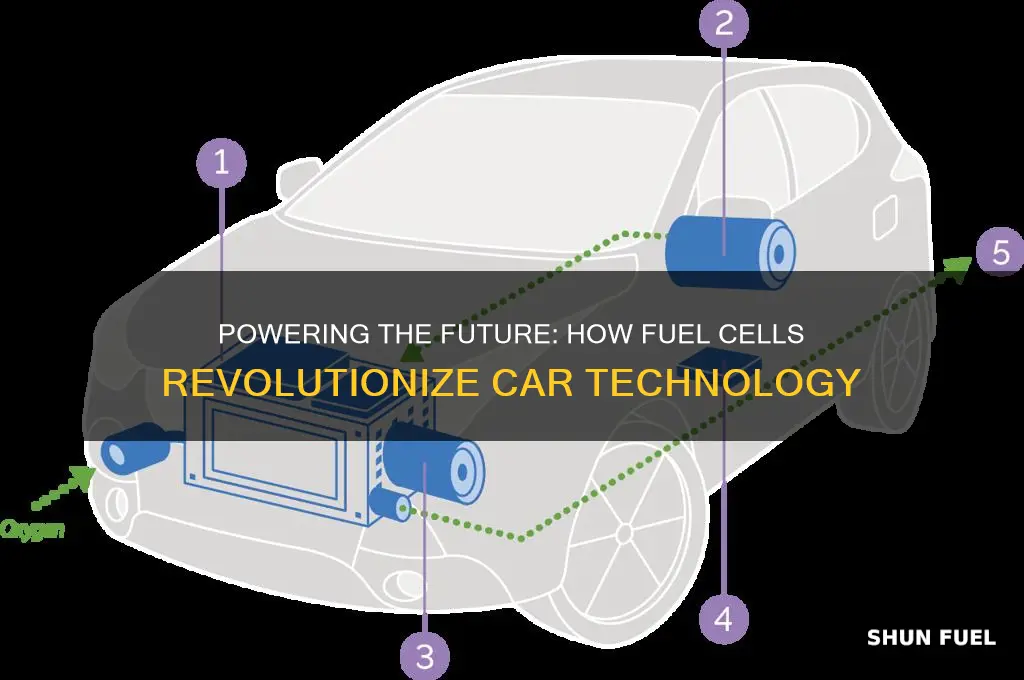
Fuel cells are an innovative technology that has the potential to revolutionize the automotive industry. These devices convert chemical energy from a fuel, typically hydrogen, directly into electricity through a process called electrochemical reaction. In cars, fuel cells serve as a clean and efficient power source, offering an alternative to traditional internal combustion engines. By utilizing the reaction between hydrogen and oxygen to produce electricity, fuel cells can power an electric motor, providing a more sustainable and environmentally friendly way to drive. This technology is a key component in the development of zero-emission vehicles, reducing the carbon footprint of the transportation sector.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Technology Type | Hydrogen fuel cell |
| Energy Conversion | Electrochemical reaction of hydrogen and oxygen to produce electricity, heat, and water |
| Power Output | Typically 50-150 kW for vehicles, with higher power outputs possible in larger systems |
| Efficiency | Around 60-65% efficiency in converting chemical energy to electrical energy |
| Energy Storage | Limited by the amount of hydrogen stored, usually in high-pressure tanks |
| Performance | Instant torque, smooth acceleration, and quiet operation |
| Range | Varies, but typically around 300-400 miles on a full tank of hydrogen |
| Refueling Time | Similar to conventional vehicles, typically under 5 minutes |
| Emissions | Only water vapor and warm air are emitted, making it an environmentally friendly technology |
| Cost | High upfront cost, but potentially lower operating costs compared to internal combustion engines |
| Infrastructure | Requires hydrogen refueling stations, which are still developing in many regions |
| Applications | Primarily used in electric vehicles (EVs) for range extension or as a standalone power source |
| Challenges | High cost of hydrogen production and storage, need for infrastructure development, and public perception |
| Advantages | Zero direct emissions, high energy density, rapid refueling, and low operating costs over time |
What You'll Learn
- Fuel Cell Technology: Converts chemical energy from hydrogen and oxygen into electricity, powering electric vehicles
- Efficiency: Fuel cells offer high efficiency, converting over 60% of energy into power, compared to 20-30% for internal combustion engines
- Zero Emissions: Emits only water and warm air, making fuel cell cars environmentally friendly and zero-emission vehicles
- Performance: Provides instant torque, resulting in quick acceleration and smooth driving experience
- Refueling: Similar to conventional cars, fuel cell vehicles can be refueled with hydrogen in minutes, offering convenience

Fuel Cell Technology: Converts chemical energy from hydrogen and oxygen into electricity, powering electric vehicles
Fuel cell technology is a fascinating and innovative approach to powering electric vehicles, offering a clean and efficient alternative to traditional internal combustion engines. This technology harnesses the power of chemical reactions to generate electricity, providing a sustainable and environmentally friendly solution for transportation.
