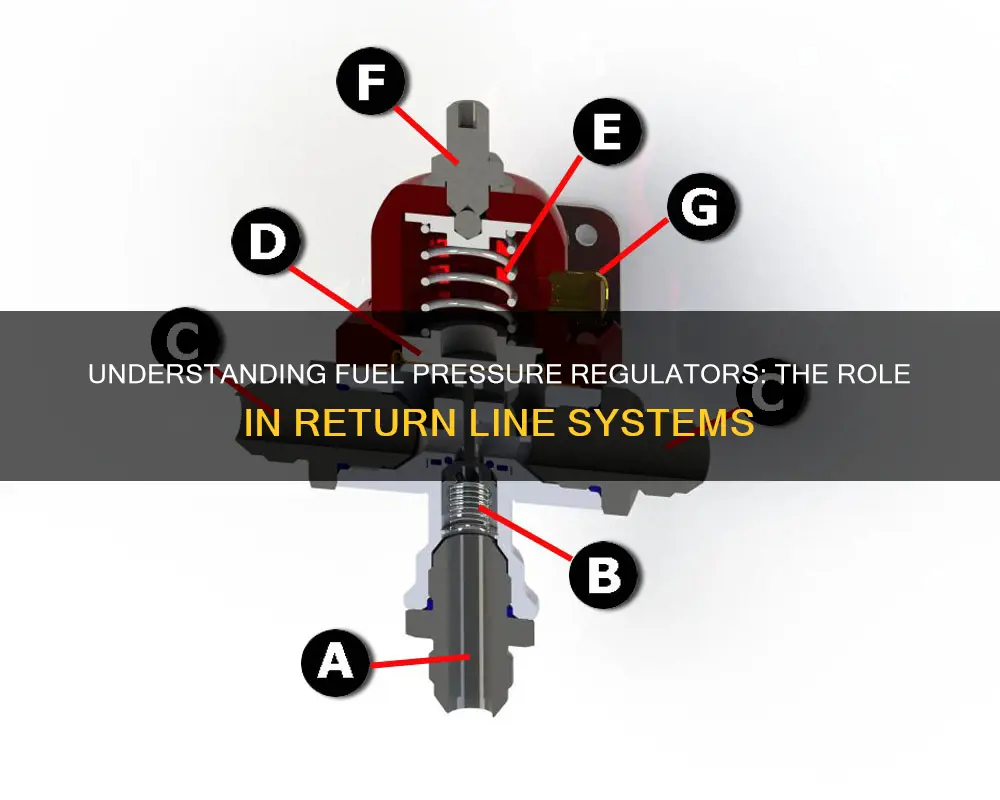
The fuel pressure regulator plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal engine performance by managing the pressure of the fuel in the return line. This component is designed to maintain a consistent and precise fuel pressure, which is vital for efficient combustion and engine operation. The regulator works by monitoring the pressure in the return line and adjusting it as needed to meet the engine's requirements. It uses a combination of valves and springs to control the flow of fuel, ensuring that the pressure remains within the desired range. Understanding the inner workings of the fuel pressure regulator is essential for maintaining a well-functioning engine and can help in diagnosing and resolving issues related to fuel pressure.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Function | The fuel pressure regulator in a return-line system controls the pressure of fuel being returned to the tank. It ensures that the fuel pressure is maintained at an optimal level to meet the engine's requirements. |
| Location | Typically, this regulator is positioned on the fuel return line, close to the fuel tank. It is designed to be easily accessible for maintenance and replacement. |
| Pressure Control | It regulates the pressure by adjusting the flow of fuel. When the engine is running, it opens to allow fuel to flow back into the tank, and when the engine is off, it closes to prevent fuel from draining. |
| Engine Compatibility | This type of regulator is commonly used in engines that require precise fuel pressure management, such as high-performance or fuel-injected engines. |
| Materials | The construction often includes durable materials like aluminum or brass to withstand fuel pressure and potential corrosion. |
| Design | It usually features a spring-loaded valve or a diaphragm that responds to pressure changes, allowing for accurate control. |
| Maintenance | Regular inspection and replacement are recommended to ensure optimal engine performance and longevity. |
| Performance | By maintaining consistent fuel pressure, it improves engine efficiency, power, and fuel economy. |
What You'll Learn
- Fuel Pressure Regulation: The regulator controls pressure in the return line to ensure optimal engine performance
- Pressure Sensor: It monitors pressure and adjusts accordingly to maintain a steady fuel flow
- Valve Mechanism: A valve opens and closes to regulate fuel flow, controlled by the sensor
- Engine Feedback: The system adjusts based on engine speed and load to maintain pressure
- Return Line Design: The design of the return line influences the regulator's effectiveness and fuel delivery

Fuel Pressure Regulation: The regulator controls pressure in the return line to ensure optimal engine performance
The fuel pressure regulator plays a critical role in maintaining the optimal fuel pressure within an engine's return line, which is essential for efficient and reliable engine operation. This component is designed to monitor and adjust the fuel pressure to ensure it falls within the ideal range required for combustion. When the engine is running, the fuel pressure regulator constantly measures the pressure in the return line, which is the line that carries the unused fuel back to the fuel tank after it has passed through the engine.
