There are many types of car fuels available today, each with its own benefits and drawbacks. The most common type of fuel vehicle is the gasoline-powered car. However, gasoline has some disadvantages as it is a non-renewable resource and produces harmful emissions when burned. Diesel is another type of fuel that is made from the fractional distillation of crude oil. Ethanol and biodiesel were some of the first automobile fuels, but they were replaced by gasoline and diesel fuel by the early 1900s. Today, most of the motor gasoline sold in the United States contains up to 10% ethanol by volume.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Non-renewable | Gasoline |
| Renewable | Ethanol, biodiesel |
| Complex refining process | Gasoline |
| High energy consumption | Gasoline |
| High emissions | Gasoline |
| Low cost | Gasoline |
| High availability | Gasoline |
| Popular choice | Gasoline |
| Made from crude oil | Gasoline, diesel |
| Contains ethanol | Gasoline |
| Blended with petroleum diesel | Biodiesel |
| Energy content | Gasoline (52%), diesel (23%) |
| Environmental impact | Gasoline |
| Fuel economy | Improved over time |
| Types of fuel | Gasoline, diesel, electric, methanol, propane, ethanol, compressed and liquefied natural gas, hybrid electricity, biodiesel, hydrogen fuel cells |
What You'll Learn
- Gasoline is the dominant transportation fuel in the United States
- Gasoline is a non-renewable resource and produces harmful emissions
- Diesel is a type of fuel that is made from crude oil
- Alternative fuels include methanol, propane, ethanol, compressed and liquefied natural gas
- Electric vehicles are powered by electricity and hybrid vehicles

Gasoline is the dominant transportation fuel in the United States
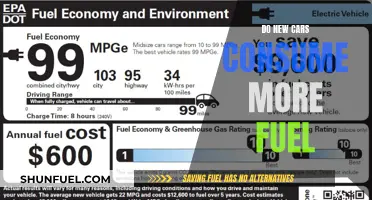
The national average fuel economy for light-duty vehicles (passenger cars, pickup trucks, vans, sport utility vehicles, and crossover vehicles) has improved over time mainly because of the fuel economy standards the federal government established for those types of vehicles. However, total motor gasoline consumption for transportation has generally increased after fuel economy standards were set because of increases in the number of vehicles in use—especially light pickup trucks, minivans, sport utility vehicles, and crossover vehicles, which have lower fuel economy than many passenger cars—and in the number of miles traveled per vehicle.
Gasoline also has some disadvantages. It is a non-renewable resource, which means that it is not sustainable in the long-term. Gasoline also produces harmful emissions when burned, which can contribute to air pollution and climate change. Additionally, the refining process of gasoline is relatively complex and requires large amounts of energy. Overall, gasoline is a popular car fuel choice due to its availability and relatively low cost. However, it is important to consider its environmental impact and non-renewable nature when deciding whether it is the right fuel for you.
Ethanol and biodiesel were some of the first automobile fuels, but they were replaced by gasoline and diesel fuel made from crude oil by the early 1900's. Today, most of the motor gasoline sold in the United States contains up to 10% ethanol by volume. Most biodiesel and renewable diesel fuel is blended with petroleum diesel. In 2022, total biofuels consumption accounted for about 6% of total U.S. transportation sector energy consumption. Ethanol's share was about 4%, and the share of biodiesel, renewable diesel, and other biofuels combined was about 2%.
Infiniti Fuel Pumps: Powering the Luxury Brand's Performance
You may want to see also

Gasoline is a non-renewable resource and produces harmful emissions
The refining process of gasoline is complex and requires large amounts of energy. This is because gasoline is made from crude oil, which is a non-renewable resource. The refining process of gasoline is also relatively complex and requires large amounts of energy. This is because gasoline is made from crude oil, which is a non-renewable resource.
Gasoline is a popular car fuel choice due to its availability and relatively low cost. However, it is important to consider its environmental impact and non-renewable nature when deciding whether it is the right fuel for you.
The alternative fuels that are being explored by the Department of Energy include: methanol, propane, ethanol, compressed and liquefied natural gas, electricity, hybrid electricity, biodiesel, and hydrogen fuel cells. These alternative fuels are being explored as a way to reduce the environmental impact of gasoline and move towards a more sustainable future.
Empty Old Fuel: A Step-by-Step Guide to Car Maintenance
You may want to see also

