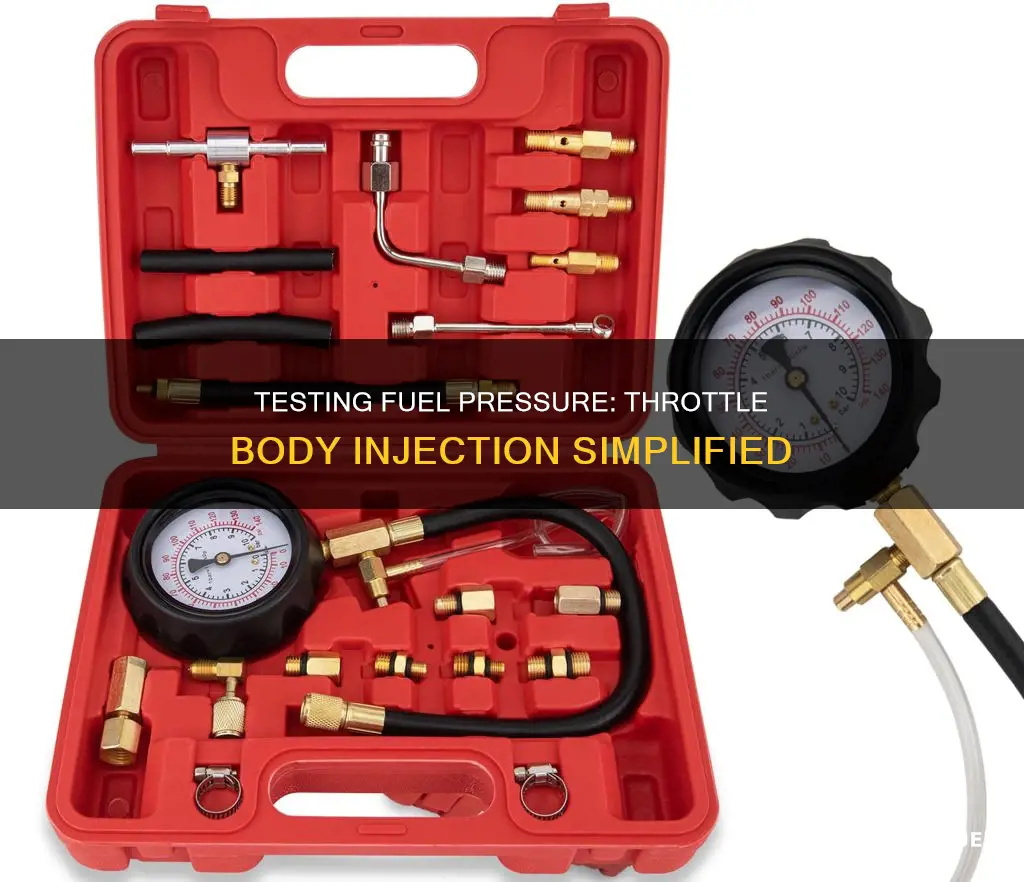
Testing fuel pressure is an essential part of fuel injection system troubleshooting. A fuel pressure tester kit is used to test fuel pressure and consists of a fuel gauge and the fuel hose it is attached to. The process of testing fuel pressure involves searching for the specifications of your vehicle to learn what readings you should expect, opening the hood, attaching the fuel hose to the fuel pump test point, and taking note of the levels indicated on the gauge. The ideal fuel pressure level typically varies depending on the engine, with older throttle-body injected systems needing as little as 10 psi and multi-port injection systems requiring up to 60 psi.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Engine requirements | Air, fuel, spark, and compression |
| Fuel pressure tester | A gauge attached to a fuel hose with multiple fittings |
| Fuel pressure tester cost | $70 to $80 for a basic kit |
| Fuel pressure tester process | Connect the tester to the fuel system, pressurize the system, and read the psi |
| "Good fuel pressure" | Depends on the engine; older throttle-body injected systems need ~10 psi, while multi-port injection can see ~60 psi |
| Zero fuel pressure | Engine won't run |
| Low fuel pressure signs | Slow startup, low performance, misfires, stalling |
| High fuel pressure signs | Excessive fuel consumption, black smoke from unburned gas, overheating catalytic converter, rough idle |
| Fuel pump test | Attach a gauge to the Schrader valve fitting on the fuel injector rail or the fuel supply line |
| Fuel pump test cost | $90 to $150 |
| Fuel pump test process | Connect the gauge to the pressure port on the engine fuel rail or use an adapter from the test kit at the fuel filter or fuel pressure feed line; turn the ignition key to the "on" position and check the psi reading |
| Normal fuel pressure | 30-80 PSI |
| Low fuel pressure causes | Fuel system leaks, failing fuel pump, clogged fuel filters, air in the filter, fuel gelling in low temperatures |
| High fuel pressure causes | Faulty fuel pump driver, malfunctioning fuel pressure regulator, obstructed return lines, malfunctioning fuel rail pressure sensors, bad release valves |
What You'll Learn

How to test fuel pressure with a fuel pressure tester kit
Testing fuel pressure with a fuel pressure tester kit is a straightforward process, but it's important to take safety precautions and understand the potential issues with your vehicle's fuel system. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to test fuel pressure using a fuel pressure tester kit:
- Safety First: Fuel under pressure can be dangerous, so it's crucial to prioritize safety. Wear safety glasses and gloves, and work in a well-ventilated area to avoid inhaling fumes. Ensure there are no sparks or open flames nearby, and have a fire extinguisher readily available.
