The fuel pressure on a 93 Ford F150 is a common issue among enthusiasts of the vehicle. The fuel pressure is typically measured in pounds per square inch (PSI) and can be tested using a fuel pressure gauge. The optimal fuel pressure for a 93 F150 with a 4.9 engine is between 55 and 60 PSI at idle. However, there have been reports of individuals measuring fuel pressures as low as 30 PSI, which is considered too low and may result in poor engine performance. In some cases, the fuel pressure regulator may need to be replaced if it is not functioning properly. Additionally, issues with the fuel pump, fuel filter, or fuel injectors can also impact fuel pressure and engine performance.
What You'll Learn

Fuel pressure gauge readings
To check the fuel pressure on a 1993 Ford F150, you will need to use a fuel pressure gauge. This can be hooked up to the fuel rail, which has a schrader valve. The schrader valve is located towards the back of the engine, on the firewall.
Once the gauge is hooked up, the pressure can be read. For a 4.9L engine, the pressure should be around 50-60 PSI, while for a V8 engine, it should be 32-40 PSI (32 at idle, 40 WOT). If the pressure is lower than expected, it could indicate a problem with the fuel pump or a blockage in a filter.
It is important to note that the fuel pressure regulator also plays a role in maintaining the correct fuel pressure. The regulator should produce 55-60 PSI at idle for a 4.9L engine, and 39 PSI for a V8 engine.
When testing the fuel pressure, the key should be turned on, and the fuel pressure gauge should be connected to the schrader valve. The fuel pump will need to be running to build up pressure. The pressure can then be read on the gauge.
Some additional steps may be required to prepare the vehicle for the fuel pressure test, such as ensuring the battery is charged and checking for any applicable trouble codes. It is also important to follow safety precautions when working with fuel and electricity.
Understanding Bosch K-Jetronic Fuel Pressure Systems
You may want to see also

Fuel pump issues
The fuel pressure on a 1993 Ford F-150 with a 4.9L engine should be around 50-60 PSI, with 30 PSI being far too low. If you are experiencing issues with your fuel pump, there are a few things you can check.
Firstly, check that you are actually getting fuel to your injectors. If you are, then the next step is to check your fuel pressure. This can be done by hooking a fuel pressure gauge to the fuel rail and grounding pin #6 of the self-test plug. You can then turn on the key and read the pressure on the gauge. If the pressure is low, it could be due to a faulty fuel pump or a blocked fuel filter.
If your fuel pump is not working, there are a few things you can check to try and diagnose the issue. Firstly, check the wiring, especially where it leads up to and connects to the relay. It may also be the relay itself that is faulty. You can also check to see if you have power to the Inertia Switch, as this is the last connection before power goes to the fuel pump. If you have voltage to the pump connector but the pump is still not working, it could be a bad ground. Try jumping from the ground in the connector to the frame.
If your 1993 Ford F-150 has dual tanks, you may experience an issue where fuel runs from one tank to the other and then overflows. This is due to a defective return flow check valve in the tank. This was the subject of a recall, so you should be able to get this issue fixed free of charge.
Understanding Fuel Line Pressure in 1988 D100 V6 Engines
You may want to see also

Fuel filter problems
The fuel filter on a 1993 Ford F150 is located amidships on the left frame rail. The filter should be changed every 15,000 miles (24,000 km) or 15 months, whichever comes first. It is important to relieve the fuel system pressure before removing the old filter. This can be done by using a Schrader valve on the fuel rail, pulling the fuel pump relay and attempting to start the engine, flipping the inertia switch, or using a fuel pressure gauge.
There is a retainer clip on both ends of the fuel filter, and a special tool is required to remove them. Alternatively, some people choose to force them off with their fingers. It is important to be cautious when removing the old filter, as there is still fuel inside, and to make sure that the new filter is installed with the arrow pointing in the correct direction.
Some common problems with the fuel filter on the 1993 Ford F150 include difficulty removing the old filter, fuel leaks, and low fuel pressure. It is important to address any fuel leaks immediately, as fuel is highly flammable and can pose a serious safety hazard. Low fuel pressure can be caused by a faulty fuel pump or a clogged fuel filter, and it can result in rough idling, difficulty starting the engine, and poor engine performance.
Understanding Fuel Injector Pressure Regulators: Performance and Control
You may want to see also

