The cost of fuel is a significant factor in the overall expense of owning and operating a vehicle. When considering alternative fuel sources for cars, it's essential to understand the financial implications. For instance, if a car were to run on a specific fuel, such as hydrogen or biofuel, the cost of this fuel would vary depending on its availability, production methods, and market demand. This introduction sets the stage for exploring the financial aspects of different fuel options for vehicles.
What You'll Learn
- Biofuels: Ethanol and Biodiesel as alternatives to gasoline and diesel
- Electricity: Battery-powered cars and the cost of charging
- Hydrogen: Fuel cell vehicles and the infrastructure for hydrogen refueling
- Solar Power: Photovoltaic systems for electric vehicles
- Wind Energy: Wind-to-hydrogen or wind-to-electricity conversion for transportation

Biofuels: Ethanol and Biodiesel as alternatives to gasoline and diesel
Biofuels, such as ethanol and biodiesel, have gained significant attention as potential alternatives to traditional fossil fuels like gasoline and diesel. These renewable energy sources offer a more sustainable and environmentally friendly approach to powering vehicles, which could have a substantial impact on fuel costs and the overall economy.
Ethanol, a biofuel derived from plant materials or agricultural waste, is a common alternative to gasoline. When used in vehicles, ethanol can be blended with gasoline in various proportions, typically up to 10% ethanol (E10) or higher. This blend, known as ethanol gasoline (E85), provides a cleaner-burning fuel option. The cost of ethanol is generally lower than that of gasoline, making it an attractive choice for cost-conscious consumers. However, it's important to note that ethanol's energy content is slightly lower than that of gasoline, which means vehicles may require slightly more fuel to travel the same distance. Despite this, the reduced cost per gallon can offset the higher fuel consumption, making ethanol a competitive alternative.
Biodiesel, on the other hand, is produced from vegetable oils, animal fats, or recycled cooking oil. It is a cleaner-burning fuel compared to diesel, emitting fewer harmful pollutants. Biodiesel can be used in its pure form (B100) or blended with conventional diesel. The cost of biodiesel production varies depending on the feedstock and production methods, but it often competes favorably with diesel prices. Biodiesel engines may require some modifications to run efficiently, but the fuel's higher cetane number can improve engine performance and reduce maintenance costs.
The switch to biofuels could have a significant impact on fuel prices. As biofuels are renewable and often locally produced, they can reduce the reliance on imported oil, which is subject to global market fluctuations. This shift could potentially stabilize fuel costs and provide a more predictable pricing structure for consumers. Additionally, the use of biofuels can contribute to a more sustainable energy economy, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting environmental conservation.
However, there are challenges and considerations associated with the widespread adoption of biofuels. The production of biofuels requires substantial land and resources, which could compete with food production and contribute to land-use changes. Additionally, the infrastructure for distributing and storing biofuels may need significant investment to support their integration into the existing fuel supply chain. Despite these challenges, the potential benefits of reduced environmental impact and more stable fuel costs make biofuels a promising area of research and development.
The Key to Car Theft: How Keys Fuel a Wave of Auto Crime
You may want to see also

Electricity: Battery-powered cars and the cost of charging
The transition to electric vehicles (EVs) is gaining momentum, and understanding the cost of charging these battery-powered cars is essential for potential buyers and policymakers alike. The cost of electricity for charging EVs can vary significantly depending on several factors, including the region, time of day, and the type of charging infrastructure used.
When considering the cost of charging an EV, it's important to note that the price per kilowatt-hour (kWh) of electricity is a critical factor. The cost of electricity can range from a few cents to over a dollar per kWh, depending on the market and local regulations. For example, in some countries, off-peak electricity rates might be much lower, making it more economical to charge during these times. On-peak rates, often used for air conditioning and heating, can be significantly higher, impacting the overall charging cost.
The efficiency of the EV's battery and its capacity also play a role in charging costs. Larger batteries with higher capacities will require more energy to charge, increasing the cost. Modern EVs often come with advanced battery management systems that optimize charging, ensuring the battery operates at its most efficient level. These systems can adjust charging rates based on the battery's state of charge, temperature, and other factors, further optimizing energy usage and cost.
Home charging infrastructure is another aspect that influences the cost of charging EVs. Installing a home charging station can provide convenience and potentially lower rates compared to public charging stations. Many governments and utility companies offer incentives and subsidies to encourage the adoption of home charging, making it an attractive option for EV owners. Public charging stations, while convenient, often have higher operational costs and may charge per session or per minute, depending on the location and provider.
Understanding the cost of electricity for charging EVs is crucial for making informed decisions about vehicle ownership and energy consumption. As the EV market grows, the focus on optimizing charging infrastructure and rates will become increasingly important to ensure a sustainable and cost-effective future for electric mobility. With the right incentives and efficient charging practices, the cost of charging an EV can be managed effectively, making it a viable and attractive alternative to traditional fuel-based transportation.
Funny Cars vs. Top Fuel Dragsters: Who's Faster?
You may want to see also

