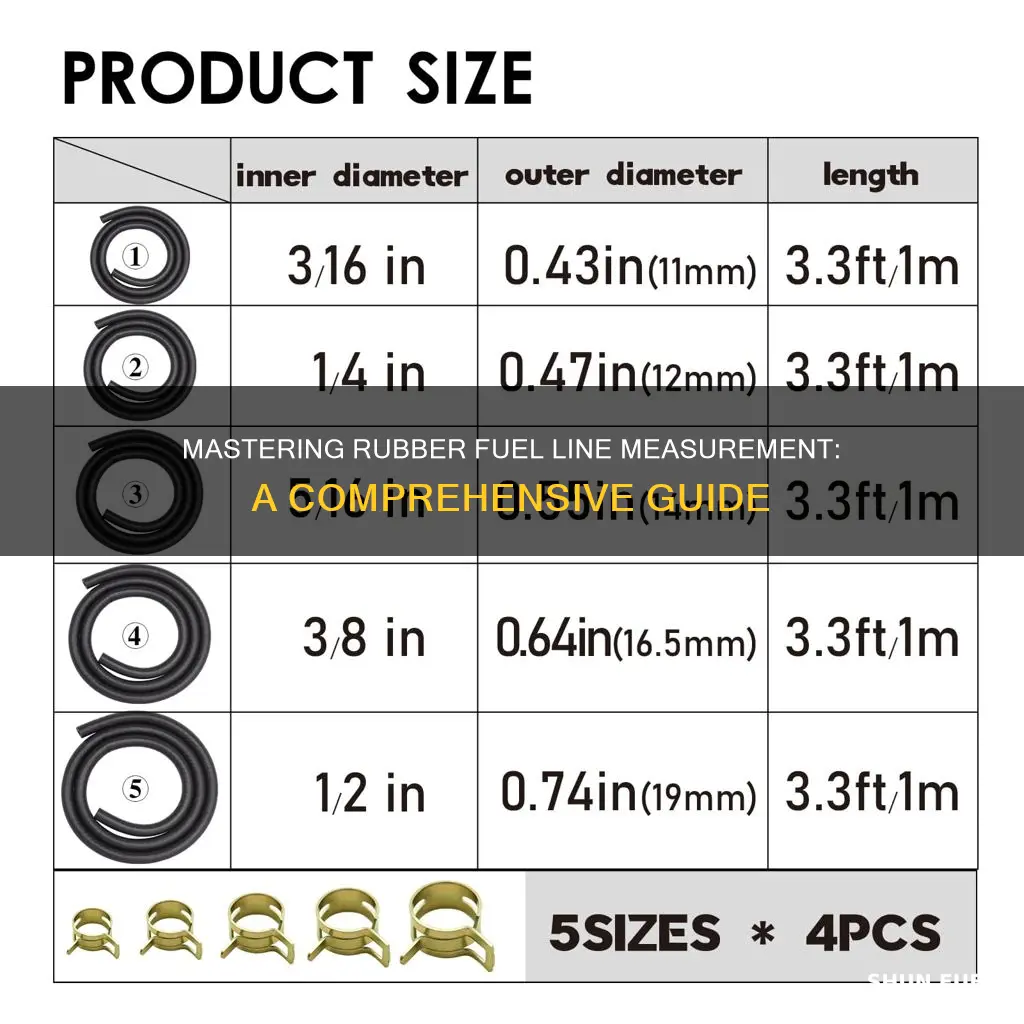
Measuring the rubber fuel line is an important step in ensuring the proper installation and functionality of a vehicle's fuel system. This process involves assessing the length and diameter of the fuel line to ensure it meets the required specifications. By accurately measuring the fuel line, you can ensure a secure fit, prevent fuel leaks, and maintain the overall performance and safety of the vehicle's fuel system. This guide will provide a step-by-step process to measure the rubber fuel line effectively.
What You'll Learn
- Length Measurement: Use a tape measure to determine the length of the rubber fuel line
- Diameter Inspection: Measure the diameter using a caliper for accurate fuel line thickness
- Flexibility Testing: Assess flexibility by bending the line to its limits
- Pressure Resistance: Test the line's ability to withstand fuel pressure without leakage
- Material Composition: Analyze the rubber composition to ensure it meets fuel line standards

Length Measurement: Use a tape measure to determine the length of the rubber fuel line
To measure the length of a rubber fuel line, you can use a simple and effective method with a tape measure. This is a straightforward process that ensures you get accurate dimensions for your fuel line. Here's a step-by-step guide:
First, ensure that the fuel line is straight and not coiled or bent. This is important to get an accurate measurement. Place the tape measure along the length of the fuel line, starting from one end and extending to the other. Make sure the tape measure is taut and in contact with the fuel line to avoid any slack. Read the measurement at the point where the tape measure meets the fuel line. This reading will give you the length of the fuel line. It's a good practice to take multiple measurements at different points to ensure accuracy, especially if the fuel line has any bends or curves.
When using a tape measure, pay attention to the markings and ensure you are measuring in the correct unit (e.g., inches or centimeters). For more precise measurements, consider using a flexible tape measure that can conform to the shape of the fuel line. This will allow you to get a more accurate reading, especially if the fuel line is curved or has a complex shape.
Additionally, if the fuel line is part of a larger assembly or system, you might need to measure it in relation to other components. In such cases, measure the length from a specific reference point, such as a mounting bracket or a connection, to ensure the measurement is relevant to the overall setup.
Remember, accurate measurements are crucial when working with fuel lines, as they ensure proper installation and compatibility. By using a tape measure, you can easily determine the length of the rubber fuel line, which is essential for various automotive or industrial applications. This simple technique allows for precise measurements, contributing to a successful and safe project.
Nylon Fuel Line: Safe Usage Guide for Your Vehicle
You may want to see also

