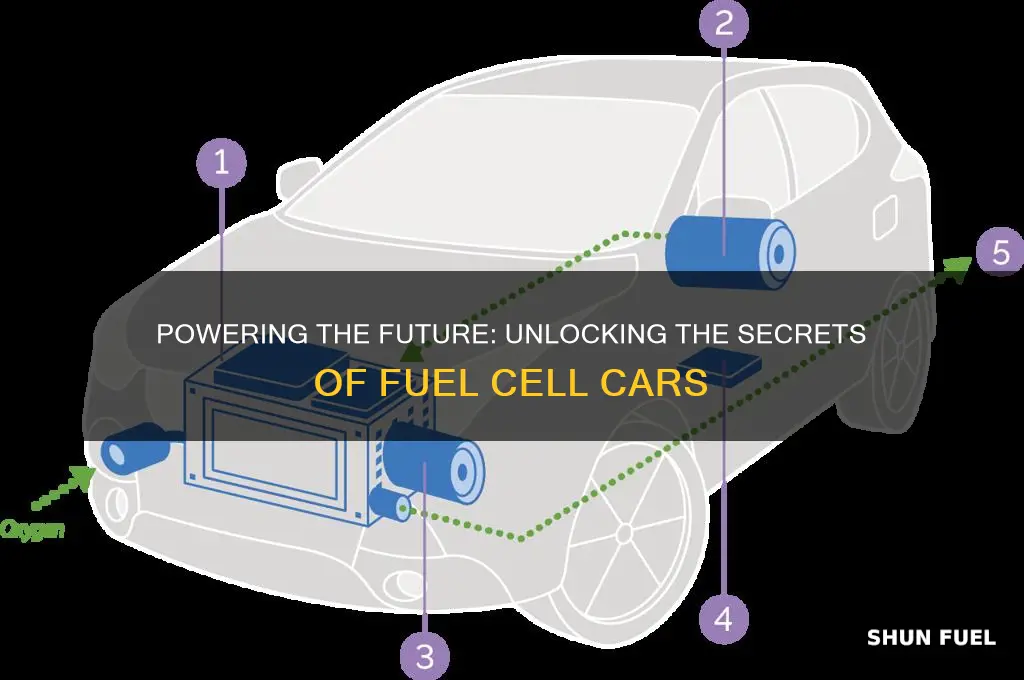
Fuel cell cars are an innovative technology that offers a cleaner and more efficient alternative to traditional internal combustion engines. These vehicles generate electricity through a process that involves the electrochemical reaction of hydrogen and oxygen, which produces electricity, water, and heat. The fuel cell's core component is a catalyst that facilitates the reaction, allowing the car to convert chemical energy into electrical power, providing a sustainable and environmentally friendly way to power vehicles.
What You'll Learn
- Fuel Cell Basics: Electrochemical reactions convert hydrogen and oxygen into electricity, heat, and water
- Catalyst Role: Platinum catalysts facilitate the breakdown of hydrogen, enabling efficient electron transfer
- Electricity Generation: Electrons flow through an external circuit, powering the car's electrical systems
- Energy Conversion: Chemical energy is converted to electrical energy with high efficiency
- Environmental Impact: Zero emissions make fuel cell cars environmentally friendly

Fuel Cell Basics: Electrochemical reactions convert hydrogen and oxygen into electricity, heat, and water
Fuel cells are innovative devices that harness the power of electrochemical reactions to generate electricity, offering a clean and efficient alternative to traditional combustion engines. At its core, a fuel cell operates through a simple yet remarkable process: it combines hydrogen and oxygen, resulting in the production of electricity, heat, and water. This electrochemical reaction is the key to unlocking the potential of fuel cells.
The basic structure of a fuel cell consists of an anode and a cathode, separated by an electrolyte. When hydrogen fuel is supplied to the anode, it undergoes a process called electrolysis, where it is split into protons and electrons. The electrons are then directed through an external circuit, creating an electric current, while the protons move through the electrolyte to reach the cathode.
At the cathode, oxygen from the air is combined with the protons and electrons, forming water as a byproduct. This electrochemical reaction can be represented by the following equation: 2H2 + O2 → 2H2O. Here, hydrogen and oxygen react to produce water, releasing energy in the form of electricity and heat. The electricity generated can power various devices, while the heat can be utilized for additional applications.
The efficiency of fuel cells lies in their ability to directly convert chemical energy into electrical energy through these electrochemical reactions. Unlike internal combustion engines, fuel cells do not require the combustion of fuel, which eliminates the production of harmful emissions like carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter. This makes fuel cells an environmentally friendly power source for various applications, including transportation, stationary power generation, and portable electronics.
In the context of fuel cell vehicles, the process is particularly fascinating. Hydrogen fuel is stored in tanks and supplied to the fuel cell stack, where the electrochemical reactions occur. The electricity generated powers the electric motor, driving the vehicle's wheels. This technology offers a promising solution for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and improving energy efficiency in the transportation sector.
Safe Driving Tips: Should You Let Your Car Run While Refueling?
You may want to see also

