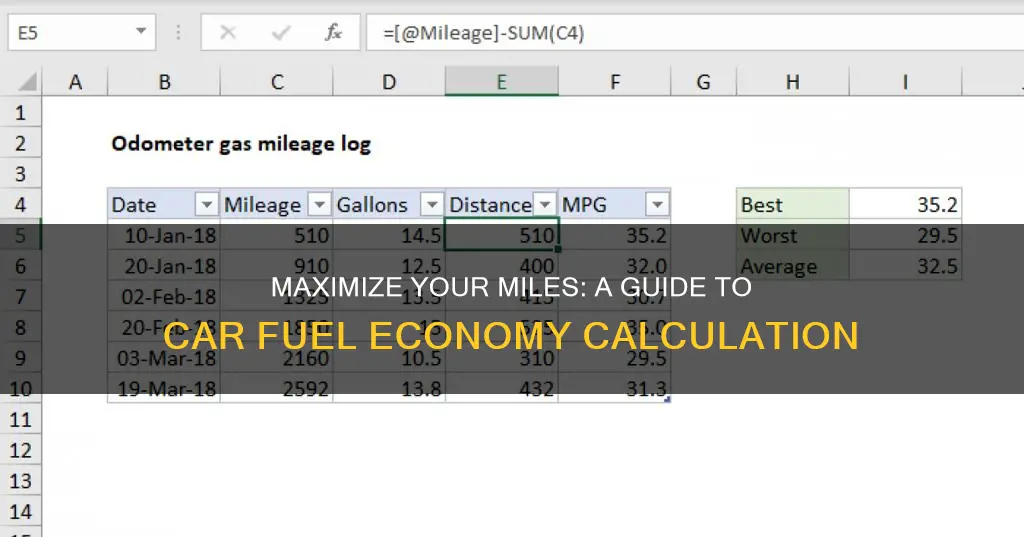
Calculating a car's fuel economy is an essential step in understanding its efficiency and performance. Fuel economy is typically measured in miles per gallon (mpg) or kilometers per liter (km/L) and represents the distance a vehicle can travel on a given amount of fuel. This metric is crucial for drivers as it directly impacts their vehicle's cost-effectiveness and environmental impact. To calculate fuel economy, you need to track the distance traveled and the amount of fuel consumed over a specific period. This can be done by manually recording data or using digital tools and apps that provide real-time fuel efficiency analysis. By following a few simple steps, you can easily determine your car's fuel economy and make informed decisions about its usage and maintenance.
What You'll Learn
- Distance and Time: Measure distance traveled and time taken to calculate fuel consumption
- Fuel Quantity: Track the amount of fuel added to the car over a period
- Engine Performance: Consider engine efficiency and power output for accurate calculations
- Environmental Factors: Account for weather, terrain, and driving conditions that affect fuel usage
- Driver Behavior: Analyze driving patterns, including speed, acceleration, and braking, to estimate fuel economy

Distance and Time: Measure distance traveled and time taken to calculate fuel consumption
To calculate fuel economy, you need to understand the relationship between distance, time, and fuel consumption. This method is a straightforward and commonly used approach to determine a vehicle's fuel efficiency. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to measure and calculate fuel consumption using distance and time:
First, you'll need to measure the distance traveled by your car. This can be done by using a trip meter, which is a built-in feature in most modern vehicles. If your car doesn't have a trip meter, you can use a simple odometer or even measure the distance manually by marking the starting and ending points and calculating the difference. Ensure you record the initial and final odometer readings or the distance marked.
Next, measure the time taken for this journey. You can use a stopwatch or a timer on your phone to record the duration. Note the start and end times of your trip, and calculate the total time taken in hours and minutes.
Now, calculate the fuel consumption. This is done by dividing the distance traveled by the amount of fuel used. Start by filling up your car's fuel tank to a known starting point, and then measure the fuel level after the trip. Calculate the difference in fuel volume, and then divide the distance traveled by this fuel consumption value. The result will give you the fuel economy in liters per 100 kilometers (L/100 km) or miles per gallon (mpg), depending on your preference.
For example, if you traveled 200 kilometers and used 5 liters of fuel, your fuel economy would be 40 L/100 km (200 km / 5 liters). This means your car consumes 40 liters of fuel to travel 100 kilometers.
It's important to note that this method provides a simple estimation of fuel economy. Factors like driving conditions, vehicle maintenance, and individual driving habits can influence the accuracy of the results. To get a more precise measurement, consider conducting multiple test drives under similar conditions and taking the average.
Is 88 Octane Fuel Right for Your Car?
You may want to see also