At its core, a fuel cell is an electrochemical device that converts chemical energy from hydrogen and oxygen into electricity through a process known as electrolysis. This process involves the movement of electrons, creating a flow of electric current. The key components of a fuel cell system include the fuel cell stack, a reformer, and an air supply system. The fuel cell stack is the heart of the system, where the chemical reaction takes place. It consists of multiple fuel cell units, each containing an anode and a cathode, separated by an electrolyte membrane. When hydrogen gas is supplied to the anode and oxygen (from air) to the cathode, a series of electrochemical reactions occur.
During these reactions, hydrogen molecules split into protons and electrons at the anode. The protons pass through the electrolyte membrane, while the electrons are directed through an external circuit, generating an electric current. This current powers the vehicle's electric motor, providing the necessary energy for propulsion. The oxygen, in the form of oxygen gas, reacts with the protons and electrons at the cathode, forming water as a byproduct. This water is then released into the atmosphere, making the process environmentally friendly.
The beauty of fuel cell technology lies in its ability to produce electricity on-demand, similar to a battery. However, unlike batteries, fuel cells do not store energy but rather generate it continuously as long as hydrogen is supplied. This makes fuel cell vehicles highly efficient and capable of providing a consistent power output. Additionally, fuel cells offer a longer driving range compared to conventional electric vehicles powered by lithium-ion batteries, making them a viable option for long-distance travel.
In summary, fuel cell technology in cars utilizes the conversion of chemical energy from hydrogen and oxygen into electricity, offering a sustainable and efficient power source. This technology has the potential to revolutionize the automotive industry, providing clean transportation options and reducing our reliance on fossil fuels. With ongoing research and development, fuel cell vehicles are becoming increasingly practical and accessible, paving the way for a greener future.
Fuel Filter: To Shut Off or Not to Shut Off?
You may want to see also

Efficiency: Fuel cells offer high efficiency, converting over 60% of energy into power, compared to 20-30% for internal combustion engines
Fuel cells have revolutionized the automotive industry by offering a highly efficient power source for vehicles, particularly in the context of electric mobility. One of the most significant advantages of fuel cells is their ability to convert a substantial amount of chemical energy into electrical power, resulting in remarkable efficiency.
In contrast to traditional internal combustion engines, fuel cells demonstrate a far superior energy conversion rate. While internal combustion engines typically convert only 20-30% of the energy stored in fuel into useful power, fuel cells can achieve an impressive efficiency of over 60%. This higher efficiency is primarily due to the direct conversion of chemical energy from hydrogen and oxygen into electricity through an electrochemical process. The reduced energy loss associated with fuel cells is a game-changer for the automotive sector, as it translates to more power output and improved overall performance.
The high efficiency of fuel cells is a result of their clean and efficient combustion process. Unlike traditional engines, fuel cells do not rely on the combustion of gasoline or diesel, which involves complex processes with inherent energy losses. Instead, they use a simple electrochemical reaction, where hydrogen gas is combined with oxygen from the air to produce electricity, water, and heat. This direct conversion process minimizes energy waste, making fuel cells a more efficient and environmentally friendly power source for vehicles.
This efficiency advantage is particularly crucial for electric vehicles (EVs) and other sustainable transportation solutions. As EVs aim to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and minimize environmental impact, fuel cells provide a powerful alternative. By offering higher efficiency, fuel cells enable EVs to travel longer distances on a single 'tank' of fuel, addressing range anxiety and making them more practical for everyday use.