Catalyst Role: Platinum catalysts facilitate the breakdown of hydrogen, enabling efficient electron transfer
The role of catalysts in fuel cell technology is pivotal, especially when it comes to platinum catalysts and their ability to facilitate the breakdown of hydrogen. This process is a fundamental step in generating electricity within fuel cell vehicles. Platinum, a precious metal, is chosen for its exceptional catalytic properties, which make it highly effective in promoting the electrochemical reactions required for power generation.
In the context of fuel cells, the primary function of the catalyst is to lower the activation energy barrier for the oxidation of hydrogen. This reaction is represented by the equation: 2H₂ → 4H⁺ + 4e⁻. Here, hydrogen gas (H₂) is split into protons (H⁺) and electrons (e⁻). The platinum catalyst provides a surface where this reaction can occur more readily. It achieves this by offering a site for the hydrogen molecules to adsorb, which is the first step in the breakdown process. This adsorption allows the hydrogen atoms to lose their electrons, forming protons and free electrons.
The efficiency of this process is crucial for the overall performance of the fuel cell. Platinum catalysts excel at facilitating the transfer of these electrons, which are then collected and used to generate electrical current. This electron transfer is a key aspect of the fuel cell's operation, as it directly contributes to the production of electricity. The more efficient the catalyst, the higher the power output of the fuel cell, making platinum an indispensable component in the design and construction of fuel cell systems.
Furthermore, the durability of platinum catalysts is an essential consideration. These catalysts need to withstand the harsh conditions within the fuel cell, including high temperatures and pressures, as well as the corrosive environment of the electrolyte. Platinum's stability and resistance to poisoning by carbon monoxide, a common byproduct of the fuel cell reaction, make it an ideal choice. Its ability to maintain its catalytic activity over extended periods ensures the long-term reliability of fuel cell vehicles.
In summary, platinum catalysts play a critical role in the operation of fuel cells by enabling the efficient breakdown of hydrogen. This process is essential for the generation of electricity, as it facilitates the transfer of electrons, which are harnessed to produce power. The unique properties of platinum, including its catalytic activity and stability, make it a key enabler in the development of clean and efficient transportation technologies.
Car Allowance Fuel Coverage: Navigating the Cost of Commuting
You may want to see also

Electricity Generation: Electrons flow through an external circuit, powering the car's electrical systems
The process of electricity generation in a fuel cell vehicle involves a unique and efficient method of converting chemical energy into electrical power. When a fuel cell car is in operation, the primary goal is to produce electricity to power the vehicle's electrical systems, including the motor, lights, and accessories. This is achieved through a complex interplay of chemical reactions and electrical processes.
At the heart of this system is the fuel cell stack, which consists of multiple individual fuel cells. Each fuel cell is a miniature power plant, where a chemical reaction occurs between oxygen and hydrogen. This reaction is facilitated by a catalyst, typically made of platinum, which accelerates the process. The hydrogen fuel is supplied to the anode (positive electrode) of the fuel cell, while oxygen from the air is fed to the cathode (negative electrode).
The chemical reaction at the anode produces protons and electrons. These electrons are then directed through an external circuit, which is connected to the fuel cell stack. As the electrons flow, they generate an electric current, providing the power needed to operate the car's electrical components. The protons, meanwhile, migrate through a special membrane, which acts as a selective barrier, allowing only protons to pass while blocking electrons.
The oxygen that is not consumed in the reaction at the anode is expelled through the vehicle's exhaust system. This process is highly efficient, producing electricity with minimal waste and no direct emissions of pollutants. The electricity generated is then used to power the electric motor, which drives the wheels and propels the vehicle forward.
In summary, the electricity generation in fuel cell cars is a result of the electron flow through an external circuit. This flow is driven by the chemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen, which occurs at the fuel cell stack. The electrons, after facilitating this reaction, are harnessed to power the car's electrical systems, showcasing a clean and innovative approach to vehicle propulsion.
F1 Fuel Strategy: Do Pit Stops Require Refueling?
You may want to see also