Fuel Quantity: Track the amount of fuel added to the car over a period
To accurately calculate your car's fuel economy, it's essential to track the amount of fuel you add to your vehicle over a specific period. This data is crucial for understanding your car's efficiency and making informed decisions about fuel usage. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to do this:
Step 1: Choose a Tracking Method
You can manually track fuel quantity by keeping a logbook or using a digital app. For a manual approach, simply record the date and the amount of fuel (in liters or gallons) you add to your car's tank each time you refuel. You can also note the initial and final fuel levels if your car has a digital fuel gauge. For digital tracking, there are numerous fuel-tracking apps available that sync with your car's fuel sensor, providing real-time data.
Step 2: Consistency is Key
Consistency is vital to obtaining accurate data. Try to track fuel quantity at the same time each time you refuel. This ensures that you're comparing like-to-like data. For instance, if you refuel in the morning, make it a habit to check the fuel level in the morning each time. This practice will help you identify any patterns or anomalies in your fuel consumption.
Step 3: Record Details
When adding fuel, record the following:
- Date and time of refueling.
- Amount of fuel added (in liters or gallons).
- Initial and final fuel levels (if applicable).
- The type of fuel used (e.g., regular, premium).
- Any relevant notes, such as weather conditions or vehicle usage (e.g., city driving, highway driving).
Step 4: Calculate and Analyze
After a month or more of consistent tracking, you can calculate your car's fuel economy. Divide the total distance traveled during the tracking period by the total fuel consumed. For example, if you traveled 1,000 miles and used 20 gallons of fuel, your fuel economy is 50 miles per gallon (mpg). Analyze this data to identify trends and factors that might affect your car's fuel efficiency.
Step 5: Compare and Improve
Compare your calculated fuel economy with the car's manufacturer-specified fuel efficiency. This comparison can help you understand if your car is performing as expected or if there are areas for improvement. You can also use this data to adjust your driving habits, such as reducing aggressive driving or optimizing your vehicle's maintenance to improve fuel economy.
Car Fuel Pump Location: Under the Hood or Behind the Seat?
You may want to see also

Engine Performance: Consider engine efficiency and power output for accurate calculations
Engine performance is a critical factor when calculating a car's fuel economy, as it directly influences how efficiently the vehicle converts fuel into power. To accurately assess fuel economy, one must consider both engine efficiency and power output. Engine efficiency refers to how effectively the engine converts the chemical energy of fuel into mechanical work. This is typically measured in terms of miles per gallon (mpg) or liters per 100 kilometers (l/100 km). Higher engine efficiency means the car can travel farther on a given amount of fuel, resulting in better fuel economy.
The power output of an engine is another crucial aspect. It represents the rate at which the engine can produce mechanical work, measured in horsepower (hp) or kilowatts (kW). A more powerful engine can accelerate the car more quickly and may offer better performance in certain driving conditions. However, increased power often comes with a higher fuel consumption rate, which can negatively impact fuel economy. Therefore, when calculating fuel economy, it's essential to consider the balance between engine power and efficiency.
To calculate fuel economy accurately, you need to understand the relationship between engine performance and fuel consumption. Start by measuring the distance traveled and the amount of fuel consumed during a specific test drive or over a period of consistent driving conditions. Then, calculate the fuel economy by dividing the distance traveled by the amount of fuel used. For instance, if a car travels 300 miles on 10 gallons of fuel, its fuel economy is 30 mpg.
Engine efficiency and power output are interconnected. Modern engines are designed to optimize both factors. For instance, some engines use advanced technologies to improve combustion efficiency, allowing more energy to be extracted from the fuel. Others may focus on reducing friction and improving the overall mechanical efficiency of the engine. These advancements contribute to better fuel economy without compromising power output.
In summary, when calculating a car's fuel economy, it is essential to consider engine performance, specifically engine efficiency and power output. Higher engine efficiency and a well-balanced power output can lead to improved fuel economy. Understanding these factors allows drivers to make informed decisions about their vehicle's performance and fuel consumption, ultimately helping them optimize their driving experience and reduce fuel costs.
Why Turning Your Car Off While Filling Up Can Be a Bad Idea
You may want to see also

Environmental Factors: Account for weather, terrain, and driving conditions that affect fuel usage
Environmental factors play a significant role in determining a car's fuel economy, and understanding these influences is crucial for accurate calculations. Weather conditions, terrain variations, and driving habits all contribute to the overall fuel consumption of a vehicle. Here's a detailed breakdown of how to account for these factors:
Weather Impact: Different weather conditions can greatly affect fuel efficiency. During colder months, engines may require more fuel to maintain optimal performance and heat the cabin. This is because the engine needs to work harder to overcome the cold, which can lead to increased fuel consumption. Similarly, in hot climates, air conditioning usage can significantly impact fuel economy. Modern vehicles often have automatic climate control systems that adjust temperature settings, and these systems can consume more fuel when set to higher temperatures. Additionally, extreme weather events like heavy rain or snow can force drivers to slow down, which may result in reduced fuel efficiency due to longer travel times and increased engine idling.
Terrain and Driving Conditions: The type of terrain and driving conditions can also influence fuel usage. Off-road driving, especially on rugged or mountainous paths, often requires more power and fuel due to the increased resistance and the need for frequent gear changes. Driving uphill contributes to higher fuel consumption as the engine must work against gravity. Conversely, driving downhill can improve fuel economy as the vehicle's speed and power requirements decrease. Urban areas with frequent stop-and-go traffic also impact fuel efficiency. Frequent acceleration and deceleration in city driving can lead to reduced fuel economy compared to steady-speed highway driving.
Driving Habits and Behavior: Driver behavior is a critical factor in fuel economy calculations. Aggressive driving, rapid acceleration, and frequent hard braking all contribute to increased fuel usage. Smooth and steady driving, on the other hand, can improve fuel efficiency. Maintaining a consistent speed and avoiding rapid changes in speed can help optimize fuel economy. Additionally, proper tire maintenance, including regular inflation checks, can reduce rolling resistance and improve overall fuel efficiency.
When calculating fuel economy, it's essential to consider these environmental and driving factors. Real-world fuel efficiency can vary significantly from the manufacturer's claimed figures due to these variables. By accounting for weather, terrain, and driving conditions, you can gain a more accurate understanding of a car's fuel efficiency and make informed decisions regarding vehicle usage and maintenance.
E85 Fuel: Which Cars Can Run on This Alternative Ethanol Blend?
You may want to see also