- Locate the Schrader Valve Fitting: Pop the hood of your vehicle and locate the Schrader valve fitting on the fuel rail. It may be hidden under a fuel rail cover or another plastic engine cover.
- Attach the Fuel Pressure Tester: Remove the Schrader valve cap and attach the appropriate fuel pressure tester fitting from your kit. Ensure it is securely threaded on to prevent leaks.
- Turn the Ignition On: Turn the ignition to the "on" position, but do not start the engine. Check the psi reading on the fuel pressure tester gauge. A stable reading indicates that the system is holding pressure well. If the pressure drops over time, it suggests a leak in the fuel system.
- Check for Leaks: If you suspect a leak, carefully inspect the system for any drips or signs of internal leakage, such as a faulty fuel injector.
- Start the Engine: Start the engine and let it idle. The fuel pressure should remain steady, within a few psi of the recommended pressure for your vehicle. You can find the recommended pressure in your vehicle's repair manual or by consulting a mechanic.
- Engine Revving: Once the engine is warmed up, slowly rev the engine and observe the fuel pressure. The pressure should rise with the increase in RPMs.
- Understanding Fuel Pressure Readings: Depending on your vehicle, the desired fuel pressure can vary. Older throttle-body injected systems may require as little as 10 psi, while multi-port injection systems can reach up to 60 psi. If you're unsure about the optimal fuel pressure for your vehicle, refer to the repair manual or seek advice from a professional.
- Interpreting Results: If your fuel pressure readings are within the specified range and respond appropriately to engine revving, it's unlikely that your engine issues are fuel-related. However, if you consistently observe low or high fuel pressure, it could indicate various issues such as a clogged fuel filter, a failing fuel pump, or problems with the fuel return line or fuel pressure regulator.
Remember to consult a professional mechanic if you're unsure about any aspects of the testing process or if you need assistance interpreting the results.
Troubleshooting Erratic Fuel Pressure Gauge on Sniper EFI
You may want to see also

How to check if your fuel pump is working
The fuel pump is an important component of your car, delivering fuel from the tank to the engine. A malfunctioning fuel pump can cause your car to limp along or not start at all. Here are some detailed and direct instructions on how to check if your fuel pump is working.
Firstly, you need to verify if the problem is fuel-related. If the engine won't start, listen for the fuel pump by putting your ear near the fuel tank and turning the ignition key to the "on" position. If working properly, the fuel pump should make an audible noise. If you cannot hear the pump, try the next test.
