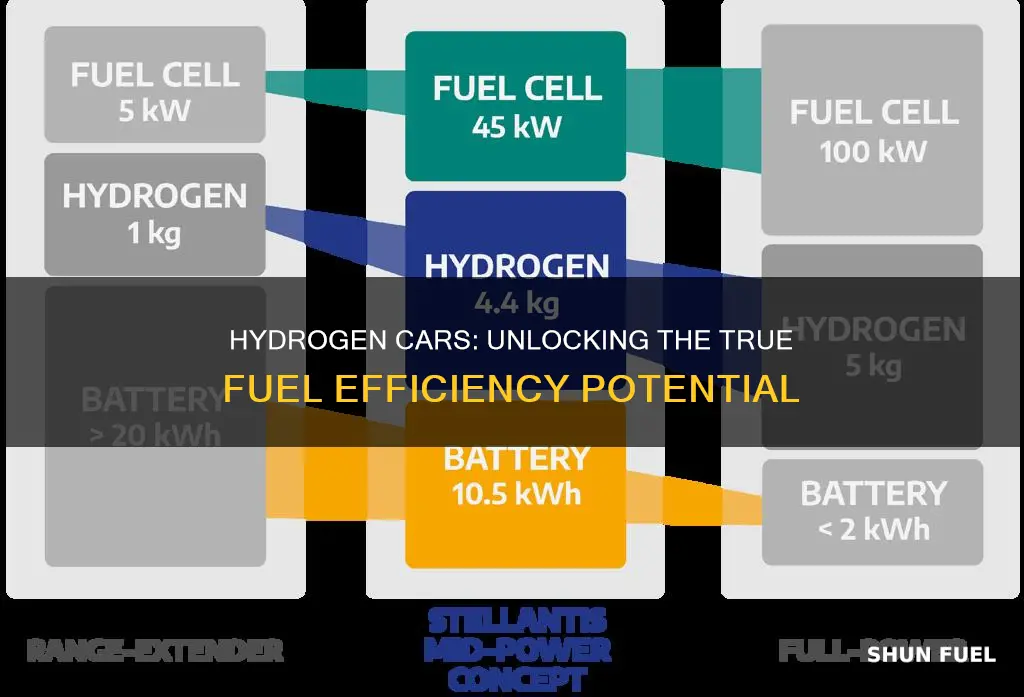
Hydrogen cars have gained attention as a potential solution to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and improve fuel efficiency. The efficiency of hydrogen vehicles is often compared to traditional gasoline or diesel cars, and many wonder if hydrogen cars are indeed more fuel-efficient. This comparison is crucial as it can influence consumer choices and the future of sustainable transportation. Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles convert chemical energy from hydrogen into electricity, offering a cleaner and potentially more efficient alternative to internal combustion engines. However, the efficiency of hydrogen cars depends on various factors, including the production and distribution of hydrogen, the efficiency of the fuel cell, and the overall energy infrastructure. Understanding these aspects is essential to evaluate the true fuel efficiency of hydrogen cars and their potential to revolutionize the automotive industry.
What You'll Learn
- Energy Conversion: Hydrogen fuel cells convert hydrogen to electricity, offering high efficiency
- Emission Reduction: Zero tailpipe emissions make hydrogen cars environmentally friendly
- Fuel Storage: Hydrogen storage systems are compact and efficient, allowing for practical use
- Infrastructure Development: Building hydrogen refueling stations is essential for widespread adoption
- Performance Comparison: Hydrogen cars can match or exceed the efficiency of traditional gasoline vehicles

Energy Conversion: Hydrogen fuel cells convert hydrogen to electricity, offering high efficiency
The concept of hydrogen fuel cells is a fascinating one, especially when it comes to their potential impact on fuel efficiency and energy conversion. These cells are a key component in the development of hydrogen-powered vehicles, which are often touted as a more efficient and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional internal combustion engines. At the heart of this technology is a simple yet powerful process: the conversion of hydrogen into electricity.
