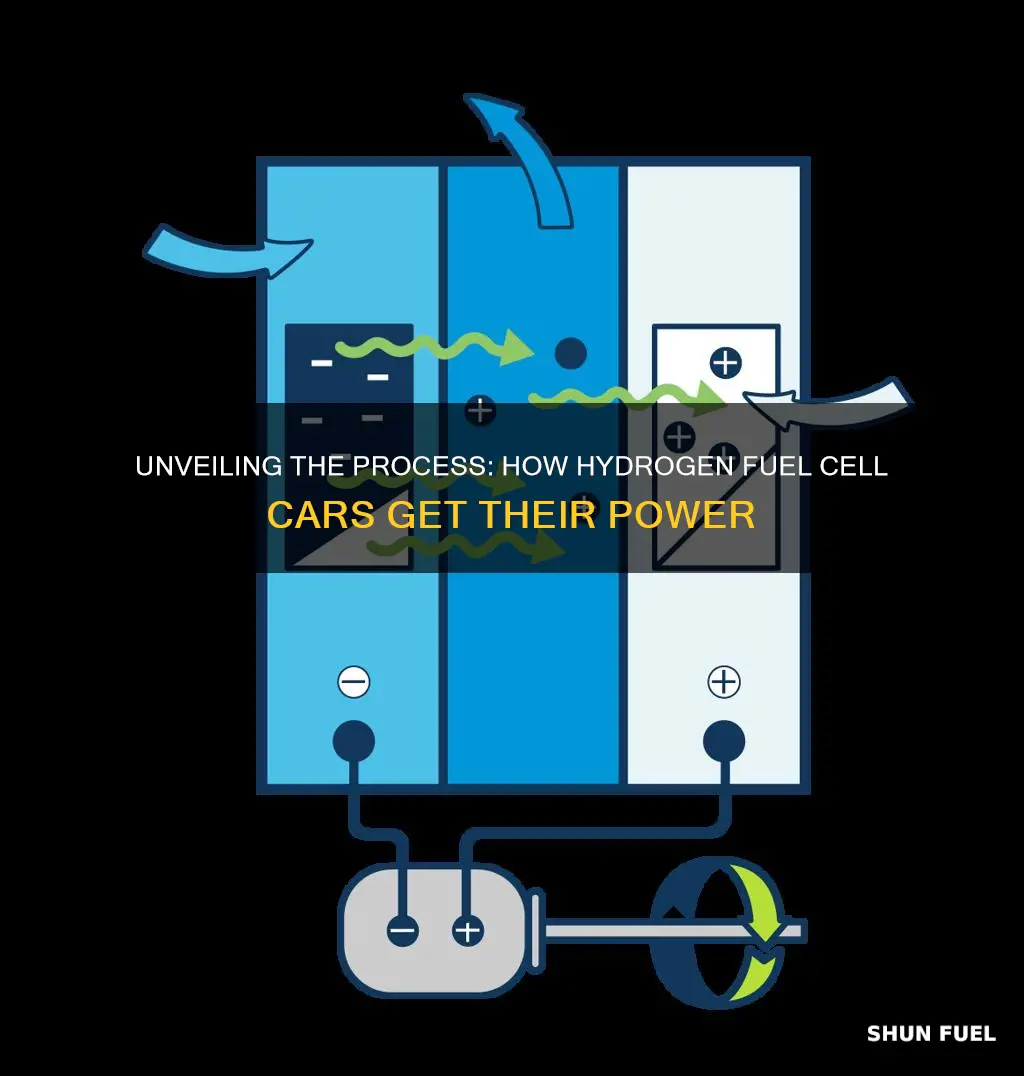
The production of hydrogen for fuel cell cars is a crucial aspect of the automotive industry's shift towards sustainable energy. Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles offer a promising alternative to traditional internal combustion engines, as they produce electricity through a chemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen, emitting only water vapor and warm air. The process begins with the extraction of hydrogen from various sources, such as natural gas, biomass, or water electrolysis. Natural gas reforming is a common method, where methane is reacted with steam to produce hydrogen and carbon monoxide. Alternatively, water electrolysis splits water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen, providing a clean and renewable source of hydrogen. These methods are essential in the development of hydrogen infrastructure to support the widespread adoption of fuel cell cars and contribute to a greener transportation future.
