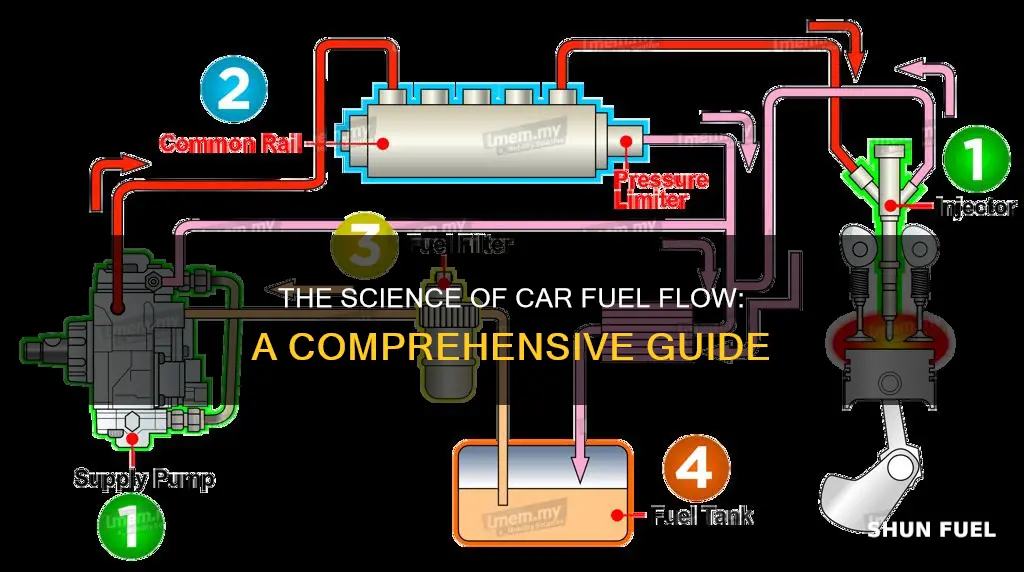
The flow of fuel in a car is a complex process that ensures the engine receives the necessary energy to run. It begins with the fuel tank, where gasoline or diesel is stored and pumped into the engine through a series of filters and pumps. The fuel injectors or carburetor precisely meter the fuel, mixing it with air to create a combustible mixture. This mixture is then ignited in the engine's cylinders, driving the pistons and ultimately powering the vehicle. Understanding this process is essential for optimizing engine performance and maintaining a car's efficiency.
What You'll Learn
- Fuel Injection: The process of injecting fuel into the engine via injectors
- Fuel Pump: A vital component that pumps fuel from the tank to the engine
- Fuel Filter: Filters out contaminants to ensure clean fuel flow
- Fuel Lines: Tubes that carry fuel from the tank to the engine
- Engine's Fuel System: The overall mechanism that manages fuel intake and combustion

Fuel Injection: The process of injecting fuel into the engine via injectors
Fuel injection is a critical component of modern vehicle engines, revolutionizing the way fuel is delivered to the combustion chamber. This process involves the precise injection of fuel into the engine's cylinders, ensuring optimal performance, efficiency, and power output. Here's an overview of the fuel injection process:
In a fuel-injected engine, the fuel system is designed to deliver a controlled amount of fuel to each cylinder at the right time. The process begins with the fuel pump, which is typically located in the fuel tank or near the engine. This pump creates pressure in the fuel lines, ensuring a steady supply of fuel to the injectors. The fuel is then directed through a series of small passages called the fuel rail, which acts as a reservoir for the injectors.
The injectors are small, precise nozzles strategically positioned near the engine's intake valves. When the engine's electronic control unit (ECU) detects a need for fuel, it sends an electrical signal to the respective fuel injector. This signal triggers the injector to open and spray a fine mist of fuel into the intake manifold or directly into the combustion chamber. The timing and amount of fuel injected are carefully controlled by the ECU, ensuring a precise air-fuel mixture.
Modern fuel injection systems use advanced technology to optimize performance. These systems include pressure sensors, temperature sensors, and flow meters to monitor the fuel pressure, temperature, and flow rate. By constantly adjusting the fuel injection timing and amount, the ECU ensures that the engine receives the ideal air-fuel mixture for efficient combustion. This results in improved power output, better fuel economy, and reduced emissions.
The process of fuel injection is a complex yet highly efficient method of delivering fuel to an engine. It allows for precise control over the air-fuel mixture, enabling engines to run smoothly, efficiently, and with minimal environmental impact. This technology has become a standard feature in most modern vehicles, offering a significant advancement over traditional carbureted systems.
Mastering Your Car's Fuel Gauge: A Beginner's Guide
You may want to see also

