Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles are an innovative and sustainable mode of transportation, and understanding how to refill their fuel cells is essential for their widespread adoption. Refilling a hydrogen fuel cell car involves a process that is both efficient and environmentally friendly. Unlike traditional gasoline or diesel vehicles, hydrogen fuel cell cars store energy in the form of hydrogen gas, which is combined with oxygen from the air to produce electricity through an electrochemical reaction. When the fuel cell's hydrogen supply is low, it needs to be replenished by connecting the vehicle to a hydrogen refueling station. This process is similar to refueling a conventional car, but instead of gasoline, the car is filled with compressed hydrogen gas, which is then stored in the fuel cell for power generation. The refueling time is relatively quick, typically taking just a few minutes, and the process is designed to be convenient and accessible for drivers, ensuring that hydrogen fuel cell vehicles can be easily integrated into our transportation infrastructure.
What You'll Learn
- Fuel Cell Design: Refilling involves replacing depleted hydrogen in fuel cells
- Hydrogen Storage: High-pressure tanks store hydrogen for refueling
- Refueling Infrastructure: Special stations with hydrogen dispensers are required
- Safety Protocols: Strict safety measures ensure refueling is safe and efficient
- Hydrogen Production: Refueling also requires a sustainable hydrogen production process

Fuel Cell Design: Refilling involves replacing depleted hydrogen in fuel cells
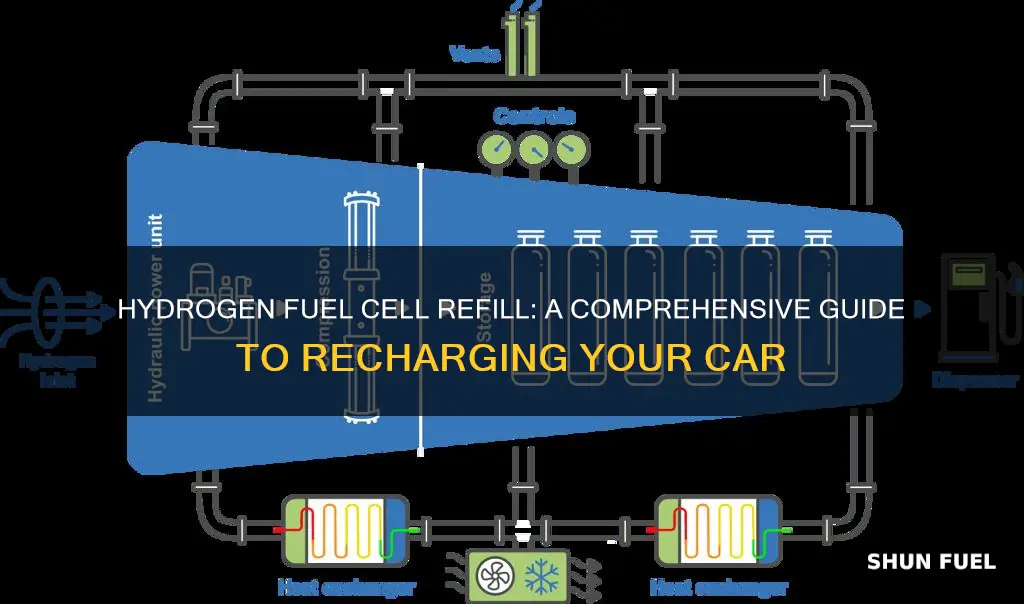
The process of refilling a hydrogen fuel cell car involves a precise and carefully designed system to replenish the depleted hydrogen within the fuel cells. This is a critical aspect of maintaining the efficiency and longevity of the vehicle's power source. When a hydrogen fuel cell car operates, the hydrogen gas is reacted with oxygen from the air in the fuel cell, producing electricity, water, and heat. This reaction is reversible, meaning that the hydrogen can be recovered and reused.
Refilling the fuel cells is essentially about replacing the hydrogen that has been consumed during the vehicle's operation. This is typically done at specialized refueling stations equipped with high-pressure hydrogen tanks. The process begins with the driver initiating the refueling request, often through an onboard control system. The vehicle then communicates with the refueling station to ensure compatibility and safety.
At the refueling station, the depleted hydrogen is extracted from the fuel cells and replaced with fresh hydrogen gas. This replacement is crucial to maintaining the vehicle's performance and range. The refueling process is designed to be efficient and rapid, ensuring minimal downtime for the driver. Specialized nozzles and connectors are used to securely attach the refueling station to the vehicle, allowing for the transfer of hydrogen under high pressure.
The design of the fuel cell system plays a significant role in this process. Fuel cells are typically arranged in stacks, with each cell containing a catalyst layer, a membrane, and two electrodes. The hydrogen gas is supplied to the anode (negative electrode) of the fuel cell, where it is oxidized, releasing electrons that generate electricity. The depleted hydrogen, now in the form of hydrogen ions, passes through the membrane to the cathode (positive electrode), where it combines with oxygen from the air to form water. This water is then expelled as a byproduct.
To refill the fuel cells, the depleted hydrogen must be separated from the other reaction products, primarily water. This is achieved through a process called hydrogen purification, which can be done using various methods such as pressure swing adsorption or membrane separation. Once purified, the hydrogen is compressed and stored in high-pressure tanks, ready for use. The design of the refueling system must ensure that the hydrogen is delivered efficiently and safely to the fuel cells, allowing the vehicle to continue its operation with minimal disruption.
Parking Tips: Maximizing Fuel Efficiency with Smart Choices
You may want to see also