The next test involves using a fuel pressure gauge to ensure there is enough fuel reaching the engine. You can either take your vehicle to a technician or purchase a fuel pressure gauge from an auto-parts store and do it yourself. Attach the gauge to the fuel pressure valve near the engine and compare the fuel pressure measurement to the recommended pressure. If there is less pressure than there should be, this is a sign that your fuel pump may be malfunctioning.
If you are still unsure, another test involves starter fluid. This test can be dangerous, so ensure you have the proper safety equipment, such as a fire extinguisher, and safety glasses. Remove the air intake and spray starter fluid into the throttle body while someone else cranks the engine. If the engine starts and runs momentarily, the problem is fuel-related and could be due to a bad pump.
If the engine is running, you can also check the fuel trim with a scan tool. The data parameter, short-term fuel trim (STFT), should be between -10 and 10, although this may vary depending on the vehicle. If the fuel trim is above 10, the engine is running lean, indicating that the fuel pump may not be delivering enough fuel.
Finally, you can perform a static fuel pressure test by connecting a mechanical fuel pressure gauge to the test port on the fuel rail. Turn the ignition to the "on" position and compare the reading to the specification in your repair manual. If the reading is significantly different, you may have a bad fuel pump.
By following these steps, you can effectively diagnose whether your fuel pump is working properly or needs to be replaced.
Fuel Pressure Maintenance for Peterbilt Trucks
You may want to see also

How to test fuel pressure on a running engine
Testing the fuel pressure on a running engine is a straightforward process, but it's important to understand the fuel system components and how they work together. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to test fuel pressure on a running engine with throttle body injection:
- Understand the Fuel System Components: Before testing, familiarize yourself with the fuel system components and their functions. The key components include the fuel pump, fuel pressure regulator, fuel injectors, pressure line, and return line.
- Start the Engine: Begin by starting the engine and letting it run for a few minutes to stabilize.
- Locate the Fuel Pressure Test Port: Identify the fuel pressure test port, which is usually located near the fuel rail or fuel injectors.
- Attach the Fuel Pressure Gauge: Connect a fuel pressure gauge to the test port. Ensure that the gauge is suitable for your vehicle's fuel system and that you have adapted fittings if necessary.
- Read the Fuel Pressure: With the engine running, observe the fuel pressure reading on the gauge. Typical injector pressures range from 13 to 16 psi for a low-pressure system and 35 to 60 psi for a high-pressure system.
- Compare to Specifications: Compare the fuel pressure reading to the manufacturer's specifications for your specific vehicle. This information can be found in the vehicle service manual.
- Diagnose Fuel Pressure Issues: If the fuel pressure reading is higher or lower than the specified range, refer to the vehicle service manual for diagnostic procedures. High fuel pressure can cause the engine to run rich, while low fuel pressure can make the engine run lean or not run at all.
- Inspect Fuel System Components: Depending on the fuel pressure reading, inspect and test the relevant fuel system components for issues. For example, a faulty fuel pressure regulator, restrictions in the return line, or a clogged fuel filter can impact fuel pressure.
- Perform Necessary Repairs: Once you have identified the cause of abnormal fuel pressure, perform the necessary repairs or replacements to restore the fuel system to proper functioning.
- Re-test Fuel Pressure: After making repairs, re-test the fuel pressure to ensure it falls within the manufacturer's specified range.
By following these steps, you can effectively test and diagnose fuel pressure issues on a running engine with throttle body injection. Remember to refer to vehicle-specific information and take appropriate safety precautions when working with fuel systems.
Testing Fuel Injectors: Pressure Diagnostics for Performance and Economy
You may want to see also

What to do if your fuel pressure is too low
If your fuel pressure is too low, the most common symptoms are an unresponsive throttle or a stalling engine. You may also experience difficulty starting your car, a check engine light on the dashboard, misfires, or low performance. Low fuel pressure can cause your car not to start, as the engine requires a lot of fuel during startup.