In summary, fuel cells' exceptional efficiency, surpassing that of internal combustion engines, is a key factor in their growing adoption in the automotive industry. This efficiency not only translates to improved performance but also contributes to a more sustainable and environmentally conscious future for transportation.
Car Fuel Tanks: Plastic or Not? Unveiling the Truth
You may want to see also

Zero Emissions: Emits only water and warm air, making fuel cell cars environmentally friendly and zero-emission vehicles
Fuel cell technology is a clean and efficient power source for vehicles, offering a promising solution to reduce the environmental impact of transportation. One of the most significant advantages of fuel cell cars is their zero-emission nature, which sets them apart from traditional internal combustion engine vehicles. These cars produce only water and warm air as byproducts, making them environmentally friendly and contributing to a greener future.
The process begins with the fuel cell, a device that converts chemical energy from a fuel source, typically hydrogen, into electricity through an electrochemical reaction. This reaction occurs at the anode, where hydrogen gas is oxidized, releasing electrons and forming protons. These protons then migrate through a special membrane to the cathode, where they combine with oxygen from the air to form water. This electrochemical process is the key to the car's zero-emission performance.
In a fuel cell vehicle, the electricity generated is used to power an electric motor, which drives the car's wheels. This setup is in contrast to conventional cars, which burn gasoline or diesel in an engine to produce power. By utilizing hydrogen fuel, these vehicles eliminate the need for combustion, thus eliminating the emission of harmful pollutants such as carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter. This is a significant improvement over traditional vehicles, which are major contributors to air pollution and climate change.
The environmental benefits of fuel cell cars extend beyond their zero-emission nature. The production of hydrogen fuel can also be achieved through renewable energy sources, such as wind or solar power, further reducing the carbon footprint of the entire process. Additionally, the infrastructure for refueling hydrogen fuel cells is being developed, making it more convenient for drivers to adopt this technology.
In summary, fuel cell cars are a breakthrough in sustainable transportation. Their ability to produce only water and warm air as emissions makes them a key player in the fight against climate change. With ongoing advancements in technology and infrastructure, fuel cell vehicles are becoming a viable and attractive option for environmentally conscious consumers, offering a cleaner and greener way to travel.
Unlocking Power: VP Racing Fuel Compatibility for Your Car
You may want to see also

Performance: Provides instant torque, resulting in quick acceleration and smooth driving experience
The performance of fuel cell vehicles is significantly enhanced by the unique characteristics of fuel cell technology. One of the most notable advantages is the ability to provide instant torque, which translates to a remarkable acceleration and a seamless driving experience. This is a stark contrast to traditional internal combustion engines, which often require time to build up power and can feel laggy, especially at lower speeds.
Fuel cells generate electricity through a chemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen, producing water and electricity as byproducts. This process is highly efficient and provides a consistent and immediate power output. When you press the accelerator pedal, the fuel cell system rapidly responds, delivering torque to the electric motor, which then drives the wheels. This instant torque delivery results in a rapid increase in speed, making the vehicle feel responsive and agile.
The quick acceleration of fuel cell cars is particularly beneficial in urban environments, where frequent stops and starts are common. The ability to accelerate swiftly and smoothly can improve overall driving efficiency and reduce the time spent in traffic. Moreover, the smooth driving experience is a direct result of the fuel cell's ability to provide a steady and continuous power supply. Unlike some electric vehicles that may experience a slight lag or drop in power, fuel cell vehicles offer a seamless and linear power delivery, making the ride feel more natural and comfortable.
This instant torque and smooth power delivery also contribute to a more responsive and engaging driving experience. The vehicle can quickly adjust to changes in speed and road conditions, providing a sense of control and confidence to the driver. Additionally, the quiet operation of fuel cell vehicles, due to the absence of a traditional engine, further enhances the overall driving pleasure by reducing noise and vibrations.
In summary, the performance characteristics of fuel cell cars, including instant torque and smooth driving, offer a compelling advantage over conventional vehicles. This technology has the potential to revolutionize the driving experience, making it more efficient, responsive, and enjoyable for drivers in urban and suburban settings.
Car Won't Start? It Might Be Time to Check Your Fuel
You may want to see also

Refueling: Similar to conventional cars, fuel cell vehicles can be refueled with hydrogen in minutes, offering convenience
The refueling process for fuel cell vehicles is remarkably similar to that of conventional cars, providing a familiar and convenient experience for drivers. When it comes to refueling, the primary difference lies in the fuel source. Just as gasoline or diesel vehicles require a visit to the gas station, fuel cell vehicles need to be refueled with hydrogen. This process is quick and efficient, typically taking just a few minutes.
