance and prompt attention to any symptoms of a faulty regulator can help prevent major issues and unexpected breakdowns. It is also recommended to replace the hose clamps for the fuel lines and the vacuum hose during regulator replacement. Additionally, checking the vacuum line to the regulator before replacing it is advised, as issues with the fuel pump or fuel filter may be the root cause of the problem.
Locating Fuel Pressure Check Points on the X164
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The fuel injection pressure regulator is located on the CP3/CP4 injection pump.
To install a fuel pressure regulator, you will need to disconnect sensors and remove bolts. You may need to use a Torx screwdriver and a pipe wrench to remove the bolts.
If your truck is experiencing hard starts, injector knocking, or smoking, it may need a new fuel pressure regulator.
Fuel pressure regulators for the LMM Duramax can be purchased from Amazon, eBay, or specialist retailers such as Dirty Hooker Diesel.