Driver Behavior: Analyze driving patterns, including speed, acceleration, and braking, to estimate fuel economy
Driver behavior plays a significant role in determining a vehicle's fuel economy, and analyzing driving patterns can provide valuable insights into how different driving habits impact fuel consumption. Here's a detailed breakdown of how to estimate fuel economy based on driver behavior:
Speed and Fuel Economy: One of the most critical factors influencing fuel economy is speed. As a general rule, fuel efficiency decreases significantly as speed increases. When a car accelerates, it requires more power, which translates to higher fuel consumption. For every additional mile per hour (mph) of speed, fuel efficiency tends to drop by a certain percentage. For instance, driving at 50 mph might yield a fuel economy of 30 miles per gallon (mpg), but increasing speed to 70 mph could result in a 15-20% decrease in efficiency, leading to a fuel economy of around 22-25 mpg. This relationship is often represented by a speed-efficiency curve, which can be used to estimate fuel economy at different speeds.
Acceleration and Braking: Aggressive driving, characterized by rapid acceleration and frequent braking, can significantly impact fuel economy. When a vehicle accelerates quickly, it demands more power from the engine, leading to increased fuel consumption. Similarly, hard braking requires additional energy to slow down the vehicle, resulting in wasted fuel. Smooth and gradual acceleration, combined with anticipatory braking, can help improve fuel economy. By maintaining a steady speed and avoiding sudden stops, drivers can optimize their fuel efficiency.
Driving Patterns and Efficiency: Analyzing driving patterns can reveal valuable trends in fuel economy. For example, a driver who frequently accelerates rapidly and brakes hard during city driving might experience lower fuel efficiency compared to someone who drives at a constant speed and uses smooth braking techniques. Long, steady drives on highways might yield better fuel economy due to reduced acceleration and braking demands. By studying these patterns, drivers can identify areas for improvement and make adjustments to their driving style to enhance fuel efficiency.
Data-Driven Analysis: Modern vehicles are equipped with onboard diagnostics that can provide real-time data on driving patterns. These systems can track speed, acceleration, braking intensity, and other parameters. By analyzing this data, drivers can gain a comprehensive understanding of their driving habits and their impact on fuel economy. Many vehicles also offer fuel economy estimates based on this data, providing an accurate representation of how different driving behaviors affect fuel consumption.
In summary, driver behavior is a critical component of calculating fuel economy. By understanding the relationship between speed, acceleration, braking, and fuel efficiency, drivers can make informed adjustments to their driving habits. This knowledge empowers individuals to make their vehicles more fuel-efficient, reducing environmental impact and potentially saving on fuel costs.
Unraveling the Mystery: Sudden Fuel Efficiency Drop in Cars
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Fuel economy, also known as fuel efficiency, is a measure of how efficiently a vehicle uses fuel. It is important to calculate because it helps drivers understand the cost of operating their cars, allows for better comparison of different vehicles, and provides insights into a vehicle's environmental impact.
You can calculate fuel economy by dividing the total distance traveled by the amount of fuel consumed. Keep a log of your fuel purchases and the corresponding mileage for a specific period. Then, divide the total miles driven by the total gallons of fuel used. This will give you your car's fuel economy in miles per gallon (mpg) or kilometers per liter (km/L).
Yes, there are standardized methods and formulas. One common approach is the EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) fuel economy test, which involves driving a vehicle on a specific test cycle and measuring fuel consumption. This method provides an estimated fuel economy value for the vehicle. Another approach is to use the 'mileage method' mentioned in question 2, which is a practical and widely used method for individual drivers.
Absolutely! There are several ways to improve fuel economy. Regular maintenance, such as checking tire pressure, ensuring proper engine tune-up, and using the recommended grade of motor oil, can make a significant difference. Driving habits also play a crucial role; maintaining a steady speed, avoiding rapid acceleration and braking, and using cruise control on highways can all contribute to better fuel efficiency.
It is recommended to calculate and monitor fuel economy regularly, especially if you are considering a new vehicle purchase. You can do this periodically, such as every month or after significant trips, to track changes in fuel efficiency. Regular monitoring helps identify any issues with the vehicle's performance and allows for timely maintenance, ensuring optimal fuel economy.