Hydrogen Storage: High-pressure tanks store hydrogen for refueling
Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles are a promising alternative to traditional internal combustion engines, and their refueling process is an essential aspect of their widespread adoption. When it comes to refueling hydrogen fuel cell cars, the storage and delivery of hydrogen in a safe and efficient manner are critical considerations. One of the primary methods for storing hydrogen in these vehicles is through the use of high-pressure tanks.
High-pressure hydrogen tanks are designed to store the gas at a pressure significantly higher than atmospheric pressure, typically ranging from 350 to 700 bars (5,000 to 10,000 psi). This high-pressure storage allows for a more compact and lightweight design compared to other storage methods. The tanks are often made of advanced materials such as carbon fiber composites or aluminum alloys, ensuring both strength and safety. These materials can withstand the extreme conditions required to store hydrogen efficiently.
The refueling process for hydrogen fuel cell cars using high-pressure tanks involves a specialized filling station. When a vehicle is connected to the refueling station, the high-pressure hydrogen is delivered directly into the tank. This process is similar to refueling a conventional vehicle with gasoline or diesel, but with a crucial difference in the fuel type. The hydrogen is typically compressed and delivered as a gas, and the refueling time can be relatively quick, often taking just a few minutes.
Safety is a paramount concern when dealing with high-pressure hydrogen tanks. To ensure the safe operation of these vehicles, strict regulations and standards are in place. These regulations include guidelines for tank design, material selection, and pressure limits. Additionally, refueling stations are equipped with various safety measures, such as pressure release valves and leak detection systems, to mitigate potential risks.
High-pressure tanks offer a practical solution for hydrogen storage, enabling the refueling of fuel cell vehicles in a manner similar to conventional cars. As the technology advances and infrastructure for hydrogen refueling stations expands, hydrogen fuel cell cars are becoming more accessible and convenient for everyday use, contributing to a more sustainable transportation future.
The Evolution of NASCAR Engines: Carburetor or Fuel Injection?
You may want to see also

Refueling Infrastructure: Special stations with hydrogen dispensers are required
To refill a hydrogen fuel cell car, a robust and specialized infrastructure is essential, as it is different from conventional refueling methods. The process involves the use of hydrogen dispensers, which are specifically designed to handle and dispense hydrogen gas safely and efficiently. These dispensers are a critical component of the refueling infrastructure for hydrogen fuel cell vehicles.
Specialized stations, often referred to as hydrogen fueling stations, are required to accommodate the unique needs of hydrogen refueling. These stations are equipped with dispensers that can deliver hydrogen gas at the necessary pressure and flow rate to the vehicle's fuel cell system. The dispensers are typically located at strategic points along highways and in urban areas to ensure convenient access for hydrogen fuel cell car owners.
The design and placement of these stations are crucial for the widespread adoption of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles. They should be easily accessible and conveniently located to encourage regular use. For instance, along major transportation routes, where drivers can quickly refuel during long journeys, and in densely populated areas to support urban mobility. The stations should also be designed with safety in mind, adhering to strict regulations and guidelines to prevent any potential hazards associated with hydrogen gas.
Refueling at these stations involves a precise and controlled process. The dispenser connects to the vehicle's fueling port, which is usually located near the front of the car. The dispenser then releases hydrogen gas at a controlled rate, ensuring the fuel cell receives the required amount for optimal performance. This process is similar to refueling a conventional vehicle but requires specialized equipment and knowledge of hydrogen handling procedures.
In summary, the refueling infrastructure for hydrogen fuel cell cars is a critical aspect of their adoption and use. Special stations with hydrogen dispensers play a vital role in providing a safe and efficient refueling experience. These stations are strategically placed to ensure accessibility and convenience, encouraging the widespread use of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles in both urban and long-distance transportation scenarios. Proper infrastructure development is key to the successful integration of hydrogen fuel cell technology into the transportation sector.
Fuel Filter Freshness: Does It Matter When Not in Use?
You may want to see also