Its primary function is to prevent excessive fuel pressure, which could lead to engine misfires, reduced performance, and potential damage over time. If the pressure is too high, the regulator reduces it by allowing fuel to flow back into the tank, ensuring a balanced and controlled environment. Conversely, if the pressure drops too low, the regulator increases it by restricting the flow, maintaining the necessary pressure for efficient fuel injection. This dynamic process is crucial for the engine's overall health and longevity.
The design of the fuel pressure regulator often includes a precision-engineered valve that opens and closes based on the pressure differential. When the pressure is within the desired range, the valve remains closed, allowing fuel to flow freely. However, when the pressure deviates from the optimal level, the valve activates, either by increasing or decreasing the resistance in the return line, thus adjusting the pressure accordingly. This mechanism ensures that the engine receives the precise amount of fuel required for each combustion cycle.
In summary, the fuel pressure regulator is a vital component that actively manages the fuel pressure in the return line. By constantly monitoring and adjusting the pressure, it ensures that the engine operates at its peak performance while protecting it from potential issues caused by either too much or too little fuel pressure. Regular maintenance and inspection of this regulator are essential to guarantee its effectiveness and, consequently, the overall reliability of the engine system.
Leaky Fuel Line: A Recipe for Smoke and Trouble
You may want to see also

Pressure Sensor: It monitors pressure and adjusts accordingly to maintain a steady fuel flow
The fuel pressure regulator is a critical component in a vehicle's fuel system, ensuring that the engine receives the precise amount of fuel required for optimal performance. One of its key functions is the use of a pressure sensor, which plays a vital role in maintaining a steady and controlled fuel flow. This sensor is designed to monitor the fuel pressure within the system and make real-time adjustments to ensure the engine operates efficiently.
When the engine is running, the pressure sensor constantly measures the fuel pressure in the return line, which is the line that carries unused fuel back to the fuel tank. This pressure is crucial because it directly impacts the engine's performance and fuel efficiency. The sensor is calibrated to detect any deviations from the ideal pressure range, which is typically between 45 and 65 psi (pounds per square inch) for most engines. If the pressure drops below this range, the sensor triggers a response to compensate.
The pressure sensor's primary task is to ensure that the fuel flow remains steady and consistent. When it detects a pressure drop, it sends a signal to the fuel pressure regulator, which then adjusts the fuel pump's output to increase the pressure. Conversely, if the pressure is too high, the sensor will prompt the regulator to reduce the pressure to maintain the optimal range. This dynamic adjustment process is essential for efficient combustion and preventing engine misfires.
In the event of a pressure sensor malfunction, the engine may experience poor performance or even stall. For instance, if the sensor fails to detect a pressure drop, the engine might not receive enough fuel, leading to a condition known as 'starvation,' where the engine struggles to start or runs poorly. On the other hand, a faulty sensor that consistently overestimates pressure could result in excessive fuel flow, causing the engine to run rich and potentially leading to performance issues.