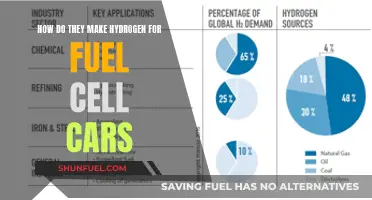
Hydrogen: Fuel cell vehicles and the infrastructure for hydrogen refueling
Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles are an exciting and rapidly evolving technology that offers a promising alternative to traditional internal combustion engine cars. These vehicles operate on a simple principle: they combine hydrogen gas with oxygen from the air to produce electricity, which then powers the car's electric motor. This process is clean and efficient, emitting only water vapor and warm air, making it an environmentally friendly option.
The concept of using hydrogen as a fuel source is not new, but the recent advancements in fuel cell technology have made it a viable and attractive option for the automotive industry. Fuel cell vehicles have the potential to revolutionize the way we power our cars, offering a sustainable and cost-effective solution. One of the most significant advantages of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles is their zero-emission nature. Unlike conventional vehicles, they do not produce harmful pollutants or greenhouse gases, making them a key player in the fight against climate change.
However, the widespread adoption of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles faces several challenges, particularly regarding the infrastructure for refueling. Hydrogen refueling stations are essential to support the growing number of fuel cell vehicles on the road. These stations need to be strategically located to ensure convenience and accessibility for drivers. The process of refueling hydrogen vehicles is relatively quick, often taking just a few minutes, which is comparable to the time required for conventional fuel refills. Despite the rapid refueling process, the cost of hydrogen fuel is a critical factor in the overall economics of fuel cell vehicles.
The cost of hydrogen fuel is influenced by various factors, including production methods, distribution, and storage. Currently, the majority of hydrogen is produced through a process called steam methane reforming, which is energy-intensive and results in significant carbon emissions. However, there is a growing focus on developing alternative production methods, such as electrolysis using renewable energy sources, which could significantly reduce the environmental impact and cost of hydrogen production. As the technology advances and production methods become more efficient, the cost of hydrogen fuel is expected to decrease, making it more competitive with conventional fuels.
In addition to the production and distribution costs, the infrastructure for storing and transporting hydrogen also plays a role in determining fuel costs. Hydrogen has unique properties that require specialized storage tanks and pipelines to ensure safe handling. The development of robust and cost-effective storage solutions is crucial for the widespread adoption of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles. Despite the initial challenges, the potential benefits of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles are driving significant investments in research and development. Governments and private entities are collaborating to establish hydrogen refueling networks, ensuring that the necessary infrastructure is in place to support the transition to cleaner transportation options.
Are Fuel-Efficient Cars Worth the Investment? Unlocking Long-Term Savings
You may want to see also

Solar Power: Photovoltaic systems for electric vehicles
The concept of solar-powered electric vehicles is an innovative approach to reducing our reliance on fossil fuels and combating climate change. Photovoltaic (PV) systems, also known as solar panels, are a key component in this technology. These systems harness the sun's energy and convert it into electricity, which can then power an electric vehicle (EV). By integrating solar power into EVs, we can significantly reduce the overall fuel costs and environmental impact of transportation.
Photovoltaic systems for electric vehicles typically consist of solar panels mounted on the vehicle's roof or hood, capturing sunlight and generating direct current (DC) electricity. This electricity is then converted into alternating current (AC) by an inverter, which can power the vehicle's electric motor. The efficiency of these systems has improved significantly over the years, allowing for longer driving ranges and reduced reliance on traditional fuel sources.
One of the primary advantages of using solar power for EVs is the potential for substantial cost savings. While the initial investment in solar panels and installation can be high, the long-term benefits are considerable. Solar energy is virtually free once the system is installed, and the electricity generated can power the vehicle, eliminating or significantly reducing fuel costs. This is especially beneficial for those who drive shorter distances or have access to ample sunlight, as the vehicle can generate its own power.
The integration of solar power with electric vehicles also contributes to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly transportation system. By reducing the demand for gasoline or diesel, solar-powered EVs help decrease greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution. This is particularly important in urban areas where traffic congestion and pollution levels are high. Additionally, the use of renewable energy sources like solar power can help diversify the energy mix and reduce the dependence on finite fossil fuel resources.
In conclusion, solar power, in the form of photovoltaic systems, offers a promising solution for reducing fuel costs and environmental impact in the transportation sector. With advancements in technology, electric vehicles equipped with solar panels can provide an efficient and sustainable mode of travel. As the world seeks to transition towards cleaner energy sources, the adoption of solar-powered EVs will play a crucial role in shaping a more environmentally conscious future.
88 Octane Fuel: Is It Safe for Your Car?
You may want to see also

