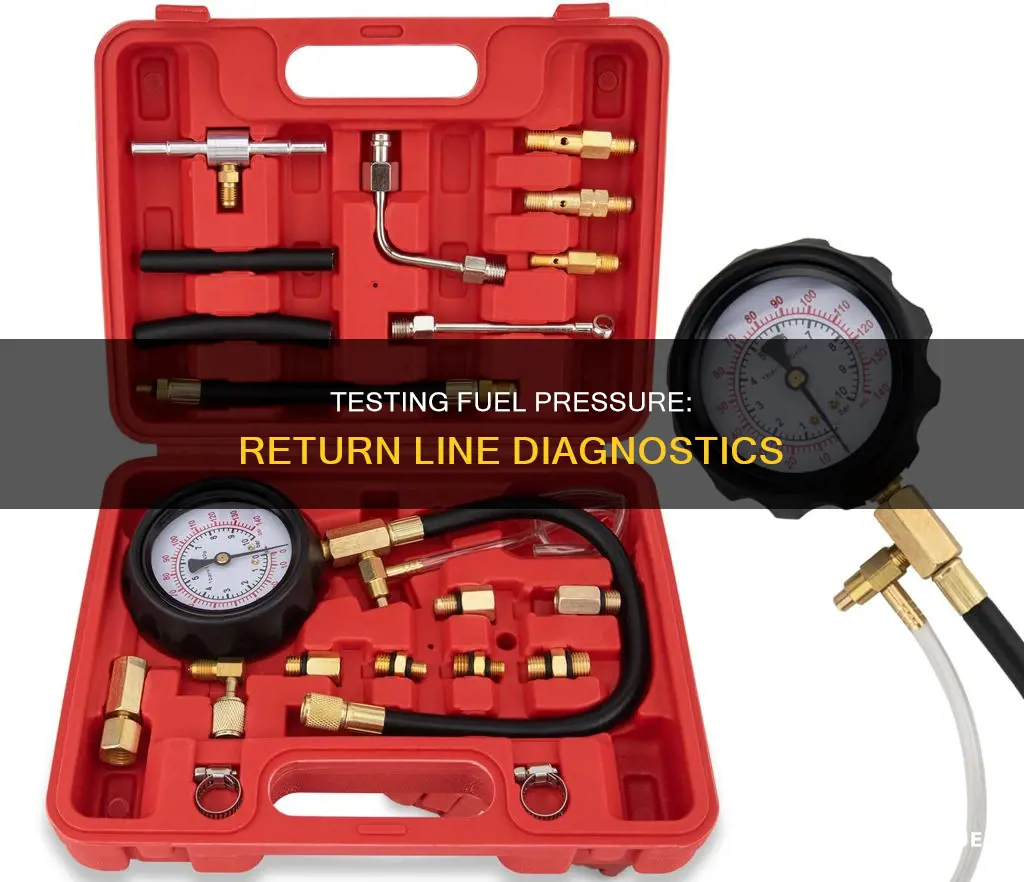
Testing fuel pressure is an essential part of fuel injection system troubleshooting. The fuel pressure tester kit consists of a fuel gauge and the fuel hose it is attached to. To test your vehicle’s fuel pressure levels, attach the gauge to the fuel pump test point and activate your engine. If your vehicle’s fuel pressure levels are too high or too low, its performance will drop significantly. A fuel return line is an integral part of the FPR system. The fuel pump is a constant volume pump. The FPR maintains fuel pressure by sending excess fuel back through the fuel return line.
What You'll Learn