Fuel Pump: A vital component that pumps fuel from the tank to the engine
The fuel pump is an essential component in a car's fuel system, responsible for delivering fuel from the tank to the engine. It operates under the principle of creating a vacuum to draw fuel upwards, overcoming the force of gravity and ensuring a steady supply of gasoline or diesel to the engine's combustion chambers. This process is crucial for efficient engine operation and performance.
In a typical fuel system, the pump is located near the fuel tank and is often driven by a small electric motor. When the engine is started, the fuel pump activates, creating a low-pressure vacuum that pulls fuel from the tank. This vacuum is generated by the pump's internal mechanism, which consists of a series of vanes or impellers that rotate within a sealed chamber. As the pump operates, it creates a suction force, drawing fuel through a small diameter line called the fuel line or fuel rail.
The fuel pump's design is critical to its function. It must be capable of handling the required fuel flow rate to meet the engine's demands while maintaining a consistent pressure to ensure efficient operation. Modern fuel pumps are often designed with precision engineering to optimize performance. They may feature advanced materials and manufacturing processes to ensure reliability and longevity, especially in high-pressure environments.
One of the key advantages of the fuel pump's design is its ability to provide a consistent fuel supply under varying conditions. When the engine is idling or operating at high speeds, the pump adjusts its output to maintain the required fuel-air mixture. This dynamic adjustment is vital for optimal engine performance and emissions control. Additionally, the pump's design often includes safety mechanisms to prevent over-pressure situations, which could lead to engine damage.
In summary, the fuel pump is a critical component that ensures the engine receives the necessary fuel for combustion. Its operation involves creating a vacuum to draw fuel, and its design must accommodate varying engine demands while maintaining efficiency and safety. Understanding the fuel pump's role provides insight into the intricate process of fuel delivery in modern vehicles.
Haddad Toyota Fuel Tank: Sold Cars, Now a Legacy
You may want to see also

Fuel Filter: Filters out contaminants to ensure clean fuel flow
The fuel filter is a crucial component in a car's fuel system, designed to maintain the cleanliness and quality of the fuel as it circulates through the engine. Its primary function is to filter out contaminants that may be present in the fuel, ensuring that only clean fuel reaches the engine's combustion chamber. This is essential for optimal engine performance, longevity, and reliability.
When fuel is supplied to the engine, it often contains impurities such as dirt, water, and other contaminants that can be harmful. These impurities can cause various issues, including engine misfires, reduced power, and even engine damage over time. The fuel filter acts as a barrier, trapping these contaminants and preventing them from entering the engine. It is typically located along the fuel line, positioned strategically to filter the fuel as it passes through.
As fuel flows through the filter, it passes through a series of small openings or pores in the filter media. This media is designed to capture and hold contaminants, allowing clean fuel to continue its journey. The filter's design and material composition are carefully chosen to ensure it can effectively trap various types of impurities. Common filter media include paper, cotton, or synthetic fibers, which are often pleated to increase surface area for better filtration.
Over time, the fuel filter may become clogged or saturated with contaminants, reducing its effectiveness. This is why regular maintenance and replacement of the fuel filter are essential. When the filter becomes dirty, it can restrict fuel flow, leading to engine performance issues. Therefore, it is recommended to check and replace the fuel filter at regular intervals, as specified by the vehicle manufacturer.
In summary, the fuel filter plays a vital role in maintaining the health and efficiency of a car's engine. By filtering out contaminants, it ensures that the fuel supplied to the engine is clean and free from impurities, promoting optimal performance and engine longevity. Regular maintenance of the fuel filter is a simple yet effective way to keep the vehicle's fuel system in top condition.
Can GMOs Power Your Car? Exploring the Potential of GMO Oil as Fuel
You may want to see also