Fuel pressure regulator issues
The fuel pressure on a 1993 Ford F-150 with a 4.9L engine should be around 50-60 PSI. However, issues with the fuel pressure regulator can cause deviations from this standard.
The fuel pressure regulator is responsible for maintaining the correct fuel pressure and ensuring the engine receives the right amount of fuel. When it malfunctions, it can cause a range of issues, including:
Engine Performance Issues
A faulty fuel pressure regulator can lead to hard-starting, rough idling, stalling, and a lack of power. The engine may struggle to crank due to insufficient fuel pressure or flood with excess fuel.
Illuminated Check Engine Light
The car's computer systems can detect engine performance problems and trigger the check engine light. However, since various issues can activate this light, further diagnostics are required to confirm a faulty fuel pressure regulator.
Black Smoke from the Exhaust
If the fuel pressure is too high, the injectors will send an excess of fuel to the chamber, resulting in incomplete combustion and black smoke.
Fuel Dripping from the Tailpipe
When extra fuel is pumped into the chamber, it may not burn completely and can drip out of the exhaust pipe.
Engine Backfires
A bad regulator can allow too much fuel into the engine, causing fuel to leak into the exhaust headers and combust, resulting in backfires.
Fuel Leakage
A broken diaphragm or seals in the fuel pressure regulator can cause fuel to leak, often accompanied by a strong fuel smell.
Fuel in the Vacuum Hose
When the diaphragm breaks, fuel can leak into the vacuum hose, which maintains negative pressure within the vehicle.
Reduced Fuel Efficiency
Improper fuel pressure can cause an unbalanced air-fuel ratio, leading to reduced fuel efficiency as the engine has to work harder.
Noisy Fuel Pump
Low fuel pressure can cause the fuel pump to strain, resulting in a loud whining sound as it draws fuel from the tank.
The Power of Pressurized Water Reactors: Fuel Choice
You may want to see also