At designated hydrogen refueling stations, the vehicle's fuel tank is connected to the refueling nozzle, which delivers compressed hydrogen gas. The hydrogen is stored in high-pressure tanks on board the vehicle, ensuring a rapid and seamless refueling experience. This process is designed to mimic the convenience of refueling traditional vehicles, allowing drivers to quickly top up their fuel cell cars and get back on the road without significant downtime.
The convenience of refueling with hydrogen is a significant advantage of fuel cell technology. Unlike some alternative fuel options, hydrogen refueling stations are becoming increasingly accessible, especially in urban areas. This infrastructure development ensures that fuel cell vehicle owners can easily find a refueling station, just as gasoline stations are readily available for conventional cars. As a result, the range anxiety often associated with electric vehicles is reduced, as drivers can quickly recharge their fuel cell vehicles during longer journeys.
Furthermore, the refueling process itself is straightforward and user-friendly. The driver simply pulls up to the designated port, connects the refueling nozzle, and initiates the process. The hydrogen gas is then transferred into the vehicle's tank, replenishing the fuel cell's energy supply. This efficient and rapid refueling method ensures that fuel cell vehicles can maintain their performance and range, making them a viable and attractive option for environmentally conscious drivers.
In summary, the refueling process for fuel cell vehicles mirrors that of conventional cars, offering convenience and efficiency. With hydrogen refueling stations becoming more widespread, drivers can enjoy the benefits of quick refueling, similar to the ease of filling up a traditional gasoline tank. This aspect of fuel cell technology addresses a key concern for potential adopters, making it an increasingly appealing choice for those seeking sustainable transportation solutions.
E87 in Flex Fuel: Compatibility and Benefits
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Fuel cells are devices that convert chemical energy from a fuel, typically hydrogen, into electricity through a process called electrochemical reaction. In electric vehicles (EVs), fuel cells replace the traditional internal combustion engine. When hydrogen gas is fed into the fuel cell, it reacts with oxygen from the air, producing electricity, heat, and water as the only byproducts. This electricity powers the vehicle's electric motor, providing a clean and efficient driving experience.
Fuel cells offer several benefits for automotive applications. Firstly, they provide a high energy efficiency, typically around 60%, which is higher than conventional internal combustion engines. This means less energy is wasted as heat, resulting in improved overall performance. Secondly, fuel cells produce zero tailpipe emissions, making them environmentally friendly and contributing to reduced air pollution. Additionally, they offer quick refueling times, similar to gasoline or diesel vehicles, and have a long driving range, addressing range anxiety concerns associated with early electric vehicles.
In a fuel cell vehicle, the process begins with the storage of compressed hydrogen gas in specialized tanks. When the driver initiates the vehicle, the hydrogen is supplied to the fuel cell stack, where it undergoes a series of chemical reactions. These reactions generate electricity, which is then used to power the electric motor. The excess heat generated during this process is managed and utilized to heat the vehicle's interior or for other auxiliary functions. The only byproduct is water vapor, which is released from the vehicle's exhaust.
While fuel cell technology has advanced significantly, there are still some challenges to overcome. One major limitation is the availability and infrastructure for hydrogen refueling. Building a comprehensive hydrogen fueling station network is essential for widespread adoption. Additionally, the cost of fuel cell systems and hydrogen storage tanks can be relatively high, although it is expected to decrease as technology improves and production scales up. Another consideration is the weight and size of fuel cell stacks, which can impact the overall vehicle design and performance.
Fuel cell vehicles and battery-electric vehicles represent two distinct approaches to powering electric cars. BEVs rely solely on battery packs, which store electrical energy and power the electric motor. They offer simplicity in terms of refueling, as they can be charged using standard electrical outlets or fast-charging stations. On the other hand, fuel cell vehicles provide a different advantage by offering a longer driving range and faster refueling times compared to BEVs. However, the infrastructure for hydrogen refueling is still developing, and the cost of fuel cell systems is a factor to consider. Both technologies are crucial in the transition to a more sustainable transportation sector.