What You'll Learn
- Electrolysis: Water electrolysis splits hydrogen from oxygen, a common method for fuel cell car hydrogen production
- Steam Methane Reforming: Natural gas reacts with steam to produce hydrogen and carbon dioxide
- Biomass Gasification: Organic matter is heated to produce a gas mixture containing hydrogen
- Photoelectrochemical Cells: Solar energy directly splits water into hydrogen and oxygen
- Biological Processes: Certain bacteria can generate hydrogen through fermentation or photosynthesis

Electrolysis: Water electrolysis splits hydrogen from oxygen, a common method for fuel cell car hydrogen production
Water electrolysis is a well-established and widely used process for producing hydrogen, and it is a key method for generating the fuel required by fuel cell cars. This process involves the decomposition of water (H2O) into its constituent elements, hydrogen (H2) and oxygen (O2), through an electrochemical reaction. The basic principle is to pass an electric current through water, which then splits the water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen gases.
The electrolysis process typically occurs within an electrolyzer, a device specifically designed for this purpose. The electrolyzer contains an anode and a cathode, separated by an electrolyte, which can be either an acidic or alkaline solution. When an electric current is applied, water molecules at the anode lose electrons and undergo oxidation, forming oxygen gas and positively charged ions. Simultaneously, at the cathode, water molecules gain electrons and are reduced, producing hydrogen gas.
The reaction can be represented by the following half-reactions:
Anode (Oxidation): 2H2O → O2 + 4H+ + 4e-
Cathode (Reduction): 2H+ + 2e- → H2
By combining these half-reactions, the overall reaction shows that water is split into hydrogen and oxygen gases, with electrons flowing through the external circuit as the current. This method of hydrogen production is highly efficient and can be scaled up to meet the demands of fuel cell car manufacturing.
Electrolysis offers several advantages for hydrogen production. Firstly, it is a clean and renewable process, as it utilizes water and electricity, both of which can be sourced from sustainable means. Secondly, the technology is mature and widely available, making it a practical choice for large-scale hydrogen production. Additionally, the process can be optimized to produce high-purity hydrogen, which is essential for fuel cell performance.
In the context of fuel cell cars, water electrolysis provides a sustainable and efficient way to generate the hydrogen fuel required for their operation. The produced hydrogen can then be stored and used in fuel cells to generate electricity, powering the vehicle's electric motor. This technology plays a crucial role in the development of hydrogen-based transportation, offering a promising alternative to conventional internal combustion engines.
Fuel Pump's Role in Lean Code: Unlocking Engine Potential
You may want to see also

Steam Methane Reforming: Natural gas reacts with steam to produce hydrogen and carbon dioxide
Steam methane reforming is a widely used process in the production of hydrogen, particularly for fuel cell cars. This method involves the reaction of natural gas with steam at high temperatures, typically around 700-1100°C (1,292-2,012°F). The process is carried out in a reformer, which is a specialized piece of equipment designed to facilitate this chemical reaction.
In the reformer, natural gas, primarily composed of methane, is mixed with steam (water vapor). The steam provides the necessary hydrogen atoms to react with methane. The reaction can be represented by the following equation:
CH₄ + H₂O → CO₂ + H₂
Here, methane (CH₄) reacts with steam (H₂O) to produce carbon dioxide (CO₂) and hydrogen gas (H₂). This reaction is highly exothermic, meaning it releases a significant amount of heat, which is why the process requires precise temperature control. The high temperature ensures that the reaction proceeds rapidly and efficiently.
The steam methane reforming process is efficient in producing hydrogen because it allows for the complete combustion of methane. This method is often used in conjunction with other processes, such as partial oxidation or autothermal reforming, to optimize hydrogen yield and minimize byproducts. The produced hydrogen is then typically cooled and compressed to the required conditions for fuel cell operation.
