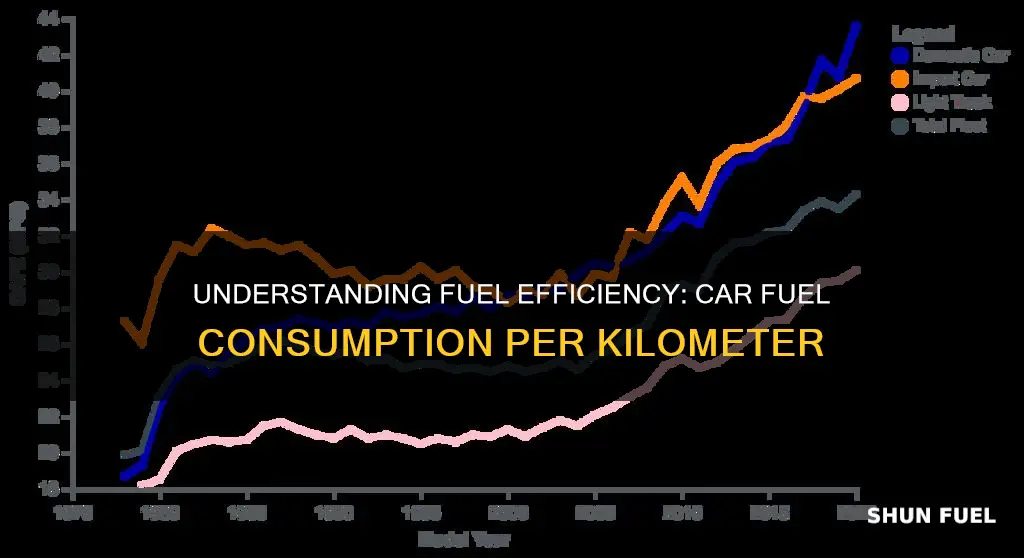
Understanding the fuel efficiency of a car is crucial for both drivers and car manufacturers. The amount of fuel a car consumes per kilometer is a key metric that determines a vehicle's environmental impact and long-term cost. This metric, often expressed in liters per 100 kilometers (l/100 km), indicates how much fuel is required to travel a certain distance. By analyzing this data, drivers can make informed decisions about their vehicle's efficiency, while manufacturers can design more sustainable and cost-effective cars.
What You'll Learn
- Fuel Efficiency Standards: Regulations set fuel efficiency targets for car manufacturers
- Engine Type and Size: Different engine types and sizes impact fuel consumption
- Driving Habits: Aggressive driving and frequent stops increase fuel usage
- Vehicle Weight and Aerodynamics: Heavier vehicles and poor aerodynamics lead to higher fuel consumption
- Tire Pressure and Maintenance: Proper tire maintenance improves fuel efficiency

Fuel Efficiency Standards: Regulations set fuel efficiency targets for car manufacturers
The concept of fuel efficiency standards is a crucial aspect of the automotive industry, aiming to reduce the environmental impact of vehicles and promote sustainable transportation. These regulations set specific targets for car manufacturers to achieve and maintain certain levels of fuel efficiency, which directly translates to lower fuel consumption per kilometer. By implementing such standards, governments worldwide are encouraging the development and production of more efficient vehicles, ultimately benefiting both the environment and consumers.
Fuel efficiency is typically measured in kilometers per liter (km/L) or miles per gallon (mpg), providing a standardized way to compare the efficiency of different vehicles. The regulations often specify a target fuel efficiency for new car models, ensuring that manufacturers design and engineer their vehicles to meet or exceed these standards. For instance, a common goal might be to achieve a certain number of kilometers per liter, meaning the car can travel a specific distance on a single liter of fuel. This approach incentivizes carmakers to invest in advanced technologies, such as improved engines, more efficient transmissions, and lightweight materials, all aimed at reducing fuel consumption.