Safety precautions when testing fuel pressure
Testing fuel pressure can be dangerous, so it is important to take safety precautions. Here are some safety measures to follow when testing fuel pressure:
- Always put safety first. Wear safety goggles and gloves to protect your eyes and hands from fuel and other hazardous materials. It is also recommended to work in a well-ventilated area to avoid inhaling fumes.
- Before beginning any test or repair procedure on a vehicle, disconnect the negative battery cable unless the procedure requires electrical power from the battery. This will reduce the risk of sparks that could ignite fuel vapors or sprays.
- Relieve the residual fuel pressure in the system before starting any work on the fuel lines, fuel pump, or fuel injectors. This will help reduce the risk of fuel leakage and potential fire hazards.
- When loosening or tightening fuel line fittings, use two wrenches to minimise stress on the fuel line. Hold the fuel line in place with one wrench while using the other to loosen or tighten the fitting.
- Always use a fire extinguisher when working on a fuel system. Fuel fires cannot be extinguished with water, so keep a Class B fire extinguisher nearby. This type of extinguisher contains dry chemicals that can deprive a fire of oxygen, preventing it from spreading.
- Wipe up any fuel leaks immediately, especially from engine surfaces. Engine surfaces can get hot enough to ignite spilled fuel while the car is running, increasing the risk of a fire.
- Dispose of any fuel-soaked cloths or materials in a suitable container. Do not leave them lying around as they pose a fire hazard.
- If you need to store excess fuel temporarily during a procedure, use a container approved by Underwriters Laboratories for fuel storage. These containers are typically made of metal or plastic and are airtight to prevent leaks and chemical reactions.
Fuel Pressure Maintenance for 2000 Civic HX
You may want to see also

How to test fuel pressure
Testing your vehicle's fuel pressure can help you diagnose starting or running issues. Before you begin, ensure you are wearing safety glasses and gloves, working in a well-ventilated area, and keep anything that could cause a spark away from you.
Step 1: Prepare your vehicle
First, check that your vehicle has at least two gallons of fuel. Even if your fuel gauge shows a full tank, it could be faulty. If there is enough fuel, make sure your vehicle's fuel pump is working. If the pump is functional, you can proceed to the next step.
Step 2: Install a fuel pressure tester
Purchase a fuel pressure test kit, which consists of a gauge designed to read fuel pressure and the attached fuel hose. With a cold engine, open the hood and locate the fuel pump test point, usually beside the fuel injectors. Remove the cap from the test point and attach the fuel hose. Ensure that the hose is properly threaded on for a leakproof fit.
Step 3: Start the engine
Turn the ignition to "on" and check the psi reading. A steady reading that remains the same after 5-10 minutes indicates that the system is holding pressure well. If the fuel pressure drops, this could mean there is a leak in the fuel system.
Step 4: Observe fuel pressure
Let the engine idle and observe the fuel pressure. You should see a steady fuel pressure within a few psi of the recommended pressure for your vehicle. The recommended pressure can be found in your vehicle owner's manual. Once the engine is warmed up, slowly rev the engine and ensure that the pressure rises with the RPMs.
Step 5: Interpret the results
If your fuel pressure holds steady, rises with engine speed, and is at the recommended pressure, your engine problem is likely not fuel-related. However, if you observe low or high fuel pressure, there may be an issue with the fuel pump, fuel filter, fuel return line, or fuel pressure regulator.
Understanding Absolute Pressure Fuel: The Basics
You may want to see also

Interpreting fuel pressure readings
Understanding Fuel Pressure Readings:
Fuel pressure readings indicate the amount of pressure in the fuel system, specifically between the fuel pump and the fuel injectors. The readings are measured in pounds per square inch (PSI). Normal fuel pressure readings typically fall between 30-80 PSI, but the ideal range can vary depending on the vehicle's engine. It is important to refer to the vehicle's owner's manual or manufacturer specifications to determine the optimal fuel pressure range.
Interpreting High and Low Readings:
If your vehicle's fuel pressure readings are higher or lower than the manufacturer's specifications, it could indicate a problem with the fuel system. High fuel pressure readings are often caused by issues in the return line fuel components, such as a faulty fuel pressure regulator or restrictions in the return line. Low fuel pressure readings, on the other hand, are usually caused by problems in the pressure line fuel components, such as a clogged fuel filter or a faulty fuel pump.
Impact on Engine Performance:
High fuel pressure will cause an engine to run rich, resulting in decreased fuel economy and poor performance. On the other hand, low fuel pressure will make an engine run lean or, in some cases, not start at all. This can lead to reduced engine power, difficulty starting, and frequent stalling. Therefore, maintaining correct fuel pressure is crucial for optimal engine performance and fuel efficiency.
Troubleshooting and Diagnostics:
If your vehicle is exhibiting symptoms such as long crank times, sudden loss of power, or rough idling, it is essential to check the fuel pressure readings. Refer to the vehicle service manual for step-by-step diagnostic procedures to identify the faulty component. Additionally, common issues such as faulty sensors, clogged fuel lines, or a loose gas cap can affect fuel pressure and should be inspected and addressed accordingly.
Safety Precautions:
It is important to prioritise safety when testing fuel pressure. Releasing fuel under pressure can pose fire hazards and safety risks. Always wear safety gear, including gloves and eye protection, and work in a well-ventilated area. Ensure there are no sources of ignition, such as smoking or sparks, during the testing process.
Why Fuel Tanks Pressurize: Understanding the Science
You may want to see also