Safety Protocols: Strict safety measures ensure refueling is safe and efficient
When it comes to refueling hydrogen fuel cell vehicles, implementing strict safety protocols is paramount to ensure the process is both safe and efficient. Hydrogen is a highly flammable and explosive gas, so any refueling operation must adhere to stringent guidelines to minimize risks. One critical aspect is the use of specialized equipment designed specifically for hydrogen refueling. These stations are equipped with advanced safety features, such as pressure regulators and leak detection systems, to prevent any accidental release of hydrogen into the atmosphere. Refueling equipment is meticulously calibrated to ensure precise control over the refueling process, reducing the chances of overfilling or underfilling the fuel cell.
Before initiating the refueling process, a thorough inspection of the vehicle and the refueling station is conducted. This includes checking for any signs of damage, corrosion, or leaks in the fuel cell system and ensuring that all safety mechanisms are functional. Refueling personnel are trained to identify potential hazards and are equipped with personal protective gear, including respirators and protective clothing, to safeguard themselves from any potential gas leaks or exposure.
Strict adherence to standard operating procedures is essential during the refueling process. This involves following a step-by-step protocol that includes locking out the fuel system, disconnecting power sources, and ensuring the vehicle is in a secure and controlled environment. Refueling personnel must communicate effectively with each other to coordinate the process, ensuring that all safety checks are completed before and after the refueling operation.
Regular maintenance and calibration of the refueling equipment are crucial to maintaining safety standards. This includes routine inspections, pressure tests, and performance checks to ensure that the equipment operates within safe parameters. Additionally, keeping detailed records of maintenance activities and any issues encountered during refueling operations helps identify potential problem areas and allows for proactive safety enhancements.
Lastly, educating both refueling personnel and vehicle owners about hydrogen safety is vital. This includes providing comprehensive training on recognizing and responding to emergencies, as well as promoting best practices for safe refueling. By fostering a culture of safety awareness, the risk of accidents and mishaps during hydrogen refueling can be significantly reduced, ensuring a more efficient and secure fueling process for hydrogen fuel cell vehicles.
Fuel Filters: Do New Cars Still Need Them?
You may want to see also

Hydrogen Production: Refueling also requires a sustainable hydrogen production process
The process of refueling a hydrogen fuel cell car involves not just delivering the hydrogen but also ensuring that it is produced sustainably. Hydrogen production is a critical aspect of the entire lifecycle of a hydrogen fuel cell vehicle, and it plays a pivotal role in the car's environmental impact. The primary goal is to minimize the carbon footprint associated with hydrogen generation, which is essential for the widespread adoption of hydrogen fuel cell technology.
Sustainable hydrogen production methods are crucial to reducing the environmental impact of refueling. One of the most promising approaches is through electrolysis, a process that uses electricity to split water (H2O) into hydrogen (H2) and oxygen (O2). This method is considered sustainable because it can be powered by renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, or hydroelectric power, which have a minimal carbon footprint. When renewable energy is used for electrolysis, the resulting hydrogen is often referred to as 'green hydrogen'.
Another sustainable technique is the reforming of natural gas, which involves a process called steam methane reforming. This method produces hydrogen by reacting natural gas with steam at high temperatures, resulting in a mixture of hydrogen and carbon dioxide. However, to make this process more environmentally friendly, carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies can be employed to capture the carbon dioxide emissions, preventing them from entering the atmosphere. This approach, known as 'blue hydrogen', is a significant step towards a more sustainable hydrogen economy.
The key to a sustainable hydrogen production process is the integration of renewable energy sources and the implementation of efficient, low-emission technologies. For instance, using wind or solar power for electrolysis ensures that the energy input for hydrogen production is clean and renewable. Additionally, advancements in fuel cell technology can improve the overall efficiency of the refueling process, reducing the amount of hydrogen required for a given distance traveled.
In summary, refueling a hydrogen fuel cell car is not just about delivering hydrogen but also about ensuring its production is sustainable. Electrolysis, powered by renewable energy, and natural gas reforming with carbon capture are two viable methods for sustainable hydrogen generation. These processes aim to minimize environmental impact, making hydrogen fuel cell technology a more attractive and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional combustion engines.
Manual Transmission: Fuel Efficiency Advantage or Myth?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Refilling a hydrogen fuel cell car is a straightforward process that involves connecting the vehicle to a hydrogen fueling station. These stations use high-pressure gas cylinders or compressed hydrogen gas to replenish the fuel. The process typically takes a few minutes, similar to refueling a conventional gasoline or diesel vehicle.
When refueling, the driver parks the car near the fueling station and opens the fuel door. The fueling nozzle is then connected to the vehicle's fueling port, usually located near the rear of the car. The hydrogen gas is delivered at high pressure, filling the fuel tank until it reaches the desired level. This process is quick and efficient, allowing for rapid refueling.
Yes, there are various methods to refill hydrogen fuel cell cars. One common method is using a high-pressure hydrogen gas cylinder, which is similar to the cylinders used in scuba diving. These cylinders are connected to the vehicle and provide a rapid refill. Another approach is through a network of hydrogen fueling stations, which use compressed hydrogen gas and specialized equipment to refill the tanks. Some vehicles also support refueling with liquid hydrogen, but this method is less common due to the low temperatures required to keep hydrogen in a liquid state.