Fuel Lines: Tubes that carry fuel from the tank to the engine
Fuel lines are an essential component of a car's fuel system, responsible for transporting fuel from the tank to the engine. These lines are typically made of flexible, durable materials such as rubber or plastic, designed to withstand the pressure and temperature changes that occur during operation. The primary function of fuel lines is to ensure a continuous and controlled supply of fuel to the engine, allowing for efficient combustion and optimal performance.
The fuel lines are connected to the fuel tank, which stores the gasoline or diesel fuel. When the engine is started, the fuel pump activates, creating suction that draws fuel from the tank through the lines. This process is regulated by the fuel pressure regulator, which maintains the appropriate pressure to ensure smooth fuel flow. The fuel lines are carefully routed to avoid any obstructions or damage, as they must withstand the vibrations and movements of the vehicle during operation.
As the fuel travels through the lines, it passes through various components such as filters and valves. These components help to ensure that only clean, high-quality fuel reaches the engine. Filters remove any contaminants or impurities that may be present in the fuel, preventing potential damage to the engine's internal components. Valves control the flow rate and pressure, ensuring that the engine receives the precise amount of fuel required for efficient combustion.
In modern vehicles, fuel lines are often made with specialized materials to enhance their performance and longevity. For example, some lines may be reinforced with braided steel to provide additional strength and flexibility. This design ensures that the lines can withstand the high pressure and temperature differentials while maintaining their structural integrity. Additionally, fuel lines are often coated with protective materials to prevent corrosion and ensure long-term reliability.
Proper maintenance and inspection of fuel lines are crucial to ensure the overall health and performance of a vehicle. Regular checks for any signs of damage, leaks, or contamination are essential. If any issues are detected, prompt repairs or replacements should be made to prevent potential engine problems. By understanding the role and importance of fuel lines, car owners can take proactive measures to maintain their vehicles and ensure a reliable and efficient driving experience.
Jet Fuel in Your Car: What You Need to Know
You may want to see also

Engine's Fuel System: The overall mechanism that manages fuel intake and combustion
The fuel system in a car's engine is a complex network designed to efficiently manage the intake and combustion of fuel, ensuring optimal performance and power output. This system is responsible for delivering the precise amount of fuel required for each combustion cycle, a process that begins with the fuel's intake and ends with its efficient combustion in the engine's cylinders.
The process starts with the fuel tank, which stores the gasoline or diesel fuel. From here, the fuel is pumped through a series of filters and pumps to ensure it is clean and at the correct pressure. Gasoline engines typically use a fuel pump, often located in the fuel tank, to deliver fuel at a high pressure to the engine. Diesel engines, on the other hand, use a common rail system, which stores fuel under high pressure and injects it directly into the engine's cylinders.
Once the fuel is at the correct pressure, it is directed through a series of passages and nozzles towards the engine's intake manifold. The intake manifold is a crucial component that distributes fuel to the individual cylinders. It is designed to ensure that each cylinder receives the exact amount of fuel required for efficient combustion. This is achieved through a precise arrangement of fuel injectors or carburetor jets, which spray the fuel into the intake manifold at specific angles and locations.
In gasoline engines, the fuel is mixed with air in the intake manifold and then directed into the engine's cylinders. Here, the fuel-air mixture is ignited by the spark plugs, causing a controlled explosion that powers the engine. In diesel engines, the fuel is injected directly into the combustion chamber, where it is ignited by the high temperatures and pressures created by the engine's operation.
The efficiency of the fuel system is critical to the engine's performance, fuel economy, and emissions. Modern engines are equipped with sophisticated electronic controls that monitor and adjust the fuel-air mixture, ensuring optimal combustion. These controls take into account various factors such as engine speed, load, and temperature to deliver the precise amount of fuel required for each operating condition. This intricate process ensures that the engine runs smoothly, efficiently, and with minimal environmental impact.
Unlocking Benefits: Fuel Cards for Personal Use
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The process begins with the fuel pump, which is typically driven by the engine. When the engine is running or when you start the car, the pump activates and sends fuel from the tank to the engine's fuel injectors or carburetor. This is a crucial step to ensure the engine receives the required amount of fuel for efficient combustion.
The fuel pump is a vital component responsible for delivering fuel from the tank to the engine. It is usually located inside the fuel tank or close to it. When activated, the pump creates pressure, pushing fuel through the fuel lines to the injectors or carburetor. This pressure ensures a consistent and controlled fuel supply, allowing for optimal engine performance.
In modern cars, fuel injection systems are commonly used. These systems precisely control the fuel-air mixture by injecting fuel directly into the engine's cylinders. The engine's computer manages this process, adjusting the fuel flow based on various sensors' input, such as engine speed, temperature, and load. This ensures efficient combustion, optimal power output, and reduced emissions.