When hydrogen fuel cells are utilized, they undergo a chemical reaction where hydrogen gas, typically sourced from compressed or liquid form, reacts with oxygen from the air. This reaction occurs at the anode, where hydrogen atoms split into protons and electrons. The electrons then flow through an external circuit, creating an electric current, while the protons migrate to the cathode. This movement of electrons and protons is the essence of energy conversion, generating electricity in the process.
The efficiency of this energy conversion process is remarkable. Hydrogen fuel cells can achieve efficiencies of up to 60%, which is significantly higher than the typical 20-30% efficiency of conventional combustion engines. This higher efficiency means that a larger portion of the energy stored in hydrogen is successfully converted into usable electricity, resulting in more efficient power generation.
Furthermore, the environmental benefits of this process are substantial. Hydrogen fuel cells produce only water and heat as byproducts, making them a clean energy source. In contrast, combustion engines release various pollutants and greenhouse gases, contributing to air pollution and climate change. By utilizing hydrogen fuel cells, we can reduce our reliance on fossil fuels and minimize the environmental impact of transportation.
In the context of hydrogen cars, this energy conversion process is a game-changer. The high efficiency of fuel cells translates to longer driving ranges and faster refueling times compared to battery-electric vehicles. Additionally, the rapid refueling process of hydrogen cars can be a significant advantage over the time-consuming charging of electric cars. As research and development in this field continue, hydrogen fuel cells are poised to play a crucial role in shaping a more sustainable and efficient transportation future.
F1 Fuel: Unlocking the Power of High-Octane Energy
You may want to see also

Emission Reduction: Zero tailpipe emissions make hydrogen cars environmentally friendly
The environmental benefits of hydrogen cars are significant, particularly in the context of emission reduction. One of the most notable advantages is the complete absence of tailpipe emissions. Unlike conventional internal combustion engine vehicles, which release a range of pollutants into the atmosphere, hydrogen cars produce zero harmful emissions. This is primarily due to the fuel cell technology they employ, which generates electricity through a chemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen, resulting in the only byproduct being water vapor. This clean energy production process means that hydrogen cars contribute to improved air quality and reduced environmental impact.
The environmental advantages of hydrogen cars extend beyond the elimination of tailpipe emissions. The production of hydrogen itself can also be environmentally friendly, especially when it is generated through renewable energy sources such as wind or solar power. This process, known as green hydrogen production, ensures that the entire lifecycle of the vehicle, from fuel creation to operation, is sustainable. As a result, hydrogen cars offer a more comprehensive approach to reducing emissions and combating climate change.
Furthermore, the zero-emission nature of hydrogen cars is particularly beneficial in urban areas, where air pollution is a significant concern. By eliminating the release of harmful gases, these vehicles can help improve the air quality in cities, leading to healthier environments for residents. This is especially important in densely populated areas where the concentration of pollutants can be higher, and the impact on public health is more pronounced.
In addition to the direct reduction of air pollution, the widespread adoption of hydrogen cars can contribute to a broader shift towards a more sustainable transportation system. As the demand for clean energy solutions increases, the infrastructure for hydrogen production and distribution can be developed, creating a more robust and environmentally friendly energy network. This shift could also stimulate innovation in various sectors, driving the development of new technologies and materials to further enhance the efficiency and sustainability of hydrogen-powered vehicles.
In summary, hydrogen cars offer a compelling solution for emission reduction and environmental sustainability. Their ability to produce zero tailpipe emissions, coupled with the potential for green hydrogen production, makes them a significant step forward in the quest for cleaner transportation. As the world seeks to reduce its carbon footprint and combat climate change, hydrogen cars present a viable and increasingly accessible option for a more environmentally friendly future.
Winter's Chill: Unveiling the Fuel Efficiency Mystery
You may want to see also

Fuel Storage: Hydrogen storage systems are compact and efficient, allowing for practical use
Hydrogen storage systems have been a key focus of research and development in the pursuit of efficient and practical hydrogen fuel utilization. One of the most significant advantages of these storage systems is their compact design, which enables a high energy density in a relatively small space. This compactness is crucial for the integration of hydrogen fuel cells into vehicles, as it allows for a more streamlined and lightweight design, enhancing overall efficiency.