These standards have a significant impact on the automotive market. Manufacturers are compelled to research and develop innovative solutions to meet the efficiency targets, which can lead to a range of benefits. Firstly, it encourages the production of more environmentally friendly vehicles, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution. Secondly, improved fuel efficiency translates to cost savings for consumers, as they spend less on fuel for their daily commute or long-distance travel. This aspect is particularly appealing to environmentally conscious consumers and those seeking cost-effective transportation solutions.
Regulations also drive the creation of more efficient vehicle designs and components. For instance, manufacturers might focus on optimizing engine performance, adopting hybrid or electric powertrains, or implementing advanced aerodynamics to reduce drag. These innovations not only contribute to better fuel efficiency but also enhance overall vehicle performance and driving experience. As a result, consumers benefit from a wider range of efficient vehicles, making it easier to find a car that suits their needs and preferences while also being environmentally responsible.
In summary, fuel efficiency standards play a pivotal role in shaping the automotive industry towards a more sustainable future. By setting clear targets, governments can encourage manufacturers to invest in research and development, ultimately resulting in vehicles that consume less fuel per kilometer. This not only benefits the environment by reducing emissions but also empowers consumers with cost-effective and efficient transportation options. Such regulations are a powerful tool in the global effort to combat climate change and promote a greener approach to mobility.
Flex Fuel Flexibility: Can Your Car Run on Regular Gas?
You may want to see also

Engine Type and Size: Different engine types and sizes impact fuel consumption
The relationship between engine type and size and fuel consumption is a critical aspect of understanding a vehicle's efficiency. Different engine configurations have varying impacts on how much fuel a car uses per kilometer, and this is a key factor in determining a vehicle's overall performance and environmental impact.
Firstly, let's consider the impact of engine displacement. Larger engines with higher displacement volumes tend to consume more fuel. This is because a larger engine has a greater capacity to burn fuel, and as a result, it requires more fuel to operate. For instance, a 3.0-liter V6 engine will generally consume more fuel than a 2.0-liter four-cylinder engine, even if they are of the same power output. This is a fundamental principle of engine design, where the volume of the combustion chamber directly influences the amount of fuel required for each power stroke.
Engine type also plays a significant role. There are various engine architectures, such as inline, V-shaped, and flat configurations, each with unique characteristics. Inline engines, for example, have cylinders arranged in a straight line, which can provide better weight distribution and often result in more efficient fuel consumption. V-shaped engines, on the other hand, have cylinders arranged in a V-formation, which can offer improved cooling and power output but may also lead to higher fuel consumption due to increased internal friction. Flat engines, or boxer engines, have cylinders arranged in two banks on opposite sides of the crankshaft, which can provide excellent balance and low-end torque but may not be as fuel-efficient as inline designs.
The complexity of the engine's design also matters. Modern engines often incorporate advanced technologies like direct fuel injection, turbocharging, and variable valve timing, which can optimize fuel consumption. For instance, turbochargers use exhaust gas energy to force more air into the engine, allowing for more efficient combustion and higher power output without significantly increasing engine size. Direct fuel injection ensures that fuel is injected directly into the combustion chamber, improving power and fuel efficiency by optimizing the fuel-air mixture.
In summary, engine type and size are crucial factors in determining a vehicle's fuel consumption. Larger engines with higher displacement volumes generally consume more fuel, while engine architecture and complexity can also impact efficiency. Modern engine technologies, such as turbocharging and direct fuel injection, offer ways to optimize fuel consumption, making it an essential consideration for both vehicle manufacturers and consumers when selecting a vehicle. Understanding these relationships can help in making informed decisions about vehicle choice and operation, contributing to more efficient and environmentally friendly transportation.
Cold Fuel's Power Boost: Time Attack Secrets Unveiled
You may want to see also

Driving Habits: Aggressive driving and frequent stops increase fuel usage
Aggressive driving and frequent stops are two common habits that significantly impact a vehicle's fuel efficiency and overall performance. These behaviors can lead to increased fuel consumption, reduced engine life, and a less enjoyable driving experience. Understanding the impact of these habits is crucial for drivers who aim to optimize their vehicle's performance and reduce fuel costs.