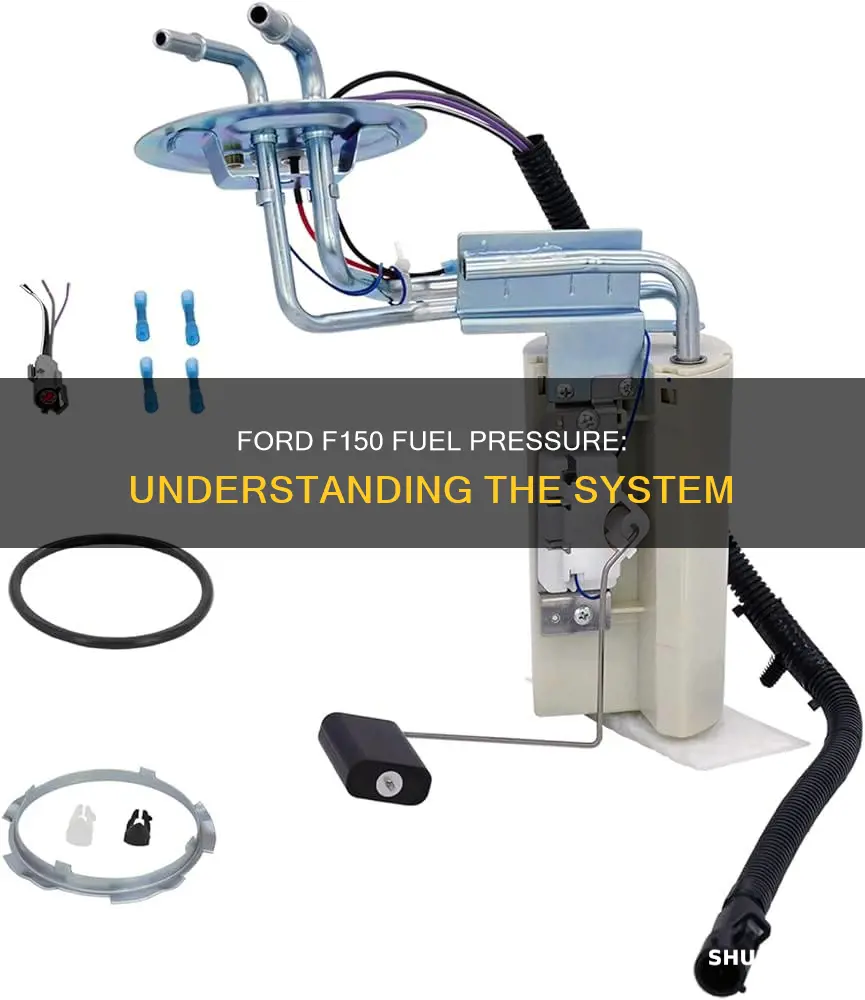
Fuel pump replacement
Step 1: Prepare your vehicle
Park your Ford F150 on a flat and safe surface and turn off the engine. If you have a dual-tank model, you will need to know which tank has the faulty fuel pump.
Step 2: Remove fuel from the tank
Before removing the fuel tank, you must siphon the gas out using a clear hose and an air pump. This step is essential for safety and to avoid spills.
Step 3: Elevate your truck
Use a standard jack to raise your truck to a height of at least 18 inches from the ground. Place the jack in the grooves along the frame of your truck. If your truck is already lifted, you may skip this step.
Step 4: Remove the heat shield
Crawl under the truck and locate the heat shield protecting the fuel pump. Use an impact wrench to remove the bolts holding the heat shield in place. Be careful not to remove the bolts for the tank straps. Once the bolts are removed, slowly remove the heat shield and set it aside.
Step 5: Remove the fuel tank
Place two floor jacks underneath the fuel tank to support it as you remove its bolts. Use an impact wrench to remove the four long bolts from the fuel tank. Loosen and twist off the straps, being careful not to force them to avoid damaging the mounting point. Set the straps and bolts aside.
With the help of an assistant, slowly lower the jacks while you hold the fuel tank. Disconnect the fuel fill line using a 1/4 inch hex socket. Once disconnected, carefully pull the fuel tank out from under the truck.
Step 6: Locate and clean the fuel pump module
Look for the round fuel pump module bolted onto the top of the fuel tank. Disconnect the fuel outlay and relay lines, as well as the evaporative hoses, from the module. Use safety clips or a 3/8" Ford Fuel Line Disconnect Tool to detach the hard-to-remove fuel lines. Clean off any dust and dirt from the top of the module with a plastic brush to prevent debris from falling into the tank.
Step 7: Remove the old fuel pump assembly
Use an 8mm wrench to remove the bolts attaching the fuel pump module to the tank. If the unit is stuck to the rubber seal, carefully pry it up with a flathead screwdriver. Lift the assembly out of the tank. Inspect the individual parts, such as the fuel pump, fuel sender, and strainer, and determine if they need replacement. If the pump is old, it is advisable to replace the entire unit with a new one.
Step 8: Install the new fuel pump assembly
Lower the new fuel pump assembly into the fuel tank, aligning it with the mark made in Step 6. Secure it with the screws and reconnect the outlay, relay lines, and evaporative hoses.
Step 9: Reassemble your truck
Reconnect all straps and bolts, and reattach the fuel fill line. Ensure that your fuel tank is securely mounted before lowering your truck from the jacks.
Notes and Precautions:
- This procedure requires working underneath your vehicle and handling fuel system components. Always prioritize your safety and follow proper procedures to avoid accidents or injuries.
- Some connections and bolts may be rusty and challenging to loosen. Use appropriate tools and techniques to avoid damage.
- When cleaning the module and tank, avoid using a metallic brush as it can produce sparks, which are a safety hazard when working near the fuel tank.
Understanding the Role of Fuel Vapor Pressure Sensors
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The fuel pressure on a 93 Ford F150 should be around 55-60 PSI at idle. However, there have been reports of individuals measuring fuel pressure at 30 PSI, which is considered too low and may result in poor engine performance.
You can test the fuel pressure by connecting a fuel pressure gauge to the Schrader valve, which is located on the passenger side of the engine, near the firewall. With the key turned on, you should see instant fuel pressure on the gauge.
Low fuel pressure can be caused by a weak fuel pump, a blockage in a filter, or a faulty fuel pressure regulator. It is recommended to check fuel filters and replace them if necessary.