To address low fuel pressure, you should first identify the cause, which could be one of the following:
- Clogged Fuel Filter: The fuel filter should be replaced regularly, as a clogged filter can restrict fuel flow and lead to low pressure.
- Bad Fuel Pump: A faulty fuel pump is a common cause of low fuel pressure. The pump may slow down or become internally damaged, resulting in insufficient fuel delivery to the engine.
- Bad Fuel Pressure Regulator: Although not a frequent issue, a faulty regulator can create too low or too high fuel pressure in the rail.
- Stuck Fuel Injector: If a fuel injector is damaged and stuck open, it can cause low fuel pressure in the rail, often indicated by misfire codes on a specific cylinder.
- Bad Fuel Pipe Line: Driving on bumpy roads or off-road may result in a damaged fuel pipe, leading to low fuel pressure.
- Fuel Pressure Sensor: In electric fuel pressure regulators, an incorrect reading from the fuel pressure sensor can lead to incorrect fuel pressure regulation.
Once you've identified the cause, you can take the necessary steps to rectify the issue. For example, if the problem is a clogged fuel filter, simply replace it with a new one. If the fuel pump is faulty, you may need to repair or replace it. It is recommended to consult a professional mechanic or refer to a repair manual specific to your vehicle model for detailed instructions on addressing low fuel pressure.
Installing a Fuel Pressure Gauge on a 1995 GMC
You may want to see also

What to do if your fuel pressure is too high
If your fuel pressure is too high, your vehicle’s engine could be overfuelled, leading to symptoms such as your engine running rough, poor fuel economy, and black smoke from the exhaust. Other symptoms include low fuel economy and constant refuelling, poor engine performance, blackened spark plugs, and spark plugs that are wet with fuel. Causes of high fuel pressure include a bad fuel regulator or a clogged return line.
If you suspect that your fuel pressure is too high, the best course of action is to take your vehicle to a trusted mechanic or auto repair shop for service. They will be able to diagnose the cause of the high fuel pressure and resolve the issue. However, if you want to try to diagnose the issue yourself, you can start by checking the fuel pressure with a fuel pressure tester. This can be done by attaching a gauge to the Schrader valve fitting on the fuel injector rail or by teeing the gauge into the fuel supply line if your vehicle lacks a test fitting.
If you determine that your fuel pressure is too high, there are a few things you can try to resolve the issue:
- Check for a clogged or kinked fuel return line.
- Look for a bad fuel pump driver module or powertrain control module. These issues will likely trigger a "check engine" light and store a code.
- Inspect the fuel pressure regulator. A faulty fuel pressure regulator can cause high fuel pressure.
- Verify that the fuel pump is working properly. A weak pump may generate enough pressure to read normally at idle but may not keep up with the engine's fuel requirements at higher speeds.
It is important to note that fuel vapors are highly flammable, so it is crucial to perform any repairs or maintenance in a well-ventilated area and have a fire extinguisher nearby.
Rebuilding Yanmar 2QM15 Fuel Pump: Step-by-Step Guide
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The ideal fuel pressure level varies from model to model. Older throttle-body injected systems may only need 10 PSI, while multi-port injection systems may need 60 PSI. Check your vehicle owner's manual for the recommended fuel pressure level.
You will need a fuel pressure test kit, which consists of a gauge designed to read fuel pressure and a fuel hose. First, ensure your tank has at least two gallons of fuel. Then, open the hood and remove the cap from the fuel pump test point, usually beside the fuel injectors. Attach the fuel hose to the test point and bleed the fuel pressure gauge to remove any air. Start the engine and read the fuel pressure level.
Fuel pressure issues occur when pressure levels are either too low or too high. High fuel pressure could be caused by a faulty fuel pressure regulator, obstructed return lines, or malfunctioning fuel rail pressure sensors. Low fuel pressure could be caused by fuel system leaks, a failing fuel pump, clogged fuel filters, or fuel gelling in low temperatures.