Aggressive driving, characterized by rapid acceleration, frequent lane changes, and high speeds, puts immense strain on a vehicle's engine and drivetrain. When a car accelerates quickly, it requires more fuel to overcome inertia and reach the desired speed. This rapid acceleration often leads to a higher engine load, causing the engine to burn more fuel. Additionally, frequent lane changes and rapid maneuvers increase aerodynamic drag, which further contributes to higher fuel consumption. Research has shown that aggressive driving can increase fuel usage by up to 50% compared to a more moderate driving style.
Frequent stops, such as at traffic lights or in heavy traffic, also play a significant role in fuel wastage. When a vehicle comes to a stop, it must idle, which means the engine continues to burn fuel even when stationary. Idling for extended periods can consume a substantial amount of fuel, especially in stop-and-go traffic conditions. Modern vehicles with advanced engine management systems can still consume a notable amount of fuel during idling, even when equipped with fuel-efficient technologies. To minimize fuel wastage, it is recommended to turn off the engine when stopped for extended periods, as restarting it uses less fuel than idling.
To improve fuel efficiency and reduce the negative impact of these driving habits, drivers can adopt several strategies. Firstly, maintaining a steady speed and avoiding rapid acceleration can significantly reduce fuel consumption. Smooth, controlled acceleration allows the engine to operate more efficiently, minimizing unnecessary fuel usage. Secondly, planning routes to avoid heavy traffic and rush hours can help reduce frequent stops and idling. Using navigation systems or traffic apps can assist in finding routes with less congestion, leading to improved fuel efficiency.
Additionally, adopting a more relaxed and patient approach to driving can have long-term benefits. Aggressive driving not only increases fuel usage but also accelerates wear and tear on the vehicle's components, potentially leading to more frequent maintenance and repairs. By driving at a moderate pace and maintaining a consistent speed, drivers can improve their overall fuel efficiency and extend the lifespan of their vehicles.
In summary, aggressive driving and frequent stops are detrimental to a vehicle's fuel efficiency. By being mindful of these driving habits and implementing strategies to improve fuel efficiency, drivers can save money on fuel costs and contribute to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly approach to transportation. Understanding the impact of driving behavior on fuel consumption is essential for every driver aiming to optimize their vehicle's performance and reduce their carbon footprint.
The Future of Fuel Cells: Are We There Yet?
You may want to see also

Vehicle Weight and Aerodynamics: Heavier vehicles and poor aerodynamics lead to higher fuel consumption
The relationship between vehicle weight and fuel efficiency is a critical aspect of automotive engineering, and it significantly impacts a car's performance and environmental footprint. Heavier vehicles require more energy to accelerate and maintain speed, which directly translates to increased fuel consumption. This is because the engine must work harder to overcome the additional mass, resulting in higher fuel usage. For every additional kilogram of weight, the car's performance is affected, and the engine has to exert more power to move the vehicle forward. This is especially noticeable when driving uphill or during rapid acceleration, where the extra weight becomes a noticeable burden on the engine.
Aerodynamics plays a pivotal role in this context as well. The design of a vehicle's body and its interaction with air significantly influence fuel efficiency. Poor aerodynamics can lead to higher fuel consumption in several ways. Firstly, when a car moves through the air, it creates drag, which is the force that opposes the vehicle's motion. This drag force increases with speed and is directly related to the car's frontal area and the shape of its body. A vehicle with a poorly designed body, such as one with protruding parts or an uneven surface, will experience more drag, requiring the engine to work harder to overcome this resistance. As a result, the car consumes more fuel to maintain a certain speed or accelerate.
The impact of weight and aerodynamics on fuel efficiency is further emphasized when considering the energy required to overcome air resistance. Heavier vehicles, due to their increased mass, need to generate more power to maintain speed, especially at higher velocities. This additional power demand directly correlates to higher fuel consumption. Similarly, a vehicle with poor aerodynamics will experience increased drag, leading to higher fuel usage as the engine struggles to propel the car forward efficiently.