What to do before buying a fuel pressure tester
Before buying a fuel pressure tester, there are a few things you should do to diagnose the problem and ensure that you are purchasing the correct equipment.
Firstly, check that there is gas in the tank. Even if your fuel gauge shows a full tank, it could be faulty, so it is worth adding at least two gallons of fuel and trying to start the engine again. If the engine starts, then you know the issue is with the fuel gauge, and you can replace it.
The next step is to verify that the fuel pump is working. To do this, ask an assistant to turn the ignition switch to "On" and listen for a two-second whir, hum, or series of rapid clicks as the fuel pump pressurizes the fuel line to the engine. If there is no noise, this could mean that the pump is not getting power or has failed. Check the fuel pump fuse and relay, and if those are fine, check the wiring to the pump. If there is voltage when turned on, then the pump has failed and needs to be replaced.
Once you have confirmed that there is fuel in the tank and the pump is working, you can move on to testing the fuel pressure. Attach a fuel pressure gauge to the fuel pump test point and activate the engine. Take a reading of the vehicle's fuel pressure level.
If the fuel pressure levels are too high or too low, this could be causing the performance issues. Good fuel pressure levels fall between 30-80 PSI, but the ideal range varies depending on the engine. You can check the specifications for your vehicle in the owner's manual.
If the fuel pressure is low, this could be caused by a clogged fuel filter or a faulty pump. If the fuel pressure is high, this could be due to bad components such as a failing fuel pump driver or a malfunctioning fuel pressure regulator.
Fuel Pressure Regulator: Rich Condition Culprit?
You may want to see also

How to connect a fuel pressure tester
To connect a fuel pressure tester, follow these steps:
Firstly, ensure your engine is entirely cold. Then, pop the hood and locate the Schrader valve fitting on the fuel rail. This may be hidden under a fuel rail cover or another plastic engine cover. Once you've found it, remove the Schrader valve cap and attach the appropriate fuel pressure tester fitting. Make sure it threads on properly for a leak-proof fit.
Next, turn the ignition to "on", not start. Check the psi reading and wait, watching for a psi drop which would indicate a leak in the system. If the reading stays the same after 5 to 10 minutes, the system is holding pressure well. If the fuel pressure drops over this time, this means there is a leak in the fuel system.
Now, start your engine and let it idle. You should see a steady fuel pressure, within a few psi of the recommended pressure. Once the engine has warmed up, slowly rev the engine, making sure the pressure rises with the RPMs. If your fuel pressure holds steady, rises with engine speed, and is at the recommended pressure, then your engine problem does not seem fuel-related.
It is important to remember that fuel vapors are extremely flammable, so ensure these steps are carried out in a well-ventilated area with a fire extinguisher nearby.
Ideal Fuel Pressure for a 2002 Vortec Engine
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can test fuel pressure on the return line. The fuel pressure regulator divides fuel between the pressure line and the return line. The fuel in the pressure line goes to the fuel injectors, and the fuel in the return line is returned to the fuel tank.
You can test fuel pressure with a fuel pressure tester kit, which consists of a fuel gauge and the attached fuel hose. First, ensure your tank has at least two gallons of fuel. Then, search for the specifications of your vehicle to learn what readings you should expect. Open the hood and attach the fuel hose to the fuel pump test point. Ask an assistant to activate the ignition, then read the vehicle's fuel pressure level. Take note of the levels indicated on the gauge.
Good fuel pressure levels fall between 30-80 PSI, but the ideal range varies depending on the engine. Older throttle-body injected systems only need 10 PSI, while multi-port injector systems usually need 60 PSI. Check your vehicle owner's manual to determine the recommended fuel pressure level for your vehicle.
Low fuel pressure can cause a slow start-up, low performance, misfires, and stalling.
High fuel pressure will cause excessive fuel consumption, black smoke from unburned gas, an overheating catalytic converter, and rough idle.