To ensure the pressure sensor functions correctly, regular maintenance and checks are necessary. This includes inspecting the sensor for any signs of damage or contamination and verifying its accuracy using specialized diagnostic tools. Proper maintenance ensures that the sensor can accurately monitor pressure, allowing the fuel pressure regulator to make precise adjustments, ultimately contributing to the overall reliability and performance of the vehicle's engine.
Fuel Line Flexibility: Exploring Compatibility and Interchangeability
You may want to see also

Valve Mechanism: A valve opens and closes to regulate fuel flow, controlled by the sensor
The valve mechanism is a critical component in the fuel pressure regulator system, especially in the context of return line fuel injection. This mechanism is responsible for precisely controlling the flow of fuel, ensuring optimal engine performance and efficiency. Here's a detailed explanation of how it works:
In the fuel pressure regulator, a solenoid-operated valve is typically used to regulate fuel flow. This valve is strategically positioned in the return line, which is the path that fuel takes from the fuel pump to the engine. The valve's primary function is to open and close in response to signals from a fuel pressure sensor. This sensor continuously monitors the fuel pressure and provides real-time data to the engine control unit (ECU). When the ECU detects that the fuel pressure is within the desired range, it sends an electric signal to the solenoid, which in turn activates the valve.
The valve's design is crucial for its functionality. It consists of a movable piston or diaphragm that is connected to the solenoid. When the solenoid receives the signal, it creates a magnetic field, pulling the piston or diaphragm towards it. This movement opens the valve, allowing fuel to flow through it. The size and design of the valve orifice determine the rate of fuel flow, ensuring that the pressure remains at the desired level.
As the fuel pressure rises, the sensor provides feedback to the ECU, which may adjust the valve's opening or closing time accordingly. This dynamic control ensures that the fuel pressure is maintained at an optimal level, even under varying load conditions. For instance, during high-load situations, the valve might open for a longer duration to meet the increased fuel demand, while in low-load conditions, it could close partially to conserve fuel.
This valve mechanism is a sophisticated solution to the challenge of managing fuel pressure in return line systems. By precisely controlling the fuel flow, it contributes to improved engine performance, better fuel efficiency, and reduced emissions. The sensor's role in providing continuous feedback allows for rapid adjustments, ensuring that the fuel pressure regulator functions effectively even in dynamic driving conditions.
Fuel Line Removal Guide: 2008 RMZ450
You may want to see also

Engine Feedback: The system adjusts based on engine speed and load to maintain pressure
The fuel pressure regulator plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal fuel delivery to the engine, especially in systems that utilize a return line. This component is designed to maintain a consistent and precise fuel pressure, which is essential for efficient combustion and engine performance. The system's ability to adjust based on engine speed and load is a key feature that enhances its functionality.
When the engine is at rest or operating at low speeds, the fuel pressure regulator reduces the pressure to a lower level. This is achieved by allowing a controlled amount of fuel to return to the tank, which helps in preventing excessive pressure buildup. By doing so, the system ensures that the engine receives the appropriate amount of fuel during these conditions, promoting stable idling and smooth start-ups.
As the engine speed increases, the fuel pressure regulator responds by increasing the pressure to meet the higher fuel demand. This adjustment is vital as it directly impacts the engine's power output and performance. The regulator calculates the required fuel pressure based on the engine's speed and load, ensuring that the fuel delivery system can provide the necessary amount of fuel for efficient combustion. This dynamic adjustment is particularly important during high-load conditions, such as when accelerating rapidly or driving uphill, where the engine requires more fuel to maintain optimal performance.
The system's feedback mechanism is a sophisticated process. It involves sensors that monitor various parameters, such as engine speed, temperature, and load. These sensors provide real-time data to the fuel pressure regulator, allowing it to make immediate adjustments. For instance, when the engine speed rises, the sensors detect this change and signal the regulator to increase the fuel pressure accordingly. This rapid response ensures that the engine receives the required fuel without any noticeable lag, resulting in a smooth and responsive power delivery.