The efficiency of hydrogen storage is achieved through various technologies, including compressed gas storage, liquid hydrogen storage, and metal hydride storage. Compressed gas storage, for instance, utilizes high-pressure tanks to store hydrogen gas, providing a practical solution for on-board fuel systems. These tanks are designed to maintain a stable pressure, ensuring the hydrogen remains in a gaseous state and ready for use. The compact nature of these storage systems allows for their placement in the vehicle's body or under the floor, minimizing any impact on the overall vehicle design.
Liquid hydrogen storage presents another efficient approach, where hydrogen is stored in a liquid state at extremely low temperatures. This method offers a higher energy density compared to compressed gas, making it suitable for applications requiring higher fuel capacities. However, the low temperature requirements and the need for specialized insulation make this system more complex and less commonly used in everyday vehicles.
Metal hydride storage is a promising technology that offers a safe and efficient way to store hydrogen. Metal hydrides, such as sodium alanate, can absorb and release hydrogen gas upon heating and cooling, respectively. This process allows for a compact and lightweight storage system, making it ideal for automotive applications. The ability to reversibly store and release hydrogen makes metal hydride storage a key enabler for the widespread adoption of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles.
In summary, hydrogen storage systems have made significant strides in terms of compactness and efficiency, addressing the practical challenges associated with hydrogen fuel utilization. These advancements have paved the way for the development of hydrogen-powered vehicles, offering a sustainable and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional internal combustion engines. The continuous research and development in this field aim to further improve storage technologies, making hydrogen cars more accessible and efficient in the future.
Monthly Gas Costs: How to Save on Your Car's Fuel Expenses
You may want to see also

Infrastructure Development: Building hydrogen refueling stations is essential for widespread adoption
The development of hydrogen refueling stations is a critical aspect of promoting the widespread adoption of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles. As the world shifts towards more sustainable transportation options, hydrogen cars are gaining traction due to their potential for zero-emission mobility. However, the success of this transition relies heavily on the availability of adequate infrastructure to support these vehicles.
Building a comprehensive network of hydrogen refueling stations is essential to address the range anxiety associated with electric vehicles. Hydrogen cars, while efficient in terms of energy output, require a different fueling infrastructure compared to traditional gasoline or diesel vehicles. Refueling stations are the 'gas stations' for hydrogen cars, and their establishment is crucial to making these vehicles a viable and attractive option for the general public. These stations provide the necessary hydrogen gas to refuel the vehicle's fuel cell, allowing for extended driving ranges and addressing the concern of limited mileage.
The process of constructing these stations involves specialized equipment and expertise. It requires the installation of high-pressure tanks to store hydrogen gas, along with sophisticated dispensing systems to ensure safe and efficient refueling. The infrastructure must adhere to strict safety regulations to handle the compressed gas, which is a unique challenge compared to conventional fueling systems. Additionally, the design and location of these stations should consider factors such as proximity to urban areas, highway access, and potential integration with existing fueling infrastructure to ensure convenience for drivers.
Government incentives and investments play a significant role in the development of this infrastructure. Financial support can encourage private companies and businesses to establish hydrogen refueling stations, especially in regions where the demand for hydrogen vehicles is growing. By providing grants, subsidies, or tax incentives, governments can accelerate the construction of these stations, making hydrogen refueling more accessible and affordable. This, in turn, will stimulate the market for hydrogen cars, leading to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly transportation ecosystem.
In summary, the creation of a robust hydrogen refueling infrastructure is a key enabler for the widespread adoption of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles. It addresses the practical concerns of vehicle owners and encourages the transition to a cleaner, more efficient transportation system. With the right support and investment, the network of hydrogen stations can grow, making hydrogen cars a viable and attractive alternative to traditional vehicles, ultimately contributing to a more sustainable future.
Understanding Premium Fuel: Which Cars Require It?
You may want to see also

Performance Comparison: Hydrogen cars can match or exceed the efficiency of traditional gasoline vehicles
The performance of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (HFCVs) in terms of efficiency is a topic of great interest in the automotive industry. When comparing hydrogen cars to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles, it's important to understand that hydrogen vehicles can indeed match or even surpass the efficiency of their gasoline counterparts. This is primarily due to the advanced technology used in hydrogen fuel cell systems.