In the context of fuel consumption per kilometer, these factors become even more critical. Heavier vehicles and those with poor aerodynamics will generally consume more fuel for the same distance traveled compared to lighter, more aerodynamic cars. This is because the engine's work is not just about overcoming the vehicle's weight but also about battling the forces of air resistance. As a result, optimizing vehicle weight and aerodynamics is essential for improving fuel efficiency and reducing the environmental impact of transportation.
To address these issues, automotive manufacturers are constantly innovating in design and engineering. Lighter materials and improved body designs are being utilized to reduce vehicle weight without compromising safety. Additionally, aerodynamic enhancements, such as streamlined body shapes, spoilers, and underbody covers, are being employed to minimize drag. These advancements not only improve fuel efficiency but also contribute to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly approach to automotive design.
Unnecessary Fuel Conditioners: A Waste of Money on New Cars?
You may want to see also

Tire Pressure and Maintenance: Proper tire maintenance improves fuel efficiency
Proper tire maintenance is an often-overlooked aspect of vehicle care, but it plays a significant role in improving fuel efficiency and overall performance. One of the most critical aspects of tire maintenance is maintaining the correct tire pressure. When tires are underinflated, they experience increased rolling resistance, which directly impacts fuel consumption. Underinflated tires have a larger contact patch with the road, leading to more friction and energy loss. This results in the engine working harder to propel the vehicle forward, ultimately leading to higher fuel consumption.
The ideal tire pressure for your vehicle can be found in the owner's manual or on a sticker inside the car door jamb. It is essential to check the pressure regularly, as it can change with temperature fluctuations. For instance, tires tend to lose pressure during the summer months due to the heat, so it's a good practice to check and adjust the pressure monthly or before long trips. Investing in a tire pressure gauge and learning how to use it properly is a valuable skill for any vehicle owner.
Maintaining proper tire pressure has multiple benefits. Firstly, it ensures a smoother ride, as properly inflated tires absorb road imperfections more effectively, reducing the impact on the vehicle's suspension. Secondly, it improves traction, especially in adverse weather conditions, making the vehicle safer to drive. Additionally, keeping tires inflated to the recommended pressure can extend their lifespan, saving money in the long run, as underinflated tires wear out faster and may require premature replacement.
Beyond tire pressure, regular tire maintenance is crucial. This includes rotating the tires to ensure even wear, especially if the vehicle has a front-wheel or rear-wheel drive system. Uneven tire wear can lead to reduced fuel efficiency and compromised handling. Additionally, keeping the tires clean and free from debris is essential, as dirt and grime can affect traction and tire performance.
In summary, proper tire maintenance is a simple yet effective way to improve fuel efficiency and overall vehicle performance. By ensuring correct tire pressure and implementing regular maintenance practices, drivers can enjoy a smoother, safer, and more economical driving experience. It is a cost-effective measure that every vehicle owner should prioritize to maximize the efficiency of their cars and contribute to a greener, more sustainable approach to transportation.
Can You Refuel a Running Car? Unlocking the Mystery
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Fuel consumption is typically measured in liters per 100 kilometers (l/100 km) or liters per kilometer (l/km). This means that for every 100 kilometers driven, a certain amount of fuel is used.
Several factors can affect a vehicle's fuel efficiency. These include the car's engine size and type, driving habits (such as acceleration and deceleration), vehicle weight, tire pressure, and aerodynamic design. Maintaining regular vehicle maintenance, such as engine tune-ups and using the recommended grade of motor oil, can also improve fuel efficiency.
There are several strategies to minimize fuel consumption. Some common practices include: maintaining steady speeds to avoid unnecessary gas usage, planning routes to minimize stop-and-go traffic, using cruise control on highways, ensuring proper tire inflation, removing unnecessary weight from the car, and adopting a more fuel-efficient driving style. Additionally, regular vehicle maintenance and keeping the engine tuned can also contribute to better fuel economy.