Diesel is a type of fuel that is made from crude oil
Diesel is a high-volume product of oil refineries. In many countries, diesel fuel is standardized. For example, in the European Union, the standard for diesel fuel is EN 590. Ultra-low-sulfur diesel (ULSD) is a diesel fuel with substantially lowered sulfur contents. As of 2016, almost all of the petroleum-based diesel fuel available in the United Kingdom, mainland Europe, and North America is of a ULSD type.
Alternatives that are not derived from petroleum, such as biodiesel, biomass to liquid (BTL) or gas to liquid (GTL) diesel are increasingly being developed and adopted. To distinguish these types, petroleum-derived diesel is sometimes called petrodiesel in some academic circles.
Electric Revolution: Unveiling the Fossil-Free Future of Cars
You may want to see also

Alternative fuels include methanol, propane, ethanol, compressed and liquefied natural gas
The Department of Energy is actively exploring alternative fuels that can be used in cars. These include methanol, propane, ethanol, compressed and liquefied natural gas, electricity, hybrid electricity, biodiesel, and hydrogen fuel cells.
Ethanol and biodiesel were some of the first automobile fuels, but they were replaced by gasoline and diesel fuel made from crude oil by the early 1900s. Today, most of the motor gasoline sold in the United States contains up to 10% ethanol by volume. Most biodiesel and renewable diesel fuel is blended with petroleum diesel. In 2022, total biofuels consumption accounted for about 6% of total U.S. transportation sector energy consumption. Ethanol's share was about 4%, and the share of biodiesel, renewable diesel, and other biofuels combined was about 2%.
Gasoline is the dominant transportation fuel in the United States, followed by distillate fuels (mostly diesel fuel) and jet fuel. Gasoline includes motor gasoline and aviation gasoline. On an energy content basis, gasoline (excluding fuel ethanol) accounted for 52% of total energy consumption by the U.S. transportation sector in 2022. Distillate fuels, mostly diesel (excluding biofuels blended with diesel), accounted for 23%, and jet fuel accounted for 12%.
Gasoline is a non-renewable resource and produces harmful emissions when burned, which can contribute to air pollution and climate change. The refining process of gasoline is relatively complex and requires large amounts of energy. Overall, gasoline is a popular car fuel choice due to its availability and relatively low cost. However, it is important to consider its environmental impact and non-renewable nature when deciding whether it is the right fuel for you.
Diesel is a type of fuel that is made from the fractional distillation of crude oil, similar to gasoline.
Troubleshooting: Revive Your Ride with These Steps to Start a Car with a Bad Fuel Filter
You may want to see also

Electric vehicles are powered by electricity and hybrid vehicles
The most common type of fuel vehicle is the gasoline-powered car. However, gasoline is a non-renewable resource and produces harmful emissions when burned, which can contribute to air pollution and climate change. Diesel is a type of fuel that is made from the fractional distillation of crude oil, similar to gasoline.
The national average fuel economy for light-duty vehicles has improved over time, mainly because of the fuel economy standards the federal government established for those types of vehicles. However, total motor gasoline consumption for transportation has generally increased because of increases in the number of vehicles in use and in the number of miles traveled per vehicle.
The alternative fuels that are being actively explored by the Department of Energy include methanol, propane, ethanol, compressed and liquefied natural gas, electricity, hybrid electricity, biodiesel, and hydrogen fuel cells.
Unveiling the Process: How Cars Convert Fossil Fuels into Power
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
There are many types of car fuels, each with its own benefits and drawbacks. The most common type of fuel vehicle is the gasoline-powered car. Other types of fuel vehicles include diesel, electric, and those powered by compressed and liquefied natural gas.
There are many different types of car fuels because each type has its own advantages and disadvantages. For example, gasoline is a popular car fuel choice due to its availability and relatively low cost, but it is also a non-renewable resource that produces harmful emissions when burned.
Gasoline is a popular car fuel choice due to its availability and relatively low cost. It is also a dominant transportation fuel in the United States, followed by distillate fuels (mostly diesel fuel) and jet fuel.
Gasoline is a non-renewable resource that produces harmful emissions when burned, which can contribute to air pollution and climate change. The refining process of gasoline is also relatively complex and requires large amounts of energy.
The Department of Energy is actively exploring alternative fuels such as methanol, propane, ethanol, compressed and liquefied natural gas, electricity, hybrid electricity, biodiesel, and hydrogen fuel cells.