Diameter Inspection: Measure the diameter using a caliper for accurate fuel line thickness
To ensure the proper functioning of your vehicle's fuel system, it is crucial to inspect the rubber fuel line for any signs of wear and tear. One essential aspect of this inspection is measuring the diameter of the fuel line to verify its thickness and integrity. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to perform this task accurately:
Gather the Tools: Before you begin, ensure you have the necessary tools for the job. You will need a caliper, which is a precision measuring device used to determine the diameter or thickness of an object. Calipers come in various types, but for this task, a digital caliper or a vernier caliper will be sufficient. Make sure it has a range that covers the expected diameter of your fuel line.
Prepare the Fuel Line: Locate the rubber fuel line that you want to inspect. It is typically found under the vehicle, running from the fuel tank to the engine. Ensure the line is accessible and secure, as you may need to temporarily support it to get accurate measurements.
Position the Caliper: Place the caliper's jaws onto the fuel line, ensuring they make contact with the outer surface of the rubber material. The jaws should be positioned at a point where the fuel line's diameter is consistent and free from any bends or kinks that might affect the measurement. For best results, measure at least three different points along the length of the fuel line to get an accurate average.
Take the Measurement: Once the caliper is positioned correctly, activate the measuring function. Read the displayed value, which represents the diameter of the fuel line. Take note of this measurement and compare it to the manufacturer's specifications or the original dimensions of the fuel line. A significant deviation from the expected thickness could indicate potential issues.
Record and Analyze: Record the measured diameter and make a note of any discrepancies or changes compared to previous measurements. If you find any abnormalities, further investigation may be required. This inspection is vital as it helps identify potential fuel leaks, reduced performance, or even safety hazards associated with worn-out fuel lines. Regularly checking the diameter ensures that your vehicle's fuel system remains reliable and efficient.
Fuel Line Sizing for Older Mercury Outboards: A Guide
You may want to see also

Flexibility Testing: Assess flexibility by bending the line to its limits
Flexibility testing is a critical aspect of evaluating the performance and durability of rubber fuel lines. This test method focuses on assessing the material's ability to bend and flex without permanent deformation, ensuring it can withstand the various movements and vibrations encountered during vehicle operation. Here's a detailed guide on how to perform flexibility testing:
Test Setup: Begin by securing the fuel line to a sturdy frame or fixture that can mimic the real-world conditions it will experience. This setup should allow for controlled bending and movement. Ensure the line is taut and free of any kinks or twists that might interfere with the test results.
Bending Procedure: Gradually apply force to the fuel line by bending it at different angles and radii. Start with gentle bends and increase the force gradually. The goal is to push the material to its limits without causing any permanent bends or kinks. Observe the line's behavior during this process. Note any points of stress, cracks, or signs of material failure.
Flexibility Assessment: As you bend the line, pay close attention to its flexibility and resilience. A flexible fuel line should be able to return to its original shape without any permanent set. Record the angles and forces required to achieve certain levels of bending. Compare these results with the manufacturer's specifications or industry standards to determine if the material meets the required flexibility criteria.
Repeat Testing: Perform multiple flexibility tests at various points along the fuel line to ensure comprehensive coverage. This is especially important for lines with complex shapes or those that are subject to different bending stresses in different areas. By repeating the test, you can identify any consistent failure points or areas of weakness.
Analysis and Reporting: After the testing, analyze the data collected. Look for patterns in the material's behavior, such as specific angles or forces that cause issues. Document any defects or failures observed during the test. This information is crucial for designing robust fuel lines and ensuring they meet the necessary performance standards. Flexibility testing is an essential quality control measure, especially in the automotive industry, where fuel lines must withstand the rigors of daily use.
Fuel Line Disconnect: A Step-by-Step Guide for 2007 Cobalt Owners
You may want to see also