This process is a cornerstone of hydrogen production for fuel cell vehicles, ensuring a steady supply of hydrogen gas, a clean and efficient energy source for transportation. It is a well-established technology, and its scalability makes it a viable option for large-scale hydrogen production, contributing to the development of sustainable and environmentally friendly transportation solutions.
Unveiling the Fuel Injection Mystery: Do Cars Need Them?
You may want to see also

Biomass Gasification: Organic matter is heated to produce a gas mixture containing hydrogen
The process of biomass gasification is an intriguing and sustainable method to produce hydrogen, a key component in fuel cell cars. This technique involves the thermal decomposition of organic matter, such as agricultural residues, wood chips, or even certain types of waste, to generate a valuable gas mixture. The process begins with the careful selection and preparation of the feedstock, ensuring it is free from contaminants that could hinder the efficiency of the gasification process.
Once the organic matter is ready, it is fed into a gasifier, a specialized reactor designed to facilitate the gasification reaction. The reactor is typically heated to extremely high temperatures, often ranging from 700°C to 1100°C (1,292°F to 1,992°F). At these elevated temperatures, the organic material undergoes thermal decomposition, breaking down into a synthesis gas or syngas. This syngas is a mixture of carbon monoxide (CO), carbon dioxide (CO2), hydrogen (H2), and other trace gases. The beauty of this process lies in the fact that hydrogen, a clean-burning fuel, is a significant component of the syngas.
The gasification process can be carried out in different ways, including pyrolytic, thermal, and chemical gasification. Pyrolytic gasification involves heating the organic matter in the absence of oxygen, leading to the formation of a char or solid residue. This char can then be further processed to extract additional hydrogen. Thermal gasification, on the other hand, uses controlled combustion to produce syngas. Chemical gasification employs catalysts to facilitate the breakdown of organic matter into simpler gases.
One of the advantages of biomass gasification is its ability to utilize a wide range of organic materials. This makes it an attractive option for regions with abundant agricultural or forest waste. By converting these waste streams into valuable hydrogen, the process not only contributes to a more sustainable energy economy but also helps in waste management and resource conservation. The produced hydrogen can then be used directly in fuel cell cars, providing a clean and renewable energy source for transportation.
In summary, biomass gasification is a promising technology for hydrogen production, offering a sustainable and efficient way to generate the fuel required for fuel cell cars. This process showcases the potential of organic matter as a valuable resource, transforming waste into a clean energy carrier. With further research and development, biomass gasification could play a significant role in the widespread adoption of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles, contributing to a greener and more environmentally friendly transportation sector.
Electric Cars: The Green Revolution in Transportation
You may want to see also

Photoelectrochemical Cells: Solar energy directly splits water into hydrogen and oxygen
The process of generating hydrogen for fuel cell cars through photoelectrochemical cells (PECs) is an innovative and sustainable approach to producing clean energy. PECs harness the power of sunlight to directly split water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen, offering a promising method for hydrogen production. This technology is particularly appealing due to its potential to provide a renewable and abundant source of hydrogen, a key component in fuel cell vehicles.
At the heart of PECs are specialized materials, often semiconductors, that can absorb sunlight and initiate the water-splitting reaction. When sunlight strikes the PEC material, it excites electrons, creating a flow of charge carriers. This process is known as the photo-induced charge separation. The excited electrons are then utilized to drive the electrochemical reaction of water, which occurs at the surface of the PEC material. Here, water molecules (H2O) are split into hydrogen ions (H+) and electrons. The electrons, now free, can move through the material, while the hydrogen ions remain bound to the surface, facilitating the formation of hydrogen gas.
The PEC's design is crucial to its efficiency. The material's surface must be optimized to promote the adsorption and desorption of water molecules, allowing for efficient charge transfer. Researchers often use transition metal oxides, such as titanium dioxide (TiO2), zinc oxide (ZnO), and iron oxide (Fe2O3), due to their suitable band gaps and high surface areas. These materials can be engineered to enhance their light absorption capabilities, ensuring that a significant portion of the incident sunlight is utilized for the water-splitting process.
One of the challenges in PEC technology is the stability and durability of the materials used. The PEC material must withstand prolonged exposure to sunlight, water, and other environmental factors without degrading. Researchers are exploring various strategies to improve stability, including the use of protective coatings, surface modifications, and the development of new materials with enhanced resistance to corrosion and photodegradation.