Hydrogen fuel cells convert chemical energy from hydrogen and oxygen into electricity, with water being the only byproduct. This process is highly efficient, and the energy produced can be used to power an electric motor, providing excellent performance. The efficiency of hydrogen fuel cells is often measured by their power-to-weight ratio, which is significantly higher than that of internal combustion engines. This means that hydrogen cars can deliver substantial power while maintaining a lightweight structure, resulting in better overall efficiency.
In terms of real-world performance, hydrogen vehicles have demonstrated impressive efficiency in various tests and comparisons. For instance, the Toyota Mirai, a popular hydrogen fuel cell vehicle, has been tested to achieve a combined efficiency of around 62 miles per gallon equivalent (MPGe) in city and highway driving cycles. This efficiency is comparable to or even better than some of the most fuel-efficient gasoline vehicles on the market, such as the Toyota Prius, which typically achieves around 54 MPGe. The Mirai's efficiency is further enhanced by its lightweight design and advanced aerodynamics, ensuring a smooth and efficient driving experience.
Additionally, hydrogen fuel cell technology has the potential to offer rapid refueling, which is a significant advantage over the time-consuming process of refueling gasoline vehicles. This rapid refueling capability can be a game-changer for long-distance travel, providing a convenient and efficient solution for drivers. The efficiency and performance of hydrogen cars are not just theoretical but have been proven in real-world applications, with many manufacturers investing in and developing hydrogen-powered vehicles to meet the growing demand for sustainable transportation.
In summary, hydrogen cars can indeed match or exceed the efficiency of traditional gasoline vehicles. Their advanced fuel cell technology, lightweight design, and impressive power-to-weight ratio contribute to excellent performance and efficiency. As the automotive industry continues to evolve towards more sustainable solutions, hydrogen fuel cell vehicles are poised to play a significant role in the future of transportation, offering a viable and efficient alternative to conventional gasoline-powered cars.
Unveiling the Green Lie: Electric Car Batteries' Fossil Fuel Connection
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Yes, hydrogen cars are generally more fuel-efficient. Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles convert 60-70% of the energy in hydrogen to electricity, which powers the car, whereas ICE cars typically convert only about 20-30% of the energy in gasoline to useful work. This higher efficiency means less energy is wasted as heat, making hydrogen cars more efficient in terms of energy usage.
Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles and battery-electric vehicles (BEVs) both offer high energy efficiency compared to ICE cars. However, the efficiency of the energy conversion process differs. Hydrogen cars have an efficiency advantage over BEVs when it comes to the overall energy chain, including the production and distribution of electricity. While BEVs are efficient in converting electrical energy to power the car, the production and transmission of electricity can vary in efficiency depending on the source and method of electricity generation.
Energy efficiency in hydrogen cars refers to how effectively the chemical energy in hydrogen is converted into useful mechanical energy to move the vehicle. The process involves electrochemical reactions in the fuel cell, where hydrogen and oxygen react to produce electricity, water, and heat. This efficient conversion of chemical energy to electrical energy results in a higher overall efficiency compared to the combustion of fossil fuels in traditional engines.
Several factors influence the fuel efficiency of hydrogen cars: the type of fuel cell used, the efficiency of the fuel cell stack, the weight and design of the vehicle, and the infrastructure for hydrogen refueling. Modern fuel cell systems have high power densities, allowing for efficient energy conversion. Additionally, the lightweight design of hydrogen cars and the availability of hydrogen refueling stations contribute to their overall efficiency and practicality.
The high efficiency of hydrogen cars translates to a longer driving range and improved performance. With a more efficient energy conversion process, hydrogen fuel cell vehicles can store and utilize energy more effectively, resulting in a greater driving range per unit of hydrogen fuel. This efficiency also means that hydrogen cars can accelerate faster and maintain higher speeds with less energy consumption, making them a competitive alternative to ICE vehicles in terms of performance and efficiency.