Energy Conversion: Chemical energy is converted to electrical energy with high efficiency
Fuel cells are innovative devices that play a crucial role in the development of electric vehicles, offering a clean and efficient alternative to traditional internal combustion engines. The primary function of a fuel cell is to generate electricity through a chemical reaction, converting the chemical energy stored in fuel, typically hydrogen, into electrical energy. This process is highly efficient and produces minimal environmental impact, making it an attractive option for sustainable transportation.
At the heart of a fuel cell's energy conversion process is the electrochemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen. When hydrogen fuel enters the cell, it undergoes a redox reaction, releasing electrons and forming water as a byproduct. This reaction is facilitated by a catalyst, often made of precious metals like platinum, which accelerates the chemical transformation. The electrons released during this reaction are captured and directed through an external circuit, creating an electric current. This current can then power an electric motor, which drives the vehicle's wheels, or it can be used to charge a battery, providing additional energy storage.
The efficiency of this energy conversion is remarkable. Fuel cells can achieve power conversion efficiencies of up to 60%, significantly higher than the typical 20-30% efficiency of internal combustion engines. This higher efficiency is due to the direct conversion of chemical energy to electrical energy, bypassing the less efficient step of converting chemical energy to thermal energy and then to mechanical work, as in conventional engines.
Furthermore, the environmental benefits of this process are substantial. The only byproduct of the chemical reaction is water vapor, making fuel cell vehicles virtually emission-free. This is in stark contrast to gasoline or diesel engines, which release pollutants such as nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide, and particulate matter. By eliminating these harmful emissions, fuel cell technology contributes to improved air quality and reduced environmental impact.
In summary, fuel cells revolutionize the way chemical energy is converted into electrical energy, offering a highly efficient and environmentally friendly solution for powering vehicles. The direct conversion process, coupled with the absence of combustion, results in a cleaner and more sustainable approach to transportation, making fuel cell cars a promising technology for the future of green mobility.
The Truth About Water-Powered Cars: Can You Buy One?
You may want to see also

Environmental Impact: Zero emissions make fuel cell cars environmentally friendly
The environmental benefits of fuel cell vehicles are significant, primarily due to their zero-emission nature. Unlike traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles, fuel cell cars produce no direct exhaust emissions, making them a cleaner and more sustainable transportation option. This is a crucial advantage in the fight against air pollution and climate change.
At the heart of a fuel cell car's power generation is the fuel cell stack, which is the core component responsible for converting chemical energy into electrical energy. This process involves the reaction of hydrogen fuel and oxygen from the air, producing electricity, water, and heat. The key advantage here is that the only byproduct of this reaction is water vapor, which is harmless to the environment. This is in stark contrast to ICE vehicles, which emit a range of pollutants, including carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter, contributing to air pollution and global warming.
The environmental impact of fuel cell cars extends beyond their zero-emission tailpipe. The production and transportation of hydrogen fuel also need to be considered. While some hydrogen is produced through carbon-intensive processes, such as steam methane reforming, there is a growing trend towards using renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar power, to generate hydrogen. This 'green' hydrogen production method significantly reduces the carbon footprint of the entire fuel cell vehicle system.
Furthermore, the infrastructure required to support fuel cell cars is also becoming more environmentally friendly. The development of hydrogen refueling stations, for example, can be designed with energy-efficient and sustainable practices in mind. These stations can utilize renewable energy sources to power the hydrogen compression and dispensing processes, further reducing the overall environmental impact.
In summary, fuel cell cars offer a promising solution to reduce the environmental impact of transportation. Their zero-emission nature, coupled with the potential for green hydrogen production and sustainable infrastructure, makes them a key player in the transition to a cleaner and more sustainable future. As technology advances and infrastructure improves, fuel cell vehicles could play a significant role in mitigating the environmental challenges associated with conventional transportation methods.
External Fuel Filter: How to Check Your Car's Filter
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Fuel cells in electric vehicles (EVs) generate electricity through a chemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen. This process occurs within the fuel cell stack, which is the heart of the fuel cell system. The fuel cell stack consists of multiple fuel cell units, each containing an anode (negative electrode), a cathode (positive electrode), and an electrolyte membrane. When hydrogen fuel is supplied to the anode, it undergoes oxidation, releasing electrons and forming protons. These electrons flow through an external circuit, providing the electricity needed to power the vehicle's electric motor and other accessories. The protons, along with electrons, travel through the electrolyte membrane to reach the cathode. At the cathode, oxygen from the air combines with the protons and electrons to form water, completing the reaction. This efficient and clean process allows fuel cell EVs to produce electricity with minimal environmental impact.
Hydrogen fuel cell cars offer several advantages over traditional internal combustion engine vehicles. Firstly, they produce electricity through a zero-emission process, as the only byproduct is water vapor, making them environmentally friendly. This is a significant improvement over gasoline or diesel engines, which release harmful pollutants like carbon dioxide and nitrogen oxides. Secondly, hydrogen fuel cells provide a high energy density, allowing for longer driving ranges compared to battery-electric vehicles. This is particularly beneficial for long-distance travel and reduces the anxiety associated with running out of power. Additionally, hydrogen refueling is relatively quick, taking only a few minutes, which is comparable to the time required for gasoline refueling.
The electrolyte is a critical component in a fuel cell's electricity generation process. It is a thin, permeable membrane that separates the anode and cathode compartments within the fuel cell stack. The primary function of the electrolyte is to facilitate the movement of protons (H+) from the anode to the cathode while preventing the flow of electrons. This is achieved through the unique properties of the electrolyte material, often a polymer or ceramic compound. As the protons migrate through the electrolyte, they carry electrons from the anode to the cathode, creating a flow of electricity. The electrolyte also helps maintain the chemical balance between the two electrodes, ensuring the efficient operation of the fuel cell. This design allows for the direct conversion of chemical energy from hydrogen into electrical energy, making fuel cells a highly efficient power source for vehicles.