Pressure Resistance: Test the line's ability to withstand fuel pressure without leakage
To test the pressure resistance of a rubber fuel line, you can follow these detailed steps:
- Prepare the Test Setup: Begin by acquiring a pressure gauge capable of measuring the specific fuel pressure you intend to apply. Ensure the gauge is calibrated and functioning accurately. Additionally, you'll need a controlled environment, such as a laboratory or a dedicated test chamber, to conduct the experiment.
- Mount the Fuel Line: Securely attach the fuel line to the test setup, ensuring it is properly clamped or secured to prevent any movement during the test. The line should be positioned in a way that simulates its typical installation in a vehicle or engine.
- Apply Fuel Pressure: Gradually increase the fuel pressure through the gauge until it reaches the desired level. This pressure should be representative of the fuel pressure encountered in a real-world application. Monitor the gauge to ensure a steady and controlled increase in pressure.
- Monitor for Leaks: With the fuel line under pressure, closely observe for any signs of leakage. Inspect the line for visible wet spots or drips, especially at connections and bends. Pay attention to the material's integrity, checking for any cracks, tears, or bulging areas that could indicate potential failure points.
- Record Results: Document the pressure value at which any leaks are observed. Record the time it takes for the leak to occur, as well as the specific location of the leak. This data will be crucial for analyzing the fuel line's performance and identifying areas for improvement.
- Repeat and Analyze: Conduct multiple tests at different pressure levels to ensure a comprehensive assessment. By comparing the results, you can determine the fuel line's pressure resistance capacity and identify any patterns or trends in its performance. This iterative process will provide valuable insights into the material's suitability for various fuel pressure applications.
Remember, this test is essential for ensuring the safety and reliability of fuel lines in automotive or industrial settings, where fuel pressure can vary significantly. By following these steps, you can accurately evaluate the pressure resistance of rubber fuel lines and make informed decisions regarding their use.
The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Right Size Clamp for Your 1/4" Fuel Line
You may want to see also

Material Composition: Analyze the rubber composition to ensure it meets fuel line standards
When it comes to ensuring the quality and performance of rubber fuel lines, analyzing the material composition is a critical step. This process involves a detailed examination of the rubber to verify that it adheres to the necessary standards and specifications for fuel line applications. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to approach this analysis:
Sample Collection: Begin by collecting a representative sample of the rubber fuel line material. It is essential to have a physical sample to perform the necessary tests and inspections. Ensure that the sample is taken from a location that is free from any contaminants or damage, as this could affect the accuracy of the analysis.
Rubber Composition Analysis: The next step is to analyze the chemical composition of the rubber. This can be done through various laboratory techniques. One common method is spectroscopy, where infrared (IR) or Raman spectroscopy is employed to identify the types of rubber compounds present. Look for the presence of specific additives and fillers, such as carbon black, which are commonly used to enhance the mechanical properties of fuel lines. The analysis should also include testing for the content of elastomers like natural rubber, synthetic rubbers (e.g., neoprene, EPDM), and reinforcing agents.
Standard Compliance: Compare the results of your analysis with industry standards and specifications for fuel line rubber. These standards often include guidelines on the acceptable ranges for various additives, fillers, and elastomer types. For instance, the rubber should have sufficient elasticity to withstand fuel expansion and contraction without cracking. It should also be resistant to fuel degradation, ensuring it doesn't absorb or release harmful substances over time. Common standards to refer to include ASTM D1418 (for rubber fuel hose) and ISO 1707 (for fuel hose materials).
Physical Property Testing: In addition to chemical analysis, perform physical property tests on the rubber sample. This includes evaluating its durometer (a measure of hardness), tensile strength, elongation, and tear resistance. These properties are crucial for ensuring the rubber can withstand the mechanical stresses of fuel line applications, such as vibrations and pressure fluctuations.
Quality Assurance: By thoroughly analyzing the material composition and comparing it to the required standards, you can ensure that the rubber fuel line meets the necessary performance criteria. This process is vital for maintaining the integrity of the fuel system, preventing leaks, and ensuring the safety and efficiency of the vehicle's fuel delivery system.
Bleed Air from Fuel Line: A Guide for 2000 Chevy Tahoe Owners
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Measuring a rubber fuel line involves determining its inner diameter and length. Start by using a caliper to measure the diameter at multiple points along the line to ensure accuracy. Take measurements at different sections to account for any variations in thickness. Then, measure the overall length of the line by laying it flat and using a tape measure.
Accuracy is crucial when measuring fuel lines. Use a micrometer for precise measurements, especially if the line has a small diameter. Take multiple readings at different points to get an average, ensuring you capture any potential variations in thickness. Calipers can also be used for larger lines, but a micrometer provides even greater precision.
Measuring coiled or bent fuel lines can be challenging. In such cases, it's best to measure the straightened length. Carefully lay the line flat on a clean surface, ensuring it's straight and taut. Use a flexible measuring tape or a ruler to measure the length accurately. Avoid stretching the line, as it may affect the measurement.
Rubber fuel lines often have some flexibility, which can make measurements tricky. In this case, measure the line while it's in a relaxed state. Avoid stretching or pulling the line, as it may provide an inaccurate representation of its true length. Measure at room temperature to account for any temperature-related expansion or contraction.
While measurements provide size and length, they don't directly indicate wear. However, you can assess the condition by examining the line for any cracks, tears, or signs of deterioration. Compare the measurements with the manufacturer's specifications to ensure it falls within the acceptable range. Regular visual inspections and measurements can help identify potential issues with the fuel line's integrity.