Despite the challenges, photoelectrochemical cells offer a promising avenue for hydrogen production, especially in the context of fuel cell cars. With ongoing research and development, PEC technology has the potential to provide a sustainable and efficient method for generating hydrogen, contributing to the widespread adoption of fuel cell vehicles and reducing our reliance on fossil fuels. This approach aligns with the global efforts to combat climate change and transition towards a cleaner, more sustainable energy future.
Flex Fuel Confusion: Premium Gas, Explained!
You may want to see also

Biological Processes: Certain bacteria can generate hydrogen through fermentation or photosynthesis
The production of hydrogen for fuel cell cars can be achieved through various methods, including biological processes that harness the capabilities of certain bacteria. These microorganisms have evolved unique mechanisms to generate hydrogen as a byproduct of their metabolic activities, offering a sustainable and renewable approach to hydrogen production.
One such biological process involves fermentation, a metabolic pathway utilized by bacteria like * Clostridium* species. These bacteria possess the enzyme hydrogenase, which catalyzes the reversible conversion of protons and electrons into hydrogen gas. In the absence of oxygen, these bacteria can ferment organic compounds, such as glucose, and in the process, they release hydrogen as a byproduct. This fermentation process can be harnessed to produce hydrogen gas, which can then be utilized in fuel cell cars. By optimizing the culture conditions and providing the necessary nutrients, researchers can cultivate these bacteria to enhance hydrogen production efficiency.
Another biological approach is through photosynthesis, a process commonly associated with plants but also employed by specific bacteria. Photosynthetic bacteria, such as *Cyanobacteria*, contain chlorophyll and can perform photosynthesis, similar to plants. During photosynthesis, these bacteria convert sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into oxygen and hydrogen gas. This process is particularly intriguing as it mimics the natural photosynthetic pathways found in plants. By cultivating these photosynthetic bacteria in specialized bioreactors, researchers can generate hydrogen gas through this renewable process.
The use of bacteria for hydrogen production offers several advantages. Firstly, these microorganisms can thrive in diverse environments, including anaerobic conditions where traditional hydrogen production methods might struggle. Secondly, the biological processes are often gentle on the environment, producing minimal waste compared to certain industrial hydrogen production techniques. Furthermore, the scalability of bacterial cultures allows for the potential large-scale production of hydrogen, making it a promising candidate for powering fuel cell cars.
In summary, certain bacteria have evolved remarkable biological processes to generate hydrogen through fermentation and photosynthesis. These methods provide a sustainable and renewable approach to hydrogen production, offering an alternative to traditional industrial processes. By understanding and optimizing these bacterial capabilities, researchers can contribute to the development of efficient hydrogen fuel systems for vehicles, paving the way for a greener and more sustainable transportation future.
E15 Fuel: Understanding Compatibility and Benefits for Your Vehicle
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Hydrogen is typically produced through a process called steam methane reforming, which involves reacting natural gas (methane) with steam in the presence of a catalyst to generate hydrogen and carbon dioxide. This method is widely used due to its scalability and established infrastructure.
Yes, hydrogen can be produced from renewable sources such as wind, solar, and biomass. These methods involve using electricity from renewable energy sources to power the electrolysis of water, splitting it into hydrogen and oxygen. This approach is gaining popularity as it offers a more sustainable and environmentally friendly way of producing hydrogen.
Hydrogen production can be energy-intensive, especially when using steam methane reforming. However, advancements in technology and the integration of renewable energy sources are making the process more efficient. Additionally, efforts are being made to develop alternative methods like biomass gasification and electrolysis, which can reduce the energy requirements and environmental impact.
One of the main challenges is the cost and availability of raw materials. Natural gas, used in steam methane reforming, is a finite resource, and its price volatility can impact the overall cost of hydrogen production. Furthermore, the infrastructure required for large-scale hydrogen production and distribution is still being developed, which poses logistical challenges. Researchers and engineers are working on overcoming these obstacles to make hydrogen fuel cell technology more accessible and economically viable.