Furthermore, the fuel pressure regulator's ability to adapt to varying engine loads is crucial for overall engine health. During high-load situations, the regulator maintains a higher fuel pressure to meet the increased demand, preventing potential performance issues. Conversely, during low-load conditions, it reduces the pressure to conserve fuel and optimize efficiency. This dynamic adjustment based on engine feedback ensures that the fuel pressure remains within the optimal range, promoting better fuel economy and engine longevity.
Chevy Equinox Fuel Line Removal: A Step-by-Step Guide
You may want to see also

Return Line Design: The design of the return line influences the regulator's effectiveness and fuel delivery
The return line plays a critical role in the functionality of a fuel pressure regulator, especially in systems where the regulator is located downstream of the fuel pump. The design of this return line is crucial for ensuring optimal fuel delivery and pressure regulation. Here's an overview of how return line design impacts the regulator's performance:
Line Diameter and Length: The diameter and length of the return line are essential factors. A larger diameter allows for smoother fuel flow, reducing the likelihood of pressure drops and ensuring a consistent fuel supply to the regulator. Longer lines, while sometimes necessary for engine layout, can introduce additional challenges. Longer lines may result in increased fuel temperature due to heat dissipation, which can affect the regulator's performance. Designers often aim for a balance between line length and diameter to optimize fuel flow and minimize potential issues.
Material Selection: Choosing the right material for the return line is vital. Materials like stainless steel or aluminum alloys are commonly used due to their durability and resistance to corrosion. These materials ensure that the line can withstand the corrosive effects of fuel and high temperatures, especially in high-performance applications. The material also influences the line's flexibility, which is important for accommodating engine movement and potential vibrations.
Line Routing and Placement: Proper routing and placement of the return line are critical. The line should be positioned to avoid excessive bends or kinks, as these can restrict fuel flow and cause pressure drops. Additionally, the line should be kept as short as possible to minimize the risk of fuel degradation due to heat and light exposure. Careful routing also helps prevent interference with other engine components, ensuring smooth operation.
Pressure Relief Valves: In some designs, pressure relief valves are incorporated into the return line. These valves are crucial for maintaining safe fuel pressure and preventing excessive pressure buildup. When the fuel pressure exceeds a certain threshold, the valve opens, allowing excess pressure to be released. This feature is essential for protecting the fuel system and the engine from potential damage caused by overpressure.
Optimizing Fuel Delivery: The return line design directly impacts the regulator's ability to maintain stable fuel pressure. A well-designed return line ensures that the regulator receives a consistent and properly pressurized fuel supply. This consistency is vital for accurate fuel metering and injection, especially in high-performance engines where precise fuel delivery is critical for optimal performance and emissions.
Fuel Line Fixes: Can You Repair the Irreparable?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The fuel pressure regulator is a critical component in a vehicle's fuel system, especially in return line configurations. Its main role is to maintain a consistent and controlled fuel pressure within the engine's intake system. It ensures that the fuel delivered to the engine is at the optimal pressure required for efficient combustion.
The regulator operates by monitoring the fuel pressure in the return line and adjusting it as needed. It typically consists of a precision-engineered valve that opens and closes based on the pressure differential. When the pressure is too high, the valve closes, reducing the flow and preventing excessive fuel pressure. Conversely, if the pressure drops, the valve opens, allowing more fuel to pass through and maintain the desired pressure.
A malfunctioning fuel pressure regulator can lead to several issues. Common symptoms include engine misfires, reduced power, rough idling, or difficulty starting the engine. If the regulator fails to control pressure properly, it may result in either too much or too little fuel reaching the engine, causing performance problems and potential damage to the engine over time.
Yes, in some cases, fuel pressure regulators can be adjusted or calibrated to restore optimal performance. This process involves using specialized tools to fine-tune the regulator's settings. However, it is often recommended to seek professional assistance for such adjustments, as improper calibration can lead to further complications. Regular maintenance and inspection of the fuel system, including the pressure regulator, are essential to ensure the vehicle's longevity and reliable operation.