Wind Energy: Wind-to-hydrogen or wind-to-electricity conversion for transportation
Wind energy has emerged as a promising alternative to traditional fossil fuels, offering a clean and renewable power source for various applications, including transportation. The concept of using wind power to fuel vehicles is an innovative approach to reducing our reliance on gasoline and diesel, which are major contributors to environmental pollution and climate change. This exploration delves into the potential of wind-to-hydrogen and wind-to-electricity conversion technologies for powering vehicles, examining their feasibility, benefits, and challenges.
One of the primary methods to utilize wind energy for transportation is through the conversion of wind power into hydrogen. This process involves using wind turbines to generate electricity, which is then employed to split water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen through electrolysis. The produced hydrogen can be stored and utilized as a fuel for vehicles, offering a means to power cars, trucks, and other transportation modes. Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles have already been developed and are being tested, demonstrating the potential for zero-emission transportation. The efficiency of this process is a critical factor in determining its viability. While wind-to-hydrogen systems can achieve efficiencies of around 60%, the overall energy efficiency of the entire process, including transportation, is still a subject of research and optimization.
Another approach is to convert wind energy directly into electricity, which can then be used to power electric vehicles (EVs). Wind turbines generate electricity, which is fed into the grid or stored in batteries. EVs can be charged using this electricity, eliminating the need for gasoline or diesel. This method has the advantage of a well-established infrastructure for electricity distribution and charging stations. The cost of electricity from wind power has been steadily decreasing, making it an economically viable option for EV charging. However, the intermittent nature of wind power requires careful management and storage solutions to ensure a consistent power supply for transportation.
The integration of wind energy into transportation systems presents several advantages. Firstly, it significantly reduces greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to a cleaner and more sustainable environment. Wind power is a renewable resource, meaning it will not deplete over time, unlike finite fossil fuels. This sustainability aspect is crucial for long-term energy planning. Additionally, wind energy can help diversify the energy mix, reducing the dependence on a single fuel source and enhancing energy security.
However, there are challenges to be addressed. The initial investment in wind infrastructure and conversion technologies can be substantial, requiring significant capital expenditure. The intermittent nature of wind power also poses a technical challenge, as it requires efficient energy storage solutions to ensure a stable power supply for transportation. Furthermore, the development of hydrogen infrastructure and the establishment of a comprehensive hydrogen fuel distribution network are necessary for the widespread adoption of wind-to-hydrogen vehicles.
In conclusion, wind energy offers a viable pathway towards a more sustainable transportation sector. The wind-to-hydrogen and wind-to-electricity conversion methods present opportunities to reduce fuel costs and environmental impact. While challenges exist, ongoing research and technological advancements are paving the way for a greener future, where wind power plays a pivotal role in powering our vehicles. As the world seeks to transition towards cleaner energy sources, these innovative approaches to wind energy utilization will be instrumental in shaping a more environmentally conscious transportation system.
Car Fuel Filter: Uncovering the Inner Workings
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The cost of charging an electric vehicle (EV) depends on various factors, including the car's battery capacity, the charging speed, and the local electricity rates. On average, charging an EV can range from $0.05 to $0.20 per kWh. For example, if your EV has a 100 kWh battery and the electricity rate is $0.15 per kWh, it would cost approximately $15 to fully charge the battery.
Hybrid vehicles use a combination of a traditional internal combustion engine and an electric motor, often resulting in lower fuel consumption and reduced fuel costs. The exact cost depends on the specific hybrid model and its efficiency. On average, hybrids can offer fuel savings of 20-50% compared to similar conventional cars, translating to fuel costs that are 20-50% lower.
Biofuel costs can vary depending on the type of biofuel and its availability. Biodiesel, for instance, is often priced similarly to conventional diesel, while ethanol blends might be slightly cheaper. The price can range from $2 to $4 per gallon, depending on the region and market demand.
Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles have the potential to offer very low fuel costs. Hydrogen fuel is typically priced at around $4-6 per kilogram, and the energy content is comparable to gasoline. The cost of refueling a hydrogen car is often lower than filling a conventional vehicle, especially with the potential for on-board refueling stations.
Natural gas vehicles (NGVs) generally have lower fuel costs compared to gasoline-powered cars. CNG is often priced at a discount to gasoline, with prices ranging from $2 to $4 per gallon of gasoline equivalent. This can result in significant savings for drivers, especially for vehicles with high mileage.